
com.aliyun.sdk.service.ecs20140526.AsyncClient Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of alibabacloud-ecs20140526 Show documentation
Show all versions of alibabacloud-ecs20140526 Show documentation
Alibaba Cloud Ecs (20140526) Async SDK for Java
// This file is auto-generated, don't edit it. Thanks.
package com.aliyun.sdk.service.ecs20140526;
import com.aliyun.core.utils.SdkAutoCloseable;
import com.aliyun.sdk.service.ecs20140526.models.*;
import darabonba.core.*;
import darabonba.core.async.*;
import darabonba.core.sync.*;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public interface AsyncClient extends SdkAutoCloseable {
static DefaultAsyncClientBuilder builder() {
return new DefaultAsyncClientBuilder();
}
static AsyncClient create() {
return builder().build();
}
CompletableFuture acceptInquiredSystemEvent(AcceptInquiredSystemEventRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture activateRouterInterface(ActivateRouterInterfaceRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture addBandwidthPackageIps(AddBandwidthPackageIpsRequest request);
/**
* When you call this operation, take note of the following items:
* * Up to 20 tags can be added to each ECS resource.
* * `Tag.N.Key` must match `Tag.N.Value` based on the value of N.
* * If you add a tag that has the same key (`Tag.N.Key`) as an existing tag on the specified resource, the new tag value (`Tag.N.Value`) overwrites the original tag value.
*
*/
CompletableFuture addTags(AddTagsRequest request);
/**
* Before you create a dedicated host, you can call the [DescribeAvailableResource](~~66186~~) operation to query the resources available in a specific region or zone.
* We recommend that you understand the billing methods of resources before you create a dedicated host. You are charged for resources used by the created dedicated host. For more information, see [Billing overview](~~68978~~).
* * You can create up to 100 pay-as-you-go or subscription dedicated hosts at a time.
* * After a dedicated host is created, you can use the returned dedicated host ID as the value of a request parameter to call the [DescribeDedicatedHosts](~~134242~~) operation to query the state of the dedicated host.
* * After you submit a request to create a dedicated host, an error is returned if a specific parameter is invalid or if the requested resources are insufficient. For more information about error causes, see the "Error codes" section of this topic.
* * After a dedicated host is created, you can call the [ModifyInstanceDeployment](~~134248~~) operation to migrate ECS instances from a shared host to the dedicated host. You can also migrate ECS instances from another dedicated host to the created dedicated host.
*
*/
CompletableFuture allocateDedicatedHosts(AllocateDedicatedHostsRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
* > This operation has been upgraded. We recommend that you do not use it. For information about the new version of this operation, see [AllocateEipAddress](~~120192~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture allocateEipAddress(AllocateEipAddressRequest request);
/**
* Take note of the following items:
* * The instance to which you want to assign a public IP address must be in the **Running** (`Running`) or **Stopped** (`Stopped`) state.
* * If `OperationLocks` in the response of the DescribeInstances operation contains `"LockReason" : "security"` for an instance, the instance is [locked for security reasons](~~25695~~) and cannot be assigned a public IP address.
* * You can assign only one public IP address to an instance. If the instance already has a public IP address, the `AllocatedAlready` error code is returned.
* * After you assign a public IP address to an instance, you must restart the instance ([RebootInstance](~~25502~~)) or start the instance ([StartInstance](~~25500~~)) for the public IP address to take effect.
* If an instance resides in a virtual private cloud (VPC), you can assign a public IP address to the instance or associate an elastic IP address (EIP) with the instance. For more information, see [AssociateEipAddress](~~2518064~~).
* > After you associate an EIP with an instance that resides in a VPC, you cannot assign a public IP address to the instance.
*
*/
CompletableFuture allocatePublicIpAddress(AllocatePublicIpAddressRequest request);
/**
* * Each disk can have only one automatic snapshot policy.
* * Each automatic snapshot policy can be applied to multiple disks.
*
*/
CompletableFuture applyAutoSnapshotPolicy(ApplyAutoSnapshotPolicyRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* You can specify IPv6 addresses in the CIDR block of the vSwitch to which the ENI is connected. You can also specify the number of IPv6 addresses that the system assigns to the ENI. Take note of the following items:
* * IPv6 must be enabled on the vSwitch to which the ENI is connected. For more information, see [Enable IPv6 for a vSwitch](~~98923~~).
* * The ENI must be in the Available (Available) or InUse (InUse) state.
* * If you want to assign IPv6 addresses to a primary ENI, make sure that the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance to which the ENI is attached is in the Running (Running) or Stopped (Stopped) state.
* * The maximum number of IPv6 addresses that can be assigned to an ENI varies based on the instance type of the instance to which the ENI is attached.
* * If the ENI is in the Available (Available) state, up to 10 IPv6 addresses can be assigned to the ENI.
* * If the ENI is attached to an ECS instance, the maximum number of IPv6 addresses that can be assigned to the ENI varies based on the instance type. For more information, see [Overview of instance families](~~25378~~).
* * After the operation is called, you can obtain the IPv6 addresses that are assigned to the ENI from the response.
*
*/
CompletableFuture assignIpv6Addresses(AssignIpv6AddressesRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * The ENI to which you want to assign secondary private IP addresses must be in the Available (Available) or InUse (InUse) state.
* * When you assign private IP addresses to a primary ENI, the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance to which the ENI is attached must be in the Running (Running) or Stopped (Stopped) state.
* * When an ENI is in the Available state, you can assign up to 49 secondary private IP addresses to the ENI. When an ENI is attached to an instance, the number of secondary private IP addresses that can be assigned to the ENI varies based on the instance type. For more information, see [Overview of instance families](~~25378~~).
* * After the operation is called, you can obtain the assigned secondary private IP addresses from the response.
*
*/
CompletableFuture assignPrivateIpAddresses(AssignPrivateIpAddressesRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture associateEipAddress(AssociateEipAddressRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture associateHaVip(AssociateHaVipRequest request);
/**
* When you call this operation, take note of the following items:
* * The instance that you want to connect to a VPC must be in the **Running** or **Stopped** state.
* * The ClassicLink feature must be enabled for the destination VPC. For more information, see [Create a ClassicLink connection](~~65413~~).
* * The instance and the VPC must reside in the same region.
*
*/
CompletableFuture attachClassicLinkVpc(AttachClassicLinkVpcRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * The disk must be in the **Unattached** (`Available`) state.
* * When you attach the disk as a data disk to an ECS instance, take note of the following items:
* * The ECS instance must be in the **Running** (`Running`) or **Stopped** (`Stopped`) state.
* * If the disk was separately purchased, the billing method of the disk must be pay-as-you-go.
* * If the disk is a system disk that was detached from an ECS instance, no limits apply to the billing method of the disk.
* * If the disk is an elastic ephemeral disk that was detached from an ECS instance, the disk can be attached only to the instance.
* * When you attach the disk as the system disk to an ECS instance, take note of the following items:
* * The ECS instance must be the original instance from which the system disk was detached.
* * The ECS instance must be in the **Stopped** (`Stopped`) state.
* * Logon credentials must be configured.
* * The disk cannot be an elastic ephemeral disk.
* * If the response contains `{"OperationLocks": {"LockReason" : "security"}}` when you query information about an ECS instance, the instance is locked for security reasons and no operations are allowed on the instance.
*
*/
CompletableFuture attachDisk(AttachDiskRequest request);
CompletableFuture attachInstanceRamRole(AttachInstanceRamRoleRequest request);
/**
* Take note of the following items:
* * SSH key pairs are not supported on Windows instances.
* * If an SSH key pair is bound to an instance, authentication by using the username and password is disabled for the instance.
* * If you bind an SSH key pair to an instance in the **running** state, you must call the [RebootInstance](~~25502~~) operation to restart the instance for the key pair to take effect.
* * If you bind an SSH key pair to an instance in the **stopped** state, you must call the [StartInstance](~~25500~~) operation to start the instance for the key pair to take effect.
* * If an instance is already bound to an SSH key pair, the new SSH key pair will replace the original one.
*
*/
CompletableFuture attachKeyPair(AttachKeyPairRequest request);
/**
* Take note of the following items:
* * The ENI must be in the **Available** state. You can attach an ENI to only one instance that resides in the same zone and VPC as the ENI.
* * The instance must be in the Running or Stopped state. When you attach ENIs to instances of specific instance types, make sure that the instances are in the Stopped state. For more information, see the "Instance types of the ECS instances that must be in the Stopped (Stopped) state" section in the [Bind an ENI](~~58503~~) topic.
* >If the last start time of the instance (including the start time of the instance if it is a new instance, the last restart time of the instance, and the last reactivation time of the instance) is before April 1st, 2018 and the instance is in the Running state, you must call the RebootInstance operation to restart the instance. If you do not call the RebootInstance operation to restart the instance, you cannot attach the ENI to the instance.
* * You can attach multiple ENIs to one instance. For more information, see [ENI overview](~~58496~~).
* * The vSwitch to which the ENI is connected must be in the same zone and VPC as the vSwitch to which the instance is connected.
* * This operation is an asynchronous operation. After you call this operation to attach an ENI, you can view the status or events of the ENI to check whether the ENI is attached. The following figure shows the transitions between the statuses of the ENI.
* 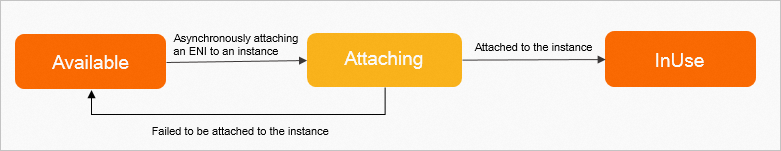
* - If the ENI is in the Attaching state, the ENI attachment request is sent and the ENI is being attached to the specified instance.
* - If the ENI is in the InUse state, the ENI is attached to the specified instance.
* - If the ENI is in the Available state, the ENI failed to be attached.
* **For examples on how to call this operation, see** [Attach an ENI](~~471550~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture attachNetworkInterface(AttachNetworkInterfaceRequest request);
/**
* Take note of the following items:
* * The total number of outbound and inbound rules in each security group cannot exceed 200. For more information, see the "Security group limits" section in [Limits](~~25412#SecurityGroupQuota1~~).
* * The valid values of Priority range from 1 to 100. A smaller value indicates a higher priority.
* * When multiple security group rules have the same priority, drop rules take precedence.
* * The source can be a CIDR block that is specified by SourceCidrIp, Ipv6SourceCidrIp, or SourcePrefixListId. The source can also be Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances in a security group that is specified by SourceGroupId.
* * You cannot reference security groups as sources or destinations in the rules of advanced security groups.
* * You can reference up to 20 security groups as sources or destinations in the rules of each basic security group.
* * If the specified security group rule already exists in the security group, the call is successful but no security group rule is created.
* * Parameters and their `Permissions.N`-prefixed counterparts cannot be specified at the same time. We recommend that you use the `Permissions.N`-prefixed parameters.
* * You can determine a security group rule by specifying one of the following groups of parameters. You cannot determine a security group rule by specifying only one parameter.
* * Parameters used to specify an inbound security group rule that controls access from a specific CIDR block: IpProtocol, PortRange, SourcePortRange (optional), NicType, Policy, and SourceCidrIp. For a security group of the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) type, you must set NicType to intranet. For a security group of the classic network type, you can set NicType to either internet or intranet. Sample request:
* http(s)://ecs.aliyuncs.com/?Action=AuthorizeSecurityGroup
* &SecurityGroupId=sg-bp67acfmxazb4p****
* &Permissions.1.SourceCidrIp=10.0.0.0/8
* &Permissions.1.IpProtocol=TCP
* &Permissions.1.PortRange=22/22
* &Permissions.1.NicType=intranet
* &Permissions.1.Policy=Accept
* &
* * Parameters used to determine an inbound security group rule that controls access from a security group: IpProtocol, PortRange, SourcePortRange (optional), NicType, Policy, SourceGroupOwnerAccount, and SourceGroupId. In this case, you must set NicType to intranet. For mutual access between security groups in the classic network, you can allow or deny another security group within the same region access to your security group. The security group that is allowed access to your security group can belong to your own Alibaba Cloud account or another Alibaba Cloud account specified by SourceGroupOwnerAccount. For mutual access between security groups in VPCs, you can allow or deny another security group within the same VPC access to your security group. Sample request:
* http(s)://ecs.aliyuncs.com/?Action=AuthorizeSecurityGroup
* &SecurityGroupId=sg-bp67acfmxazb4p****
* &Permissions.1.SourceGroupId=sg-1651FBB**
* [email protected]
* &Permissions.1.IpProtocol=TCP
* &Permissions.1.PortRange=22/22
* &Permissions.1.NicType=intranet
* &Permissions.1.Policy=Drop
* &
* * Parameters used to determine an inbound security group rule that controls access from a prefix list: IpProtocol, PortRange, SourcePortRange (optional), NicType, Policy, and SourcePrefixListId. In this case, prefix lists support only security groups in VPCs. NicType must be set to intranet. Sample request:
* http(s)://ecs.aliyuncs.com/?Action=AuthorizeSecurityGroup
* &SecurityGroupId=sg-bp67acfmxazb4p****
* &Permissions.1.SourcePrefixListId=pl-x1j1k5ykzqlixdcy****
* [email protected]
* &Permissions.1.IpProtocol=TCP
* &Permissions.1.PortRange=22/22
* &Permissions.1.NicType=intranet
* &Permissions.1.Policy=Drop
* &
* * For information about examples on security group rule settings, see [Security groups for different use cases](~~25475~~) and [Security group quintuple rules](~~97439~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture authorizeSecurityGroup(AuthorizeSecurityGroupRequest request);
/**
* In the security group-related API documents, outbound traffic refers to the traffic that is sent by the source device and received at the destination device.
* When you call this operation, take note of the following items:
* * The total number of inbound and outbound security group rules in each security group cannot exceed 200. For more information, see the "Security group limits" section in [](~~25412#SecurityGroupQuota1~~).
* * You can set Policy to accept or drop for each security group rule to allow or deny access.
* * The valid value of Priority ranges from 1 to 100. A smaller value indicates a higher priority.
* * When several security group rules have the same priority, drop rules take precedence.
* * The destination can be a CIDR block specified by DestCidrIp, Ipv6DestCidrIp, or DestPrefixListId or can be Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances in a security group specified by DestGroupId.
* * For advanced security groups, security groups cannot be used as authorization objects.
* * For each basic security group, a maximum of 20 security groups can be used as authorization objects.
* * If the specified security group rule exists in the security group, the call is successful but no security group rule is created.
* * The `Permissions.N` prefix is added to some parameters to generate new parameters. Original parameters and corresponding parameters prefixed with Permissions.N cannot be configured together. We recommend that you use parameters prefixed with `Permissions.N`.
* * You can determine a security group rule by configuring one of the following groups of parameters. You cannot determine a security group rule by configuring only one parameter.
* * Parameters used to specify a security group rule that controls access to a specified CIDR block: IpProtocol, PortRange, SourcePortRange (optional), NicType, Policy, and DestCidrIp. Sample request:
* http(s)://ecs.aliyuncs.com/?Action=AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgress
* &SecurityGroupId=sg-bp67acfmxazb4ph***
* &Permissions.1.IpProtocol=ICMP
* &Permissions.1.DestCidrIp=10.0.0.0/8
* &Permissions.1.PortRange=-1/-1
* &Permissions.1.NicType=intranet
* &Permissions.1.Policy=Accept
* &
* * Parameters used to specify a security group rule that controls access to a security group: IpProtocol, PortRange, SourcePortRange (optional), NicType, Policy, DestGroupOwnerAccount, and DestGroupId. Sample request:
* http(s)://ecs.aliyuncs.com/?Action=AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgress
* &SecurityGroupId=sg-bp67acfmxazb4ph***
* &Permissions.1.DestGroupId=sg-bp67acfmxazb4pi***
* [email protected]
* &Permissions.1.IpProtocol=TCP
* &Permissions.1.PortRange=22/22
* &Permissions.1.NicType=intranet
* &Permissions.1.Policy=Drop
* &
* * Parameters used to specify a security group rule that controls access to a prefix list: IpProtocol, PortRange, SourcePortRange (optional), NicType, Policy, and DestPrefixListId. In this case, prefix lists support only security groups in virtual private clouds (VPCs). NicType must be set to intranet. Sample request:
* http(s)://ecs.aliyuncs.com/?Action=AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgress
* &SecurityGroupId=sg-bp67acfmxazb4ph***
* &Permissions.1.DestPrefixListId=pl-x1j1k5ykzqlixdcy****
* [email protected]
* &Permissions.1.IpProtocol=TCP
* &Permissions.1.PortRange=22/22
* &Permissions.1.NicType=intranet
* &Permissions.1.Policy=Drop
* &
*
*/
CompletableFuture authorizeSecurityGroupEgress(AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgressRequest request);
CompletableFuture cancelAutoSnapshotPolicy(CancelAutoSnapshotPolicyRequest request);
/**
* When you call this operation, take note of the following items:
* * After you cancel an image copy task, the image copy created in the destination region is deleted, and the copied image remains unchanged.
* * If the image copy task is complete, the CancelCopyImage operation fails, and an error is returned.
*
*/
CompletableFuture cancelCopyImage(CancelCopyImageRequest request);
/**
* Before you call this operation, make sure that the image build task to be canceled is in the BUILDING, DISTRIBUTING, or RELEASING state.
*
*/
CompletableFuture cancelImagePipelineExecution(CancelImagePipelineExecutionRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture cancelPhysicalConnection(CancelPhysicalConnectionRequest request);
CompletableFuture cancelSimulatedSystemEvents(CancelSimulatedSystemEventsRequest request);
CompletableFuture cancelTask(CancelTaskRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture connectRouterInterface(ConnectRouterInterfaceRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* After a public IP address is converted into an EIP, the EIP is billed separately. Make sure that you fully understand the billing methods of EIPs. For more information, see [Billing overview](~~122035~~).
* When you call this operation, make sure that the ECS instance meets the following requirements:
* * The instance is in the **Stopped** (`Stopped`) or **Running** (`Running`) state.
* * The instance has no EIPs associated.
* * The instance has no configuration change tasks that have not taken effect.
* * The public bandwidth of the instance is not 0 Mbit/s.
* * If the instance is a subscription instance, the billing method for network usage of the instance must be `pay-by-traffic`. The public IP address of a subscription instance that uses the `pay-by-bandwidth` billing method for network usage cannot be converted into an EIP. This requirement does not apply to pay-as-you-go instances. For more information, see [Change the billing method for network usage](~~178883~~).
* * If the instance is a subscription instance that resides in a VPC, the instance does not expire within 24 hours.
*
*/
CompletableFuture convertNatPublicIpToEip(ConvertNatPublicIpToEipRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* After you copy a custom image to the destination region, you can use the image copy (new image) to create ECS instances by calling the RunInstances operation or replace the system disks of instances by calling the ReplaceSystemDisk operation in the destination region.
* Take note of the following items:
* * Only custom images that are in the `Available` state can be copied.
* * Custom images that you want to copy must belong to your Alibaba Cloud account or be shared to you by others, and cannot be copied across accounts.
* * When an image is being copied, the image copy cannot be deleted by calling the [DeleteImage](~~25537~~) operation. However, you can cancel the ongoing image copy task by calling the [CancelCopyImage](~~25539~~) operation.
* * A region supports only up to five concurrent image copy tasks. Excess image copy tasks are queued for execution.
* * You can configure `ResourceGroupId` to specify the resource group to which to assign the new image. If you do not configure `ResourceGroupId`, the new image is assigned to the default resource group.
*
*/
CompletableFuture copyImage(CopyImageRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * New snapshots (snapshot copies) cannot be used to roll back the disks for which source snapshots (copied snapshots) were created.
* * Local snapshots cannot be copied.
*
*/
CompletableFuture copySnapshot(CopySnapshotRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* After you use an activation code to register a server that is not provided by Alibaba Cloud as an Alibaba Cloud managed instance, you can use a variety of online services provided by Alibaba Cloud, such as Cloud Assistant, CloudOps Orchestration Service (OOS), and Apsara Devops on the managed instance.
* If a server is not provided by Alibaba Cloud, you can register the server as an Alibaba Cloud managed instance only if the server has Internet connectivity and runs one of the following operating systems:
* * Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 and Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 and later
* * CentOS 6, CentOS 7, and CentOS 8 and later
* * Debian 8, Debian 9, and Debian 10 and later
* * Ubuntu 12, Ubuntu 14, Ubuntu 16, and Ubuntu 18 and later
* * CoreOS
* * OpenSUSE
* * Red Hat 5, Red Hat 6, and Red Hat 7 and later
* * SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12, and SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 and later
* * Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2016, and Windows Server 2019 and later
* You can have up to 5,000 activation codes per Alibaba Cloud region. When the number of activation codes exceeds 1,000, the usage of the activation codes must be greater than 50% before you can create additional activation codes.
* > To obtain the usage of activation codes, go to the **ECS Cloud Assistant** page, click the **Manage Instances** tab, and then click **Register Instance**.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createActivation(CreateActivationRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * Auto Provisioning is a service that allows quick deployment of an instance cluster that consists of preemptible instances and pay-as-you-go instances. Auto Provisioning supports push-button deployment of instance clusters across different billing methods, instance families, and zones. For more information, see [Use auto provisioning group-related API operations to create multiple ECS instances at the same time](~~200772~~).
* * Auto Provisioning uses auto provisioning groups to schedule and maintain computing resources. You can use auto provisioning groups to obtain a steady supply of computing resources. This helps reduce the impact on compute capacity when preemptible instances are reclaimed.
* * Auto Provisioning is provided free of charge. However, you are charged for instance resources that are created in auto provisioning groups. For more information, see [Overview of preemptible instances](~~52088~~) and [Pay-as-you-go](~~40653~~).
* * When you specify both a launch template (`LaunchTemplateId`) and extended configurations (`LaunchConfiguration.*` parameters), LaunchTemplateId takes precedence.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createAutoProvisioningGroup(CreateAutoProvisioningGroupRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* When you call this operation to create an automatic snapshot policy, you can specify the days of the week on which to create automatic snapshots, the retention period of the automatic snapshots, and whether to enable cross-region replication for the snapshots in the policy to meet your diverse data backup requirements. After the automatic snapshot policy is created, call the [ApplyAutoSnapshotPolicy](~~25531~~) operation to apply the policy to disks. If you want to modify the automatic snapshot policy, call the [ModifyAutoSnapshotPolicyEx](~~25529~~) operation.
* Take note of the following items:
* * You can create up to 100 automatic snapshot policies per region for a single Alibaba Cloud account.
* * If an automatic snapshot is being created when the time scheduled for creating another automatic snapshot is due, the new snapshot task is skipped. This may occur when a disk contains a large volume of data. For example, you have scheduled snapshots to be created at 09:00:00, 10:00:00, 11:00:00, and 12:00:00 for a disk. The system starts to create a snapshot for the disk at 09:00:00. The process takes 80 minutes to complete because the disk contains a large volume of data and ends at 10:20:00. In this case, the system does not create a snapshot at 10:00, but creates a snapshot at 11:00.
* * For information about how to copy a snapshot from one region to another region, see the "Background information" section in [Copy a snapshot](~~159441~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture createAutoSnapshotPolicy(CreateAutoSnapshotPolicyRequest request);
/**
* When you create a capacity reservation, you can specify attributes such as a zone and an instance type. The system uses a private pool to reserve resources that match the specified attributes. For more information, see [Overview of Immediate Capacity Reservation](~~193633~~).
* * Currently, only immediate capacity reservations are supported. Immediate capacity reservations take effect immediately after you purchase them. After you purchase an immediate capacity reservation, you are charged for the specified instance type based on the pay-as-you-go billing method regardless of whether you use the capacity reservation to create pay-as-you-go instances. Billing stops when you manually release the capacity reservation or when the capacity reservation expires and is automatically released.
* * You can call the [CreateInstance](~~25499~~) or [RunInstances](~~63440~~) operation to specify private pool attributes when you create instances. To modify the attributes of a private pool, you can call the [ModifyInstanceAttachmentAttributes](~~190006~~) operation. If an instance matches a private pool associated with a capacity reservation, you are charged based on the configurations of the instance such as the instance type, disks, and public bandwidth.
* * Before you use a private pool associated with a capacity reservation to create pay-as-you-go instances, you are charged only for the specified instance type.
* * You can apply savings plans or regional reserved instances to offset hourly billing of unused immediate capacity reservations, and hourly fees of the instances that match the immediate capacity reservations. However, you cannot use zonal reserved instances to offset the hourly fees. We recommend that you purchase reserved instances or savings plans before you purchase immediate capacity reservations. This way, you can access resources free of charge within the coverage of the reserved instances or savings plans.
* > You can call the CreateCapacityReservation operation to create only immediate capacity reservations. You can create immediate or scheduled capacity reservations in the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) console. For more information, see [Overview](~~193626#section-oil-qh5-xvx~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture createCapacityReservation(CreateCapacityReservationRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * You can create commands of the following types:
* * Batch commands (RunBatScript), applicable to Windows instances
* * PowerShell commands (RunPowerShellScript), applicable to Windows instances
* * Shell commands (RunShellScript), applicable to Linux instances
* * You can specify the Timeout parameter to set the maximum timeout period for executions of a command on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances. If an execution times out, [Cloud Assistant Agent](~~64921~~) forcefully terminates the command process by canceling the process ID (PID) of the command.
* * For a one-time task, when the execution times out, the state of the command ([InvokeRecordStatus](~~64845~~)) becomes Failed.
* * For a scheduled task, take note of the following items:
* * The timeout period takes effect on each execution.
* * When an execution times out, the state ([InvokeRecordStatus](~~64845~~)) of the command becomes Failed.
* * The timeout of one execution does not affect the subsequent executions.
* * You can retain up to 500 to 50,000 Cloud Assistant commands in each region. You can also apply for a quota increase. For information about how to query and increase quotas, see [Manage quotas](~~184116~~).
* * You can use WorkingDir to specify the execution directory of a Cloud Assistant command. For Linux instances, the default execution directory of Cloud Assistant commands is the home directory of the root user, which is `/root`. For Windows instances, the default execution directory of Cloud Assistant commands is the directory where the Cloud Assistant Agent process resides, such as `C:\\Windows\\System32`.
* * You can enable the custom parameter feature for a Cloud Assistant command by setting EnableParameter to true. When you set CommandContent, you can define custom parameters in the {{parameter}} format. Then, when the [InvokeCommand](~~64841~~) operation is called, the key-value pairs of custom parameters are passed in. For example, if a command is `echo {{name}}`, the Parameters parameter can be used to pass in the `` key-value pair when the InvokeCommand operation is called. The name key of the custom parameter is automatically replaced by the paired Jack value to generate a new command. As a result, the `echo Jack` command is run.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createCommand(CreateCommandRequest request);
CompletableFuture createDedicatedHostCluster(CreateDedicatedHostClusterRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
* You can call this operation to file a demand for an ECS instance type. Alibaba Cloud provides the requested resources based on your demand.
* You can file demands only for I/O optimized instance types and instances of the virtual private cloud (VPC) type.
* > This operation is in internal preview and has not been officially released. We recommend that you do not call this operation.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createDemand(CreateDemandRequest request);
CompletableFuture createDeploymentSet(CreateDeploymentSetRequest request);
CompletableFuture createDiagnosticMetricSet(CreateDiagnosticMetricSetRequest request);
CompletableFuture createDiagnosticReport(CreateDiagnosticReportRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * You can enable the multi-attach (`MultiAttach`) feature when you create a disk. Before you enable the multi-attach feature, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the feature and its limits. For more information, see [NVMe disks](~~256487~~) and [Enable multi-attach](~~262105~~).
* * You can create disks of the following disk categories: basic disks, ultra disks, standard SSDs, Enterprise SSDs (ESSDs), ESSD Entry disks, ESSD AutoPL disks, standard elastic ephemeral disks, and premium elastic ephemeral disks.
* * Before you can create a disk, you must complete real-name verification. Complete real-name verification on the [Real-name Verification](https://account.console.aliyun.com/#/auth/home) page in the Alibaba Cloud Management Console.
* * When you create disks, you may be charged for the resources used. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the billing methods of Elastic Compute Service (ECS) resources before you create a disk. For more information, see [Billing overview](~~25398~~).
* * By default, `DeleteAutoSnapshot` is set to `true` when a disk is created. This indicates that the automatic snapshots of the disk are deleted when the disk is released. You can call the [ModifyDiskAttribute](~~25517~~) operation to change the parameter value.
* * If you do not specify a performance level when you create an ESSD, the performance level of the ESSD is automatically set to PL1. To change the performance level of the ESSD, you can call the [ModifyDiskSpec](~~123780~~) operation.
* * By default, `Portable` is set to `true` and the billing method is pay-as-you-go for a disk that is created by calling the CreateDisk operation.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createDisk(CreateDiskRequest request);
/**
* Elasticity Assurance provides a new way to purchase and use resources with flexibility and assurance. It offers assured resource reservations for pay-as-you-go Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances. For more information, see [Overview of Elasticity Assurance](~~193630~~).
* * Elasticity assurances are not refundable after purchase.
* * Elasticity assurances are applicable to only pay-as-you-go ECS instances.
* * Elasticity assurances support only the unlimited mode. Therefore, you can set `AssuranceTimes` only to `Unlimited`. Elasticity assurances in unlimited mode can be applied an unlimited number of times within their effective period and take effect immediately after they are purchased.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createElasticityAssurance(CreateElasticityAssuranceRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture createForwardEntry(CreateForwardEntryRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture createHaVip(CreateHaVipRequest request);
CompletableFuture createHpcCluster(CreateHpcClusterRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * You can use the created custom image only if the image is in the Available (Available) state.
* * If the response contains `{"OperationLocks": {"LockReason" : "security"}}` when you query the information of an instance, the instance is locked for security reasons. No operations are allowed on the instance.
* * To optimize the image, we recommend that you specify DetectionStrategy when you create the image. For more information, see [Overview of image check](~~439819~~).
* You can call the CreateImage operation to create a custom image by using one of the following methods. The following request parameters are sorted by priority: `InstanceId` > `DiskDeviceMapping` > `SnapshotId`. If your request contains two or more of these parameters, the custom image is created based on the parameter that has a higher priority.
* * **Method 1**: Create a custom image from an instance. You need to only specify the ID of the instance by using `InstanceId`. The instance must be in the Running (`Running`) or Stopped (`Stopped`) state. After you call the CreateImage operation, a snapshot is created for each disk of the instance. When you create a custom image from a running instance, cache data may not be written to disks. In this case, the data of the custom image may be slightly different from the data of the instance. We recommend that you stop instances by calling the [StopInstances](~~155372~~) operation before you create custom images from the instances.
* * **Method 2**: Create a custom image from the system disk snapshot of an instance. You need to only specify the ID of the system disk snapshot by using `SnapshotId`. The specified system disk snapshot must be created after July 15, 2013.
* * **Method 3**: Create a custom image from multiple disk snapshots. You must specify data mappings between the snapshots and the disks to be created by using the parameters that start with `DiskDeviceMapping`.
* When you use Method 3 to create a custom image, take note of the following items:
* * You can specify only one snapshot to use to create the system disk in the custom image. The device name of the system disk must be /dev/xvda.
* * You can specify up to 16 snapshots to use to create data disks in the custom image. The device names of the data disks are unique and range from /dev/xvdb to /dev/xvdz in alphabetical order.
* * You can leave `SnapshotId` empty. In this case, an empty data disk with the specified size is created.
* * The specified disk snapshot must be created after July 15, 2013.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createImage(CreateImageRequest request);
/**
* Take note of the following items:
* * Only custom image components can be created.
* * The images must run Linux operating systems. This indicates that you must set `SystemType` to Linux.
* * You must set the image component type to image build component by setting the `ComponentType` parameter to Build.
* * You can use Dockerfile to edit the content of image components, and then pass the edited content into the `Content` parameter. The content size must not be greater than 16 KB. `FROM` commands cannot be used in image components. An image component supports up to 127 commands. For information about supported commands, see [Description of commands supported by Image Builder](~~200206~~).
* You can use image components to create image templates in the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) console, but cannot call API operations to use image components to create image templates. For more information, see [Overview of Image Builder](~~197410~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture createImageComponent(CreateImageComponentRequest request);
/**
* You can use image templates to specify custom image content and create images across regions and accounts. When you call this operation, take note of the following items:
* * You can create only custom image templates.
* * You can configure only public, custom, or shared Linux images or image families as the source images when you create image templates.
* * When you use an image template to create an image, you must create an intermediate Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance to help create the image. The intermediate instance is billed by using the pay-as-you-go billing method. For more information, see [Pay-as-you-go](~~40653~~).
* For the `BuildContent` parameter that specifies the content of image templates, take note of the following items:
* * If the `BuildContent` value contains `FROM` commands, the `FROM` commands override the values of `BaseImageType` that specifies the type of the source images and `BaseImage` that specifies the source image.
* * If the `BuildContent` value does not contain `FROM` commands, the system creates a `FROM` command that consists of the `BaseImageType` and `BaseImage` values in the format of `:` and adds the command to the first line of the template content.
* * You can use Dockerfile to edit the content of image templates and then pass the edited content into the `BuildContent` parameter. The content of an image template cannot exceed 16 KB in size and can contain up to 127 commands. For information about commands supported by image templates, see [Description of commands supported by Image Builder](~~200206~~).
* You can use image components to create image templates in the ECS console, but cannot call API operations to use image components to create image templates. For more information, see [Overview of Image Builder](~~197410~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture createImagePipeline(CreateImagePipelineRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* > You can call the [DescribeAvailableResource](~~66186~~) operation to query available resources in a specific region or zone. If you want to batch create instances that automatically enter the Running state after they are created, we recommend that you call the [RunInstances](~~63440~~) operation.
* Take note of the following items:
* * **Billing**:
* * You must familiarize yourself with ECS billing methods before you create an instance because you may be charged for the resources used by the instance. For more information, see [Billing overview](~~25398~~).
* * If you create a subscription instance (`PrePaid`), available coupons in your account are used by default.
* * **Instance type**:
* * You can use the `IoOptimized` parameter to specify whether to create an I/O optimized instance.
* * Instance type selection: See [Instance families](~~25378~~) or call the [DescribeInstanceTypes](~~25620~~) operation to query the performance data of instance types, or see [Best practices for instance type selection](~~58291~~) to learn about how to select instance types.
* * Query of available resources: Call the [DescribeAvailableResource](~~66186~~) operation to query resources available in a specific region or zone.
* > If the `QuotaExceed.ElasticQuota` error is returned when you call this operation, it indicates that the maximum number of instances of the specified instance type in the region has been reached, or the maximum number of vCPUs for all instance types in a zone has been reached. You can go to the [ECS console](https://ecs.console.aliyun.com/?spm=a2c8b.12215451.favorites.decs.5e3a336aMGTtzy#/privileges/quota) or [Quota Center](https://quotas.console.aliyun.com/products/ecs/quotas) to request a quota increase.
* * **Image**:
* * The image determines the system disk configurations of the new instance. The system disk of the new instance is a clone of the specified image.
* * If you want to create instances with 512 MiB of memory, you cannot use Windows Server images except for Windows Server Semi-Annual Channel images.
* * If you want to create instances with 4 GiB or more of memory, you cannot use 32-bit OS image.
* * **Network type**:
* * Each instance that resides in a virtual private cloud (VPC) must be connected to only a single vSwitch.
* * If `VSwitchId` is specified, the security group specified by `SecurityGroupId` and the vSwitch specified by `VSwitchId` must belong to the same VPC.
* * The value of `PrivateIpAddress` varies based on the value of `VSwitchId`. `PrivateIpAddress` cannot be separately specified. If `VSwitchId` and `PrivateIpAddress` are specified, the IP address specified by `PrivateIpAddress` must be an idle IP address in the CIDR block of the specified vSwitch.
* * **Public bandwidth**:
* * Starting November 27, 2020, the maximum bandwidth value that is available for you to create ECS instances or change ECS instance configurations is subject to the throttling policy of your account. To increase the bandwidth limit, submit a ticket. The throttling policy imposes the following constraints: In a single region, the total maximum bandwidth value of all instances that use the pay-by-traffic billing method for network usage cannot exceed 5 Gbit/s and the total maximum bandwidth value of all instances that use the pay-by-bandwidth billing method for network usage cannot exceed 50 Gbit/s.
* * If you call the `CreateInstance` operation to create an instance, no public IP addresses are assigned to the instance. You can call the [AllocatePublicIpAddress](~~25544~~) operation to assign a public IP address to an instance.
* * Network usage fees vary based on the settings of `InternetChargeType` and `InternetMaxBandwidthOut`.
* * The value of `InternetMaxBandwidthIn` does not affect billing because inbound data traffic is free of charge.
* * If `InternetChargeType` is set to PayByBandwidth, `InternetMaxBandwidthOut` specifies the fixed bandwidth. A fixed bandwidth is a specified amount of public bandwidth allocated to an instance that uses the pay-by-bandwidth billing method for network usage.
* * If `InternetChargeType` is set to PayByTraffic, `InternetMaxBandwidthOut` specifies the peak bandwidth. A peak bandwidth is the maximum amount of public bandwidth that an instance can consume when the instance uses the pay-by-traffic billing method for network usage. Network usage costs are calculated based on the volume of network traffic.
* * **Security group**:
* * If no security groups are available in the region where you want to create an instance, you must call the [CreateSecurityGroup](~~25553~~) operation to create a security group in that region first.
* * The maximum number of instances that a security group can contain varies based on the security group type. For more information, see the "Security group limits" section in the [Limits](~~25412~~) topic.
* * Instances in the same security group can communicate with each other over the internal network. By default, instances in different security groups cannot communicate with each other. You can allow communication between instances by allowing mutual access between the security groups to which the instances belong. For more information, see [AuthorizeSecurityGroup](~~25554~~) and [AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgress](~~25560~~).
* * **Storage**:
* * The instance is assigned a system disk whose capacity varies based on the size of the specified image. The size of the system disk must be at least `20 GiB` and greater than or equal to the image size. For information about system disk categories, see the description of `SystemDisk.Category`.
* * The system disk of an I/O optimized instance can only be an enhanced SSD (ESSD) (`cloud_essd`), a standard SSD (`cloud_ssd`), or an ultra disk (`cloud_efficiency`).
* * The maximum size of a data disk varies based on the disk category. For more information, see the description of `DataDisk.N.Size`.
* * Up to 16 data disks can be added to an instance. Mount points /dev/xvd\\[b-z] are automatically assigned to data disks in ascending alphanumeric order.
* > If the `QuotaExceed.DiskCapacity` error is returned when you call this operation, it indicates that the maximum capacity of the disks of the selected disk category in the specified zone has been reached. You can go to the [Quota Center](https://quotas.console.aliyun.com/products/disk/quotas) to query and request a quota increase.
* * **User data**: If the instance type supports user data, you can use the UserData parameter to pass in user data.[](~~49121~~) User data is encoded in Base64. We recommend that you do not pass in confidential information (such as passwords or private keys) in plaintext as user data. This is because the system does not encrypt `UserData` values when API requests are transmitted. If you must pass in confidential information, we recommend that you encrypt and encode the information in Base64 before you pass in the information. Then decode and decrypt the information in the same way within the instance.
* * **Others**: When you call API operations by using Alibaba Cloud CLI or SDKs, you must delete periods (.) from some request parameters before you use the parameters. For example, use `SystemDiskCategory` instead of `SystemDisk.Category` as a request parameter.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createInstance(CreateInstanceRequest request);
/**
* In addition to calling the CreateKeyPair operation to create a key pair, you can use a third-party tool to create a key pair and then call the [ImportKeyPair](~~51774~~) operation to upload the key pair to an Alibaba Cloud region.
* Up to 500 key pairs can be created in each region. For more information, see the "SSH key pair limits" section in [Limits](~~25412~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture createKeyPair(CreateKeyPairRequest request);
/**
* ## Description
* Launch templates contain preset configurations used to create instances, such as the region, image ID, instance type, security group ID, and public bandwidth settings. If a specific parameter is not included in a launch template, you must manually specify the parameter when you use the launch template to create an instance.
* After you create a launch template (`CreateLaunchTemplate`), its version number is set to 1 by default. You can create multiple versions (`CreateLaunchTemplateVersion`) for the launch template. Version numbers start from 1 and increment by one. If you do not specify a template version number when you use a launch template to create instances ([RunInstances](~~63440~~)), the default version is used.
* When you call this operation, take note of the following items:
* * You can create up to 30 launch templates in each region. Each launch template can have up to 30 versions.
* * Most parameters in launch templates are optional. When you create a launch template, ECS does not verify the existence or validity of specified parameter values. The validity of the parameter values are verified only when you use the launch template to create instances.
* * If you set a specific parameter in a launch template, you cannot filter out this parameter when you use the launch template to create instances ([RunInstances](~~63440~~)). For example, if you set the `HostName` parameter to LocalHost in a launch template and do not set the `HostName` parameter when you call the `RunInstances` operation to create instances from the launch template, the created instance still has a hostname of `LocalHost`. If you want to overwrite the `LocalHost` value of HostName provided by the launch template, you can set `HostName` to MyHost or another value when you call the `RunInstances` operation.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createLaunchTemplate(CreateLaunchTemplateRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* If you want to modify the parameters of a launch template version, you can create another version with different parameter settings for the launch template. You can create up to 30 versions for each launch template.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createLaunchTemplateVersion(CreateLaunchTemplateVersionRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture createNatGateway(CreateNatGatewayRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * This operation is a synchronous operation. After an ENI is created, it immediately enters the Available (`Available`) state and can be attached to an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
* * If NetworkInterfaceId is empty in the response, no ENI is created. Call the operation again to create an ENI.
* * An ENI can be attached only to a single instance that resides in a virtual private cloud (VPC).
* * When an ENI is detached from an instance and attached to another instance, the attributes of the ENI remain unchanged and network traffic is redirected to the new instance.
* * When you call this operation to create an ENI, you can assign up to 49 secondary private IP addresses to the ENI.
* * If you want to assign IPv6 addresses when you create an ENI, make sure that IPv6 is enabled for the vSwitch with which you want to associate the ENI. For more information, see [What is an IPv6 gateway?](~~98896~~)
* * A quota is imposed on the number of ENIs that can be created per Alibaba Cloud region per account. You can view the quota in the ECS console. For more information, see [View and increase resource quotas](~~184115~~).
* **For information about examples on how to call this operation, see** [Create an ENI](~~471552~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture createNetworkInterface(CreateNetworkInterfaceRequest request);
/**
* Before you call this operation, submit a ticket to apply for using this operation.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createNetworkInterfacePermission(CreateNetworkInterfacePermissionRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture createPhysicalConnection(CreatePhysicalConnectionRequest request);
/**
* * A prefix list is a collection of network prefixes (CIDR blocks) and can be referenced to configure network rules for other resources. For more information, see [Overview](~~206223~~).
* * When you create a prefix list, take note of the following items:
* * You must specify an IP address family (IPv4 or IPv6) for the prefix list, and cannot change the IP address family after the prefix list is created. You cannot combine IPv4 and IPv6 CIDR blocks in a single prefix list.
* * You must specify the maximum number of entries that the prefix list can contain. You cannot modify the maximum number of entries after the prefix list is created.
* * You can specify entries for the prefix list. Each entry consists of a CIDR block and the description for the CIDR block. The total number of entries cannot exceed the maximum number of entries that you specified.
* * For more information about the limits on prefix lists and other resources, see [Limits](~~25412~~).
* * You can create Resource Access Management (RAM) users and grant them minimum permissions. This eliminates the need to share the AccessKey pair of your Alibaba Cloud account with other users and reduces security risks for your enterprises. For information about how to grant permissions on prefix lists to RAM users, see [Grant a RAM user permissions on prefix lists](~~206175~~)
*
*/
CompletableFuture createPrefixList(CreatePrefixListRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture createRouteEntry(CreateRouteEntryRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture createRouterInterface(CreateRouterInterfaceRequest request);
CompletableFuture createSavingsPlan(CreateSavingsPlanRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * You can create up to 100 security groups in a single Alibaba Cloud region.
* * To create a security group of the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) type, you must specify VpcId.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createSecurityGroup(CreateSecurityGroupRequest request);
/**
* You can use the ECS console, call [ECS API](~~63962~~) operations, or use CloudMonitor to view the scheduled simulated system events.
* The following descriptions provide the lifecycle of a simulated system event:
* * Scheduled: The state of the simulated system event is automatically changed to Scheduled after it is scheduled.
* * Executed: The state of the simulated system event is automatically changed to Executed at the time specified by the NotBefore parameter if no manual intervention is involved.
* * Canceled: The state of the simulated system event is changed to Canceled if you cancel the event by calling the [CancelSimulatedSystemEvents](~~88808~~) operation.
* * Avoided: The state of the simulated system event generated from maintenance-triggered instance restart can be changed to Avoided if you restart the instance before the scheduled time of the simulated system event. The maintenance-triggered instance restart is indicated by the SystemMaintenance.Reboot value. For more information, see [RebootInstance](~~25502~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture createSimulatedSystemEvents(CreateSimulatedSystemEventsRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* The local snapshot feature is replaced by the instant access feature. Take note of the following items:
* * If you have used the local snapshot feature before December 14, 2020, you can use the Category parameter.
* * If you have not used the local snapshot feature before December 14, 2020, new snapshots of your enhanced SSDs (ESSDs) at performance levels 0, 1, 2, and 3 (PL0, PL1, PL2, and PL3 ESSDs) and ESSD AutoPL disks are instantly available after creation without the need for additional configurations, regardless of whether the snapshots are manually or automatically created. The InstantAccess, InstantAccessRetentionDays, and DisableInstantAccess parameters in this operation that are related to the instant access feature no longer take effect. Available is added to the response parameters of the DescribeSnapshots and DescribeSnapshotGroup operations to indicate whether the snapshot is available.
* In the following scenarios, you cannot create snapshots for a disk:
* * The number of manual snapshots of the disk has reached 256.
* * A snapshot is being created for the disk.
* * The Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance to which the disk is attached has never been started.
* * The ECS instance to which the disk is attached is not in the **Stopped** (`Stopped`) or **Running** (`Running`) state.
* * If the response contains `{"OperationLocks": {"LockReason" : "security"}}` when you query the information of the instance, the instance is locked for security reasons and all operations are prohibited on it.
* When you create a snapshot, take note of the following items:
* * If a snapshot is being created, you cannot use this snapshot to create a custom image by calling the [CreateImage](~~25535~~) operation.
* * When a snapshot is being created for a disk that is attached to an ECS instance, do not change the instance state.
* * You can create snapshots for a disk that is in the **Expired** (`Expired`) state. If the release time scheduled for a disk arrives while a snapshot is being created for the disk, the snapshot is in the **Creating** (`Creating` state and is deleted when the disk is released.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createSnapshot(CreateSnapshotRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* You can specify `InstanceId` to create a snapshot-consistent group for disks on a specific (ECS instance. You can also specify `DiskId.N` to create a snapshot-consistent group for multiple disks on multiple ECS instances within the same zone.
* > You cannot specify both `DiskId.N` and `ExcludeDiskId.N` in the same request. If `InstanceId` is specified, you can use `DiskId.N` to specify only disks on the ECS instance specified by InstanceId and cannot use DiskId.N to specify disks across ECS instances.
* Take note of the following items:
* * The disks for which you want to create a snapshot must be in the **In Use** (`In_use`) or **Unattached** (`Available`) state.
* * If a disk is in the **In Use** (`In_use`) state, make sure that the ECS instance to which the disk is attached is in the **Running** (`Running`) or **Stopped** (`Stopped`) state.
* * If a disk is in the **Unattached** (`Available`) state, make sure that the disk has been attached to ECS instances. Snapshots cannot be created for disks that have never been attached to an ECS instance.
* * Snapshot-consistent groups can be used to create snapshots only for enhanced SSDs (ESSDs).
* * A snapshot-consistent group can contain snapshots of up to 16 disks, including system disks and data disks, and cannot exceed 32 TiB in size.
* * Snapshots that you created are stored indefinitely until you delete the snapshots. We recommend that you delete unnecessary snapshots on a regular basis to prevent excess snapshot storage fees.
* * Snapshot-consistent groups cannot be created for disks for which multi-attach feature is enabled. If disks for which the multi-attach feature is enabled are attached to an ECS instance, specify the `ExcludeDiskId.N` parameter to exclude the disks.
* For more information about the snapshot-consistent group feature, see [Create a snapshot-consistent group](~~199625~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture createSnapshotGroup(CreateSnapshotGroupRequest request);
/**
* A storage set can distribute disks or Shared Block Storage devices to different locations. You can specify the number of partitions in a storage set. A larger number of partitions indicate more discrete distribution of disks or Shared Block Storage devices.
* When you call this operation, take note of the following items:
* * The number of storage sets that you can create in a region is limited. You can call the [DescribeAccountAttributes](~~73772~~) operation to query the limit.
* * The number of partitions in a zone is limited. You can call the [DescribeAccountAttributes](~~73772~~) operation to query the limit.
*
*/
CompletableFuture createStorageSet(CreateStorageSetRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture createVSwitch(CreateVSwitchRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture createVirtualBorderRouter(CreateVirtualBorderRouterRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture createVpc(CreateVpcRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture deactivateRouterInterface(DeactivateRouterInterfaceRequest request);
/**
* $.parameters[4].schema.description
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteActivation(DeleteActivationRequest request);
CompletableFuture deleteAutoProvisioningGroup(DeleteAutoProvisioningGroupRequest request);
CompletableFuture deleteAutoSnapshotPolicy(DeleteAutoSnapshotPolicyRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteBandwidthPackage(DeleteBandwidthPackageRequest request);
CompletableFuture deleteCommand(DeleteCommandRequest request);
CompletableFuture deleteDedicatedHostCluster(DeleteDedicatedHostClusterRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
* > This operation is in internal preview and has not been officially released. We recommend that you avoid using this operation.
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteDemand(DeleteDemandRequest request);
CompletableFuture deleteDeploymentSet(DeleteDeploymentSetRequest request);
CompletableFuture deleteDiagnosticMetricSets(DeleteDiagnosticMetricSetsRequest request);
/**
* You can call this operation to delete the diagnostic reports that are no longer needed.
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteDiagnosticReports(DeleteDiagnosticReportsRequest request);
/**
* When you call this operation, take note of the following items:
* * Manual snapshots of the disk are retained.
* * You can call the [ModifyDiskAttribute](~~25517~~) operation to configure whether to retain automatic snapshots of the disk or release the snapshots along with the disk. We recommend that you delete the snapshots that are no longer needed to maintain a sufficient quota for new automatic snapshots.
* * The disk must be in the Unattached (Available) state.
* * If the specified DiskId parameter does not exist, the request is ignored.
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteDisk(DeleteDiskRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteForwardEntry(DeleteForwardEntryRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteHaVip(DeleteHaVipRequest request);
CompletableFuture deleteHpcCluster(DeleteHpcClusterRequest request);
/**
* For information about scenarios in which you cannot delete a custom image and the considerations related to custom image deletion, see [Delete a custom image](~~25466~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteImage(DeleteImageRequest request);
/**
* Only custom image components can be deleted.
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteImageComponent(DeleteImageComponentRequest request);
/**
* If an image build task based on an image template is in the BUILDING, DISTRIBUTING, RELEASING, or CANCELLING state, you cannot delete the image template. You can delete the image template only when the image build task is in the SUCCESS, FAILED, or CANCELLED state. You can call the DescribeImagePipelineExecutions operation to query the details of an image build task.
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteImagePipeline(DeleteImagePipelineRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * After an ECS instance is released, all the physical resources used by the instance are recycled. Relevant data is erased and cannot be restored.
* * When you release an ECS instance, take note of the following items for the disks attached to the instance:
* * The disks for which `DeleteWithInstance` is set to false are retained as pay-as-you-go disks after the instance is released.
* * The disks for which `DeleteWithInstance` is set to true are released along with the instance.
* * For disks for which `DeleteAutoSnapshot` is set to false, the automatic snapshots of the disks are retained after the instance is released.
* * For disks for which `DeleteAutoSnapshot` is set to true, the automatic snapshots of the disks are released along with the instance.
* * Manual snapshots of the disks are retained.
* * If `OperationLocks` in the response contains `"LockReason" : "security"` when you query the information of the instance, the instance is locked for security reasons. In this case, even if `DeleteWithInstance` is set to `false` for the disks that are attached to the instance, the system ignores the DeleteWithInstance value and releases the disks along with the instance. For more information, see [API behavior when an instance is locked for security reasons](~~25695~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteInstance(DeleteInstanceRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * After an ECS instance is released, all the physical resources used by the instance are recycled. Relevant data is erased and cannot be restored.
* * When you release an ECS instance, take note of the following items for the disks attached to the instance:
* * The disks for which `DeleteWithInstance` is set to false are retained as pay-as-you-go disks after the instance is released.
* * The disks for which `DeleteWithInstance` is set to true are released along with the instance.
* * If `DeleteAutoSnapshot` is set to false for a disk attached to the instance, the automatic snapshots of the disk are retained when the instance is released.
* * If `DeleteAutoSnapshot` is set to true for a disk attached to the instance, the automatic snapshots of the disk are released along with the instance.
* * Manual snapshots of the disks are retained.
* * If `OperationLocks` in the response contains `"LockReason" : "security"` when you query the information of the instance, the instance is locked for security reasons. In this case, even if `DeleteWithInstance` is set to `false` for the disks that are attached to the instance, the system ignores the DeleteWithInstance value and releases the disks along with the instance. For more information, see [API behavior when an instance is locked for security reasons](~~25695~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteInstances(DeleteInstancesRequest request);
/**
* When you call this operation, take note of the following items:
* * After an SSH key pair is deleted, you cannot query the SSH key pair by calling the [DescribeKeyPairs](~~51773~~) operation.
* * If an SSH key pair is bound to one or more Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances, the SSH key pair cannot be deleted.
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteKeyPairs(DeleteKeyPairsRequest request);
CompletableFuture deleteLaunchTemplate(DeleteLaunchTemplateRequest request);
CompletableFuture deleteLaunchTemplateVersion(DeleteLaunchTemplateVersionRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteNatGateway(DeleteNatGatewayRequest request);
/**
* Take note of the following items:
* * The ENI to be deleted must be in the Available state.
* * If the ENI to be deleted is attached to an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance, you must detach the ENI from the instance before you can delete the ENI. To detach the ENI, you can call the [DetachNetworkInterface](~~58514~~) operation.
* * After an ENI is deleted, the following situations occur:
* * All private IP addresses (including primary and secondary private IP addresses) of the ENI are automatically released.
* * The ENI is automatically removed from all security groups.
* * The DeleteNetworkInterface operation is an asynchronous operation. After this operation is called to delete an ENI, you can check the status or events of the ENI to determine whether the ENI is deleted. The following figure shows the transitions between the states of the ENI.
* 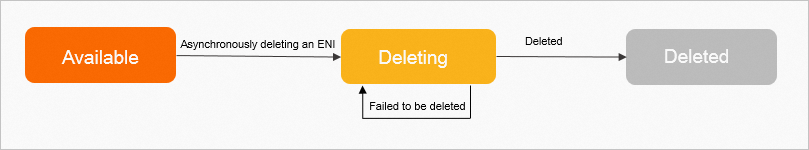
* * If the ENI is in the Deleting state, the ENI deletion request is sent and the ENI is being deleted.
* * If the ENI is not found, the ENI is deleted.
* * If the ENI is stuck in the Deleting state, the ENI fails to be deleted. You can re-initiate the request to delete the ENI.
* For information about examples on how to call the DeleteNetworkInterface operation, see [Delete an ENI](~~471553~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteNetworkInterface(DeleteNetworkInterfaceRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteNetworkInterfacePermission(DeleteNetworkInterfacePermissionRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture deletePhysicalConnection(DeletePhysicalConnectionRequest request);
/**
* If a prefix list is associated with resources, you cannot delete the prefix list. You must disassociate the prefix list from the resources before you delete the prefix list. You can call the [DescribePrefixListAssociations](~~204724~~) operation to query resources that are associated with a specific prefix list.
*
*/
CompletableFuture deletePrefixList(DeletePrefixListRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteRouteEntry(DeleteRouteEntryRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteRouterInterface(DeleteRouterInterfaceRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * Before you delete a security group, make sure that the security group does not contain instances and is not referenced by other security groups. Otherwise, the DeleteSecurityGroup request fails. You can call the [DescribeSecurityGroupReferences](~~57320~~) operation to query the reference details of the security group.
* * If the InvalidOperation.DeletionProtection error code is returned when you call the DeleteSecurityGroup operation to delete a security group or if a deletion protection-related message appears when you delete a security group in the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) console, the deletion protection feature is enabled for the security group. When you create a Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster, the deletion protection feature is enabled for an associated security group to prevent accidental deletion. You cannot manually disable the deletion protection feature for the security group. The deletion protection feature can be automatically disabled only after the ACK cluster is deleted. For more information, see [Disable deletion protection for a security group](~~353191~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteSecurityGroup(DeleteSecurityGroupRequest request);
/**
* Take note of the following items:
* * If the snapshot does not exist, the request is ignored.
* * If the snapshot has been used to create custom images, the snapshot cannot be deleted. You need to call the [DeleteImage](~~25537~~) operation to delete the custom images before you can delete the snapshot.
* * If the snapshot has been used to create disks and `Force` is not specified or is set to `false`, the snapshot cannot be deleted directly. If you want to delete the snapshot, set `Force` to true to forcibly delete the snapshot. The disks created from the snapshot cannot be re-initialized after the snapshot is forcibly deleted.
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteSnapshot(DeleteSnapshotRequest request);
/**
* If you have custom images that were created from a disk snapshot contained in a snapshot-consistent group, the disk snapshot is retained when the snapshot-consistent group is deleted. Before you can delete the disk snapshot, you must call the [DeleteImage](~~25537~~) operation to delete the custom images. After the custom images are deleted, you can call the [DeleteSnapshot](~~25525~~) operation to delete the disk snapshot.
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteSnapshotGroup(DeleteSnapshotGroupRequest request);
CompletableFuture deleteStorageSet(DeleteStorageSetRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteVSwitch(DeleteVSwitchRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteVirtualBorderRouter(DeleteVirtualBorderRouterRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture deleteVpc(DeleteVpcRequest request);
CompletableFuture deregisterManagedInstance(DeregisterManagedInstanceRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeAccessPoints(DescribeAccessPointsRequest request);
/**
* After you [create](https://account.alibabacloud.com/register/intl_register.htm) an Alibaba Cloud account, you can create a specific number of ECS instances in different regions within the account. For more information, see [Limits](~~25412~~).
* You can apply for a quota increase in the [Quota Center console](https://quotas.console.aliyun.com/products).
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeAccountAttributes(DescribeAccountAttributesRequest request);
/**
* You can use one of the following methods to check the responses:
* - Method 1: When you call the DescribeActivations operation to retrieve the first page of results during a paged query, use MaxResults to specify the maximum number of entries to return in the call. The return value of NextToken is a pagination token, which you can use in the next request to retrieve a new page of results. When you call the DescribeActivations operation to retrieve a new page of results, set NextToken to the NextToken value returned in the previous call and use MaxResults to specify the maximum number of entries to return in this call.
* - Method 2: Use PageSize to specify the number of entries to return on each page, and then use PageNumber to specify the number of the page to return. You can use only one of the preceding methods. If you specify MaxResults or NextToken, the PageSize and PageNumber request parameters do not take effect and the TotalCount response parameter is invalid.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeActivations(DescribeActivationsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeAutoProvisioningGroupHistory(DescribeAutoProvisioningGroupHistoryRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeAutoProvisioningGroupInstances(DescribeAutoProvisioningGroupInstancesRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeAutoProvisioningGroups(DescribeAutoProvisioningGroupsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeAutoSnapshotPolicyEx(DescribeAutoSnapshotPolicyExRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* The value of `DestinationResource` determines whether you need to specify additional parameters. When you select a value in the following chain for DestinationResource, the more to the right the selected value is ordered, the more parameters you must specify.
* * Sequence: `Zone > IoOptimized > InstanceType = Network = ddh > SystemDisk > DataDisk`
* * Examples:
* * If you set `DestinationResource` to `DataDisk`, take note of the following items:
* * If you set `ResourceType` to `disk` to query the categories of data disks that are not attached to ECS instances, you do not need to specify `InstanceType`.
* * If you set `ResourceType` to `instance` to query the categories of data disks that are purchased together with ECS instances, you must specify `InstanceType` and `SystemDiskCategory` due to instance type-specific limits on system disks and data disks.
* * If you set `DestinationResource` to `SystemDisk` and `ResourceType` to `instance`, you must specify `InstanceType` due to instance type-specific limits on system disks.
* * If you set `DestinationResource` to `InstanceType`, we recommend that you specify `IoOptimized` and `InstanceType`.
* * If you want to query the available ecs.g5.large resources in all zones of the China (Hangzhou) region, set `RegionId to cn-hangzhou, DestinationResource to InstanceType, IoOptimized to optimized, and InstanceType to ecs.g5.large`.
* * If you want to query the zones where ecs.g5.large resources are available in the China (Hangzhou) region, set `RegionId to cn-hangzhou, DestinationResource to Zone, IoOptimized to optimized, and InstanceType to ecs.g5.large`.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeAvailableResource(DescribeAvailableResourceRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeBandwidthLimitation(DescribeBandwidthLimitationRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeBandwidthPackages(DescribeBandwidthPackagesRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeCapacityReservationInstances(DescribeCapacityReservationInstancesRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeCapacityReservations(DescribeCapacityReservationsRequest request);
/**
* Take note of the following items:
* * This operation applies only to instances that reside in the classic network.
* * You can query a maximum of 100 instances that reside in the classic network at a time.
* * At least one of the `VpcId` and `InstanceId` parameters must be configured.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeClassicLinkInstances(DescribeClassicLinkInstancesRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeCloudAssistantSettings(DescribeCloudAssistantSettingsRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * Before you run commands on or send files to instances, especially new instances, we recommend that you query the status of Cloud Assistant on the instances by calling this operation and checking the return value of CloudAssistantStatus. Run commands on or send files to the instances only when the return value is true.
* * You can use one of the following methods to check the responses:
* * Method 1: During a paged query, when you call the DescribeCloudAssistantStatus operation to retrieve the first page of results, set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in the call. The return value of `NextToken` is a pagination token, which can be used in the next request to retrieve a new page of results. When you call the DescribeCloudAssistantStatus operation to retrieve a new page of results, set `NextToken` to the `NextToken` value returned in the previous call and set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in this call.
* * Method 2: Use `PageSize` to specify the number of entries to return on each page and then use `PageNumber` to specify the number of the page to return. You can use only one of the preceding methods. If you specify `MaxResults` or `NextToken`, the `PageSize` and `PageNumber` request parameters do not take effect and the `TotalCount` response parameter is invalid.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeCloudAssistantStatus(DescribeCloudAssistantStatusRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeClusters(DescribeClustersRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * If you specify only `Action` and `RegionId`, all available commands (`CommandId`) that you created in the specified region are queried by default.
* * You can use one of the following methods to check the responses:
* * Method 1: During a paged query, when you call the DescribeCommands operation to retrieve the first page of results, set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in the call. The return value of `NextToken` is a pagination token, which can be used in the next request to retrieve a new page of results. When you call the DescribeCommands operation to retrieve a new page of results, set `NextToken` to the `NextToken` value returned in the previous call and set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in this call.
* * Method 2: Use `PageSize` to specify the number of entries to return on each page and then use `PageNumber` to specify the number of the page to return. You can use only one of the preceding methods. If you specify `MaxResults` or `NextToken`, the `PageSize` and `PageNumber` request parameters do not take effect and the `TotalCount` response parameter is invalid.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeCommands(DescribeCommandsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeDedicatedHostAutoRenew(DescribeDedicatedHostAutoRenewRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* You can specify multiple request parameters to filter query results. Specified request parameters have logical AND relations. Only the specified parameters are included in the filter conditions. However, if `DedicatedHostClusterIds` is set to an empty JSON array (`[]`), this parameter is regarded as a valid filter condition and an empty result is returned.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeDedicatedHostClusters(DescribeDedicatedHostClustersRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeDedicatedHostTypes(DescribeDedicatedHostTypesRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* You can use one of the following methods to query the information about dedicated hosts:
* * Specify `DedicatedHostIds` to query the details of specified dedicated hosts.
* * Specify `DedicatedHostClusterId` to query the details of dedicated hosts in a dedicated host cluster.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeDedicatedHosts(DescribeDedicatedHostsRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
* You can call this operation to query the details of resources that you filed with Alibaba Cloud, including the types, delivery status, and consumption details of the resources.
* By default, the demands for I/O optimized instances of the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) type are queried.
* For information about how to create (CreateDemand), modify (ModifyDemand), and delete (DeleteDemand) demands for ECS resources, contact your account manager.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeDemands(DescribeDemandsRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* For information about instance families, see [Overview of instance families](~~25378~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeDeploymentSetSupportedInstanceTypeFamily(DescribeDeploymentSetSupportedInstanceTypeFamilyRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeDeploymentSets(DescribeDeploymentSetsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeDiagnosticMetricSets(DescribeDiagnosticMetricSetsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeDiagnosticMetrics(DescribeDiagnosticMetricsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeDiagnosticReportAttributes(DescribeDiagnosticReportAttributesRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeDiagnosticReports(DescribeDiagnosticReportsRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* You can query the following monitoring data of a disk: the read IOPS, write IOPS, read bandwidth (byte/s), write bandwidth (byte/s), read latency (microseconds), and write latency (microseconds).
* Take note of the following items:
* * You can query the monitoring data only of the disks that are in the In Use (`In_use`) state. For more information, see [Disk states](~~25689~~).
* **
* **Note** Some information may be missing from the monitoring data of a disk because the disk is not in the In Use (`In_use`) state and the system cannot obtain the relevant information.
* * Up to 400 monitoring data entries can be returned at a time. Make sure that the `TotalCount` value does not exceed 400. The value is calculated by using the following formula: `TotalCount = (EndTime - StartTime)/Period`. If the TotalCount value is greater than 400, the `InvalidParameter.TooManyDataQueried` error is returned.
* * You can query the monitoring data in the last 30 days. If the value of `StartTime` is more than 30 days earlier than the current time, an error is returned.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeDiskMonitorData(DescribeDiskMonitorDataRequest request);
/**
* ### [](#)Usage notes
* * You can specify multiple request parameters such as `RegionId`, `ZoneId`, `DiskIds`, and `InstanceId` as filters. The specified parameters are evaluated by using the "AND" operator. If you specify more than one filter, the records that match all filters are returned.
* * The value of `DiskIds` is a JSON array. If you do not specify DiskIds, the parameter is not used as a filter condition. If you set `DiskIds` to an empty JSON array, the parameter is regarded as a valid filter, and an empty result is returned.
* * You can use one of the following methods to check the responses:
* * Method 1: Use `NextToken` to specify the pagination token. Set the value to the `NextToken` value that is obtained from the previous query. Then, use `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return on each page.
* * Method 2: Use `PageSize` to specify the number of entries to return on each page, and then use `PageNumber` to specify the number of the page to return.
* You can use only one of the preceding methods. If a large number of entries are to be returned, we recommend that you use Method 1. If `NextToken` is specified, `PageSize` and `PageNumber` do not take effect and `TotalCount` in the response is invalid.
* * You can attach a disk for which the multi-attach feature is enabled to multiple instances. You can query the attachment information of the disk based on the `Attachment` values in the response.
* When you call an API operation by using Alibaba Cloud CLI, you must specify request parameter values of different data types in the required formats. For more information, see [Parameter format overview](~~110340~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeDisks(DescribeDisksRequest request);
/**
* * The full status information about an EBS device includes the lifecycle status specified by the `Status` parameter, health status specified by the `HealthStatus` parameter, and event type specified by the `EventType` parameter of the EBS device. You can filter the results based on these parameters.
* * The release time, scheduled execution time, and actual execution time of each EBS device event are identical. If you specify a period of time by using the `EventTime.Start` and `EventTime.End` parameters, all events that occurred within this period are queried. You can query events that occurred within the last seven days.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeDisksFullStatus(DescribeDisksFullStatusRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeEipAddresses(DescribeEipAddressesRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeEipMonitorData(DescribeEipMonitorDataRequest request);
/**
* When an elasticity assurance expires, data about the association between the instances and the private pool generated by the elasticity assurance becomes invalid. When you call this operation to query the expired elasticity assurance, no value is returned.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeElasticityAssuranceInstances(DescribeElasticityAssuranceInstancesRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeElasticityAssurances(DescribeElasticityAssurancesRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* The monitoring data of a secondary ENI includes the amount of traffic sent and received over the internal network, the number of packets sent and received by the secondary ENI, and the number of sent and received packets that are dropped by the secondary ENI. Specific information may be missing from the returned monitoring data. This may be because the system cannot obtain the relevant information. For example, if the instance to which the secondary ENI is attached is in the Stopped state or if the secondary ENI is not attached to an instance and is in the Available state, the monitoring data of the secondary ENI cannot be obtained. Take note of the following items:
* * Up to 400 monitoring data entries can be returned at a time. Make sure that the `TotalCount` value does not exceed 400. The value is calculated by using the following formula: `TotalCount = (EndTime - StartTime)/Period`. If the TotalCount value is greater than 400, the `InvalidParameter.TooManyDataQueried` error is returned.
* * You can query the monitoring data in the last 30 days. If the value of `StartTime` is more than 30 days earlier than the current time, an error is returned.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeEniMonitorData(DescribeEniMonitorDataRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeForwardTableEntries(DescribeForwardTableEntriesRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeHaVips(DescribeHaVipsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeHpcClusters(DescribeHpcClustersRequest request);
/**
* You can use `NextToken` to configure the query token. Set the value to the `NextToken` value that is returned in the previous call to the DescribeImageComponents operation. Then, use `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return on each page.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeImageComponents(DescribeImageComponentsRequest request);
/**
* ## Description
* * This API operation only returns the available custom images that are newly created in the specified image family. Public images, Alibaba Cloud Marketplace images, community images, or shared images are not queried.
* * If no available custom images exist in the specified image family, the response is empty.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeImageFromFamily(DescribeImageFromFamilyRequest request);
/**
* * The image template that is specified by the `ImagePipelineId` parameter cannot be a deleted image template. When an image template is deleted, the corresponding image creation task is deleted.
* * You must specify `ImagePipelineId` or `ExecutionId`.
* * You can configure the query token by using the `NextToken` parameter. Set the value of NextToken to the value of `NextToken` that was returned the last time you called the `DescribeImagePipelineExecutions` operation. Then, use the `MaxResults` parameter to specify the maximum number of entries to return on each page to query the details of the image creation task.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeImagePipelineExecutions(DescribeImagePipelineExecutionsRequest request);
/**
* You can use `NextToken` to configure the query token. Set the value to the `NextToken` value that is returned in the previous call to the `DescribeImagePipelines` operation. Then, use `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return on each page.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeImagePipelines(DescribeImagePipelinesRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeImageSharePermission(DescribeImageSharePermissionRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeImageSupportInstanceTypes(DescribeImageSupportInstanceTypesRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * You can query your custom images, public images provided by Alibaba Cloud, Alibaba Cloud Marketplace images, and shared images from other Alibaba Cloud accounts.
* * This is a paginated query. The response contains the total number of available images and the images on the returned page. By default,10 entries are displayed on each page.
* * When you call an API operation by using Alibaba Cloud CLI, you must specify request parameter values of different data types in the required formats. For more information, see [Parameter formats](~~110340~~).
* * If you set ImageOwnerAlias to system or others when you call the DescribeImages operation to query public images that are provided by Alibaba Cloud or shared images, Resource Access Management (RAM) policies are ignored in the request. For more information, see [RAM authorization](~~25497~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeImages(DescribeImagesRequest request);
/**
* A private pool is generated after an elasticity assurance or a capacity reservation is created. The private pool is associated with information about the instances that are created by using the private pool. You can configure a private pool when you create an instance. This way, the instance matches the elasticity assurance or capacity reservation that is associated with the private pool.
* When a private pool expires, data about the association between instances and the private pool becomes invalid. If you call this operation to query the information about the private pool, empty values are returned.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInstanceAttachmentAttributes(DescribeInstanceAttachmentAttributesRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeInstanceAttribute(DescribeInstanceAttributeRequest request);
/**
* * Before you configure auto-renewal or manual renewal for subscription instances, you can query the auto-renewal status of the instances.
* * This operation is applicable to only subscription instances. An error is returned if you call this operation on pay-as-you-go instances.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInstanceAutoRenewAttribute(DescribeInstanceAutoRenewAttributeRequest request);
/**
* * You can query system events that were completed within the last 30 days. No limits apply to the time range for querying uncompleted system events.
* * You can also specify InstanceEventCycleStatus to query the system events that are in the Scheduled, Executing, or Inquiring state.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInstanceHistoryEvents(DescribeInstanceHistoryEventsRequest request);
/**
* This operation is used to query the specified maintenance policy of an instance, which contains the following maintenance attributes:
* * Maintenance window: the time period that you specify for maintenance.
* * Maintenance action: the action that you specify in response to instance shutdown.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInstanceMaintenanceAttributes(DescribeInstanceMaintenanceAttributesRequest request);
/**
* * Pricing information can be queried for unexpired subscription ECS instances only when you upgrade their configurations. The pricing information cannot be queried when the instance configurations are downgraded.
* * Pricing information cannot be queried for pay-as-you-go ECS instances when you change their configurations. Prices of existing pay-as-you-go ECS instances whose configurations are changed are the same as those of new pay-as-you-go instances. You can call the [DescribePrice](~~107829~~) operation to query the latest prices of ECS instances.
* * Before you upgrade the configurations of an instance, we recommend that you call the [DescribeResourcesModification](~~66187~~) operation to query the instance types available for configuration upgrades in a specified zone.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInstanceModificationPrice(DescribeInstanceModificationPriceRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * Up to 400 monitoring data entries can be returned at a time. Make sure that the `TotalCount` value does not exceed 400. The value is calculated by using the following formula: `TotalCount = (EndTime - StartTime)/Period`. If the TotalCount value is greater than 400, the `InvalidParameter.TooManyDataQueried` error is returned.
* * You can query the monitoring data in the last 30 days. If the value of `StartTime` is more than 30 days earlier than the current time, an error is returned.
* * In some scenarios, such as when the instance is in the Stopped state, the system cannot obtain the relevant information and specific information may be missing from the returned monitoring data.
* * You cannot call this operation to obtain the CPU basic monitoring information of an ECS bare metal instance. To obtain the CPU monitoring information of an ECS bare metal instance, install the CloudMonitor agent on the instance. For more information, see [InstallCloudMonitor](~~183482~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInstanceMonitorData(DescribeInstanceMonitorDataRequest request);
/**
* ## Description
* When you call an API operation by using Alibaba Cloud CLI, you must specify request parameter values of different data types in required formats. For more information, see [Parameter format overview](~~110340~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInstanceRamRole(DescribeInstanceRamRoleRequest request);
/**
* * For information about the lifecycle states of an ECS instance, see [Instance states](~~25687~~).
* * You can also call this operation to query the list of ECS instances.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInstanceStatus(DescribeInstanceStatusRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeInstanceTopology(DescribeInstanceTopologyRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeInstanceTypeFamilies(DescribeInstanceTypeFamiliesRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * MaxResults specifies the maximum number of entries per page. The maximum value of this parameter is changed from 1600 to 100. As of November 15, 2023, only 100 can be used as the maximum value of MaxResults. If you called the DescribeInstanceTypes operation in 2022, you can use 1600 as the maximum value before November 15, 2023. If you do not specify NextToken when you call the DescribeInstanceTypes operation, only the first page of results that contains up to 100 entries is returned. If you want to retrieve more results, specify NextToken to perform paged queries, or specify filter conditions to filter results.
* * We recommend that you specify MaxResults and NextToken to perform paged queries. The first time you call the DescribeInstanceTypes operation, set MaxResults to limit the maximum number of entries that can be returned in a single call. If the number of entries to return exceeds the specified MaxResults value, the response includes a NextToken value. You can set NextToken to the return value and specify MaxResults in your next request to DescribeInstanceTypes to retrieve the next page of results.
* * The DescribeInstanceTypes operation is used to query only the specifications and performance information of instance types. To query instance types that are available in a specific region, call the [DescribeAvailableResource](~~66186~~) operation.
* * To use special instance types such as instance types that are unavailable for purchase, [submit a ticket](https://workorder-intl.console.aliyun.com/#/ticket/createIndex).
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInstanceTypes(DescribeInstanceTypesRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * The **keepalive** time of a connection to a VNC management terminal is 300 seconds. If you do not interact with the VNC management terminal for 300 seconds, the VNC management terminal is automatically disconnected.
* * If the connection is interrupted, you must recall this operation to obtain a new logon address that is specified by `VncUrl` and use the new logon address to construct a URL that can be used to reconnect to the VNC management terminal. You can reconnect to a VNC management terminal for a maximum of 30 times per minute.
* * You need to add the `vncUrl=\\*\\*\\*\\*`, `instanceId=\\*\\*\\*\\*`, and `isWindows=true/false` parameters to the end of the link `https://g.alicdn.com/aliyun/ecs-console-vnc2/0.0.8/index.html?` and use an ampersand (`&`) between the parameters.
* * `vncUrl`: the value of `VncUrl` that is returned after a successful call of this operation.
* * `instanceId`: the ID of your instance.
* * `isWindows`: specifies whether the operating system of your instance is Windows. A value of `true` indicates that the operating system is Windows. A value of `false` indicates that the operating system is not Windows.
* > You can connect to an instance without a VNC logon password. Therefore, you do not need to configure the `password` parameter.
* Sample URL:
* https://g.alicdn.com/aliyun/ecs-console-vnc2/0.0.8/index.html?vncUrl=ws%3A%2F%****&instanceId=i-wz9hhwq5a6tm****&isWindows=true
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInstanceVncUrl(DescribeInstanceVncUrlRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * You can specify multiple request parameters to filter query results. Specified request parameters have logical AND relations. Only the specified parameters are included in the filter conditions. However, if InstanceIds is set to an empty JSON array, this parameter is regarded as a valid filter condition and an empty result is returned.
* * If you are using a Resource Access Management (RAM) user or RAM role that does not have the permissions to call this operation, an empty list is returned. You can include `DryRun` in your request to check whether the empty list is caused by lack of permissions.
* * When you call the API operation by using Alibaba Cloud CLI, you must specify request parameter values of different data types in the required formats. For more information, see [Parameter formats](~~110340~~).
* * You can use one of the following methods to check the responses:
* * Method 1: During a paged query, when you call the DescribeInstances operation to retrieve the first page of results, set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in the call. The return value of `NextToken` is a pagination token, which can be used in the next request to retrieve a new page of results. When you call the DescribeInstances operation to retrieve a new page of results, set `NextToken` to the `NextToken` value returned in the previous call and set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in this call.
* * Method 2: Use `PageSize` to specify the number of entries to return on each page and then use `PageNumber` to specify the number of the page to return.
* You can use only one of the preceding methods. If a large number of entries are to be returned, we recommend that you use Method 1. When `MaxResults` or `NextToken` is specified, the `PageSize` and `PageNumber` request parameters do not take effect and the `TotalCount` response parameter is invalid.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInstances(DescribeInstancesRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* The response includes the instance status and the instance system events that are in the Scheduled state.
* You can specify a period of time to query events that occurred within the period of time.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInstancesFullStatus(DescribeInstancesFullStatusRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * After you run a command, the command may fail to run or may return unexpected results. You can call this operation to query the execution results.
* * You can query information about command executions within the last four weeks. Up to 100,000 pieces of execution information can be retained.
* * You can [subscribe to Cloud Assistant task status events](~~2669130~~) to obtain command execution results from the events. This helps you reduce the number of times to poll API operations and improve efficiency.
* * You can use one of the following methods to check the responses:
* * Method 1: During a paged query, when you call the DescribeInvocationResults operation to retrieve the first page of results, set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in the call. The return value of `NextToken` is a pagination token, which can be used in the next request to retrieve a new page of results. When you call the DescribeInvocationResults operation to retrieve a new page of results, set `NextToken` to the `NextToken` value returned in the previous call and set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in this call.
* * Method 2: Use `PageSize` to specify the number of entries per page, and then use `PageNumber` to specify the page number. You can use only one of the preceding methods. If you specify `MaxResults` or `NextToken`, the `PageSize` and `PageNumber` request parameters do not take effect and the `TotalCount` response parameter is invalid.
* * Comparison between the `DescribeInvocations` and `DescribeInvocationResults` operations:
* * Scenario in which the `RunCommand` or `InvokeCommand` operation is called to run a Cloud Assistant command on multiple instances:
* * The `DescribeInvocations` operation queries the execution status of the command on each instance and the overall execution status of the command on all instances.
* * The `DescribeInvocationResults` operation queries only the execution status of the command on each instance.
* * Scenario in which the `RunCommand` or `InvokeCommand` operation is called to run a Cloud Assistant command on a single instance:
* * The `DescribeInvocations` operation is equivalent to the `DescribeInvocationResults` operation.
* * If you want to query the status of each execution for a scheduled (recurring) task or a task that is automatically executed on instance startup (`RepeatMode is set to Period or EveryReboot`), you can call only the `DescribeInvocationResults` operation and must set `IncludeHistory` to true. The `DescribeInvocations` operation queries only the most recent execution status of the command.
* * If you want to view the command content and parameters, you can call only the `DescribeInvocations` operation and check the `CommandContent` value in the response.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInvocationResults(DescribeInvocationResultsRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * After you run a command, the command may fail to run or may return unexpected results. You can call this operation to query the execution results.
* * You can query information about command executions within the last four weeks. Up to 100,000 pieces of execution information can be retained.
* * You can [subscribe to Cloud Assistant task status events](~~2669130~~) to obtain command execution results from the events. This helps you reduce the number of times to poll API operations and improve efficiency.
* * You can use one of the following methods to check the responses:
* * Method 1: During a paged query, when you call the DescribeInvocations operation to retrieve the first page of results, use `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in the call. The return value of `NextToken` is a pagination token, which you can use in the next request to retrieve a new page of results. When you call the DescribeInvocations operation to retrieve a new page of results, set `NextToken` to the `NextToken` value returned in the previous call and set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in this call.
* * Method 2: Use `PageSize` to specify the number of entries per page, and then use `PageNumber` to specify the page number. You can use only one of the preceding methods. If you specify `MaxResults` or `NextToken`, the `PageSize` and `PageNumber` request parameters do not take effect and the `TotalCount` response parameter is invalid.
* * Comparison between the `DescribeInvocations` and `DescribeInvocationResults` operations:
* * Scenario in which the `RunCommand` or `InvokeCommand` operation is called to run a Cloud Assistant command on multiple instances:
* * The `DescribeInvocations` operation queries the execution status of the command on each instance and the overall execution status of the command on all instances.
* * The `DescribeInvocationResults` operation queries only the execution status of the command on each instance.
* * Scenario in which the `RunCommand` or `InvokeCommand` operation is called to run a Cloud Assistant command on a single instance:
* * The `DescribeInvocations` operation is equivalent to the `DescribeInvocationResults` operation.
* * If you want to query the status of each execution for a scheduled (recurring) task or a task that is automatically executed on instance startup (`RepeatMode is set to Period or EveryReboot`), you can call only the `DescribeInvocationResults` operation and must set `IncludeHistory` to true. The `DescribeInvocations` operation queries only the most recent execution status of the command.
* * If you want to view the command content and parameters, you can call only the `DescribeInvocations` operation and check the `CommandContent` value in the response.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeInvocations(DescribeInvocationsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeKeyPairs(DescribeKeyPairsRequest request);
/**
* ## Debugging
* [OpenAPI Explorer automatically calculates the signature value. For your convenience, we recommend that you call this operation in OpenAPI Explorer. OpenAPI Explorer dynamically generates the sample code of the operation for different SDKs.](https://api.aliyun.com/#product=Ecs\\&api=DescribeLaunchTemplateVersions\\&type=RPC\\&version=2014-05-26)
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeLaunchTemplateVersions(DescribeLaunchTemplateVersionsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeLaunchTemplates(DescribeLaunchTemplatesRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeLimitation(DescribeLimitationRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* You can use one of the following methods to check the responses:
* * Method 1: During a paged query, when you call the DescribeManagedInstances operation to retrieve the first page of results, set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in the call. The return value of `NextToken` is a pagination token, which can be used in the next request to retrieve a new page of results. When you call the DescribeManagedInstances operation to retrieve a new page of results, set `NextToken` to the `NextToken` value returned in the previous call and set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in this call.
* * Method 2: Use `PageSize` to specify the number of entries to return on each page and then use `PageNumber` to specify the number of the page to return. You can use only one of the preceding methods. If you specify `MaxResults` or `NextToken`, the `PageSize` and `PageNumber` request parameters do not take effect and the `TotalCount` response parameter is invalid.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeManagedInstances(DescribeManagedInstancesRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeNatGateways(DescribeNatGatewaysRequest request);
/**
* ## Debugging
* [OpenAPI Explorer automatically calculates the signature value. For your convenience, we recommend that you call this operation in OpenAPI Explorer. OpenAPI Explorer dynamically generates the sample code of the operation for different SDKs.](https://api.aliyun.com/#product=Ecs\\&api=DescribeNetworkInterfaceAttribute\\&type=RPC\\&version=2014-05-26)
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeNetworkInterfaceAttribute(DescribeNetworkInterfaceAttributeRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeNetworkInterfacePermissions(DescribeNetworkInterfacePermissionsRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* You can call the `DescribeNetworkInterfaces` operation for paged query by specifying the `MaxResults` or `NextToken` parameter. Take note of the following items:
* * During a paged query, when you call the DescribeNetworkInterfaces operation to retrieve the first page of results, set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in the call. The return value of `NextToken` is a pagination token that can be used in the next call to retrieve a new page of results.
* * When you call the DescribeNetworkInterfaces operation to retrieve a new page of results, set `NextToken` to the `NextToken` value returned in the previous call and set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in this call.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeNetworkInterfaces(DescribeNetworkInterfacesRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeNewProjectEipMonitorData(DescribeNewProjectEipMonitorDataRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describePhysicalConnections(DescribePhysicalConnectionsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describePrefixListAssociations(DescribePrefixListAssociationsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describePrefixListAttributes(DescribePrefixListAttributesRequest request);
/**
* ## Description
* You can specify the `AddressFamily`, `PrefixListId.N`, and `PrefixListName` request parameters to be queried. Specified parameters have logical AND relations. Only the specified parameters are included in the filter conditions.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describePrefixLists(DescribePrefixListsRequest request);
/**
* # [](#)Usage notes
* * The required parameters vary based on the types of resources whose prices you want to query.
* * When `ResourceType` is set to instance, you must specify `InstanceType`.
* * When `ResourceType` is set to disk, you must specify both `DataDisk.1.Category` and `DataDisk.1.Size`. When `ResourceType` is set to disk, only pay-as-you-go prices of cloud disks are returned. In this scenario, `PriceUnit` can be set only to `Hour`.
* * When `ResourceType` is set to ddh, you must specify `DedicatedHostType`.
* * When `ResourceType` is set to ElasticityAssurance, you must specify `InstanceType`.
* * When `ResourceType` is set to CapacityReservation, you must specify `InstanceType`.
* * When `ResourceType` is set to bandwidth, only the pay-by-traffic (`PayByTraffic`) price for network usage is returned.
* * When `ResourceType` is set to instance, the prices of up to four data disks can be queried.
* * By default, `ChargeType` is set to `PostPaid`. You can specify `PriceUnit` to query prices of ECS resources that have different billing cycles.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describePrice(DescribePriceRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeRecommendInstanceType(DescribeRecommendInstanceTypeRequest request);
/**
* ****
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeRegions(DescribeRegionsRequest request);
/**
* * You can call this operation to query the price for renewing a subscription instance for a specific period of time or to a synchronized expiration date.
* * Take note of the following items:
* * If you specify only the required parameters, the price for renewing an instance for one month is queried by default.
* * The renewal period-related parameter pair (`Period` and `PeriodUnit`) and the synchronized expiration date-related parameter (`ExpectedRenewDay`) are mutually exclusive. You cannot set these parameters together to query the prices for renewing a specified instance for a period of time and to a synchronized expiration date at the same time.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeRenewalPrice(DescribeRenewalPriceRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeReservedInstanceAutoRenewAttribute(DescribeReservedInstanceAutoRenewAttributeRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeReservedInstances(DescribeReservedInstancesRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeResourceByTags(DescribeResourceByTagsRequest request);
/**
* ## Debugging
* [OpenAPI Explorer automatically calculates the signature value. For your convenience, we recommend that you call this operation in OpenAPI Explorer. OpenAPI Explorer dynamically generates the sample code of the operation for different SDKs.](https://api.aliyun.com/#product=Ecs\\&api=DescribeResourcesModification\\&type=RPC\\&version=2014-05-26)
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeResourcesModification(DescribeResourcesModificationRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeRouteTables(DescribeRouteTablesRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeRouterInterfaces(DescribeRouterInterfacesRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeSavingsPlanEstimation(DescribeSavingsPlanEstimationRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeSavingsPlanPrice(DescribeSavingsPlanPriceRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeSecurityGroupAttribute(DescribeSecurityGroupAttributeRequest request);
/**
* When you call this operation, take note of the following items:
* * A security group can be referenced by the inbound or outbound rules of other security groups.
* * Up to 100 entries can be returned each time.
* * If a security group cannot be deleted by calling the [DeleteSecurityGroup](~~25558~~) operation, you can call the DescribeSecurityGroupReferences operation to check whether the security group is referenced by the rules of other security groups. If the security group is referenced by the rules of other security groups, you must remove the reference before you can delete the security group.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeSecurityGroupReferences(DescribeSecurityGroupReferencesRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * The basic information about security groups includes their IDs and descriptions. The response returns security groups in descending order of the IDs of the security groups.
* * We recommend that you use `MaxResults` and `NextToken` for a paged query. We recommend that you use `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return for each request. The return value of `NextToken` is a pagination token, which can be used in the next request to retrieve a new page of results. When you call the DescribeSecurityGroups operation to retrieve a new page of results, set `NextToken` to the `NextToken` value that is returned in the previous call and set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in this call. If the return value of `NextToken` is empty, the current page of results is the last page and no more results are to be returned.
* * When you use Alibaba Cloud CLI to call an API operation, you must specify request parameter values of different data types in required formats. For more information, see [Parameter format overview](~~110340~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeSecurityGroups(DescribeSecurityGroupsRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes:
* * When you send a file, the file may fail to be sent to specific Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances. You can call this operation to check the file sending results.
* * You can call this operation to query the file sending records within the last six weeks.
* * You can use one of the following methods to check the responses:
* * Method 1: During a paged query, when you call the DescribeSendFileResults operation to retrieve the first page of results, set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in the call. The return value of `NextToken` is a pagination token, which can be used in the next request to retrieve a new page of results. When you call the DescribeSendFileResults operation to retrieve a new page of results, set `NextToken` to the `NextToken` value returned in the previous call and set `MaxResults` to specify the maximum number of entries to return in this call.
* * Method 2: Use `PageSize` to specify the number of entries to return on each page and then use `PageNumber` to specify the number of the page to return. You can use only one of the preceding methods. If you specify `MaxResults` or `NextToken`, the `PageSize` and `PageNumber` request parameters do not take effect and the `TotalCount` response parameter is invalid.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeSendFileResults(DescribeSendFileResultsRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* You can specify multiple request parameters to be queried, such as `InstanceId`, `SnapshotGroupId.N`, and `Status.N`. Specified parameters have logical AND relations. Only the specified parameters are included in the filter conditions.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeSnapshotGroups(DescribeSnapshotGroupsRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * You can specify multiple request parameters, such as `RegionId`, `DiskIds`, and `InstanceId`, to query snapshot chains. Specified parameters have logical AND relations.
* * Only the specified parameters are used as filter conditions. If the `DiskIds` and `SnapshotLinkIds` parameters are set to empty JSON arrays, the values are considered as valid filter conditions. In this case, an empty result is returned.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeSnapshotLinks(DescribeSnapshotLinksRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * Up to 400 monitoring data entries can be returned at a time. Make sure that the `TotalCount` value does not exceed 400. The value is calculated by using the following formula: `TotalCount = (EndTime - StartTime)/Period`. If the TotalCount value is greater than 400, the `InvalidParameter.TooManyDataQueried` error is returned.
* * You can query the monitoring data of snapshot sizes in the last 30 days. If the value of `StartTime` is more than 30 days earlier than the current time, an error is returned.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeSnapshotMonitorData(DescribeSnapshotMonitorDataRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeSnapshotPackage(DescribeSnapshotPackageRequest request);
/**
* You can configure multiple request parameters such as `InstanceId`, `DiskId`, and `SnapshotIds` to query snapshots. Configured parameters have logical AND relations. Only the configured parameters are included in the filter conditions.
* When you use Alibaba Cloud CLI to call an API operation, you must specify request parameter values of different data types in required formats. For more information, see [Parameter format overview](~~110340~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeSnapshots(DescribeSnapshotsRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* If you want to view the snapshot usage of each disk in the current region, we recommend that you call the [DescribeSnapshotLinks](~~55837~~) operation to query snapshot chain information.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeSnapshotsUsage(DescribeSnapshotsUsageRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* * You can call this operation to query information about preemptible instances in the previous 30 days and select suitable instance types based on the query results. The information that you can query includes:
* * Average release rate of preemptible instances
* * Percentage of the average preemptible instance price relative to the pay-as-you-go instance price
* * Average preemptible instance price that is calculated based on the preceding percentage
* * This operation is applicable only to I/O optimized preemptible instances that reside in virtual private clouds (VPCs).
* * You can use one of the following methods to query information about preemptible instances in the previous 30 days:
* * Configure the `Cores` and `Memory` parameters or the `MinCores` and `MinMemory` parameters to query information about instance types that meet the specified vCPU and memory requirements.
* * Configure the `InstanceTypes.N` parameter to query information about specified instance types.
* * Configure the `Cores` and `Memory` parameters or the `MinCores` and `MinMemory` parameters and then configure the `InstanceTypeFamily` or `InstanceFamilyLevel` parameter to query information about instance types that meet the specified vCPU and memory requirements within the specified instance family or at a specified instance family level.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeSpotAdvice(DescribeSpotAdviceRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeSpotPriceHistory(DescribeSpotPriceHistoryRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeStorageCapacityUnits(DescribeStorageCapacityUnitsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeStorageSetDetails(DescribeStorageSetDetailsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeStorageSets(DescribeStorageSetsRequest request);
/**
* If a tag key that has no tag value is specified, all tags that contain the tag key are returned. If a tag key-value pair is specified, only tags that exactly match the key-value pair are returned.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeTags(DescribeTagsRequest request);
CompletableFuture describeTaskAttribute(DescribeTaskAttributeRequest request);
/**
* ## Debugging
* [OpenAPI Explorer automatically calculates the signature value. For your convenience, we recommend that you call this operation in OpenAPI Explorer. OpenAPI Explorer dynamically generates the sample code of the operation for different SDKs.](https://api.aliyun.com/#product=Ecs\\&api=DescribeTasks\\&type=RPC\\&version=2014-05-26)
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeTasks(DescribeTasksRequest request);
/**
* You can query the session records of Session Manager that were generated in the last four weeks.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeTerminalSessions(DescribeTerminalSessionsRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeUserBusinessBehavior(DescribeUserBusinessBehaviorRequest request);
/**
* * The returned custom data is encoded in Base64.
* * If no user data is configured for the ECS instance, an empty result is returned.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeUserData(DescribeUserDataRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeVRouters(DescribeVRoutersRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeVSwitches(DescribeVSwitchesRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeVirtualBorderRouters(DescribeVirtualBorderRoutersRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeVirtualBorderRoutersForPhysicalConnection(DescribeVirtualBorderRoutersForPhysicalConnectionRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeVpcs(DescribeVpcsRequest request);
/**
* When you call this operation, only a list of zones and some resource information of each zone are returned. If you want to query instance types and disk categories that are available for purchase in a specific zone, we recommend that you call the [DescribeAvailableResource](~~66186~~) operation.
*
*/
CompletableFuture describeZones(DescribeZonesRequest request);
CompletableFuture detachClassicLinkVpc(DetachClassicLinkVpcRequest request);
/**
* Take note of the following items:
* * The disk that you want to detach must be attached to an ECS instance and in the In Use (`In_use`) state.
* * The instance from which you want to detach a data disk must be in the **Running** (`Running`) or **Stopped** (`Stopped`) state.
* * The instance from which you want to detach a system disk must be in the **Stopped** state.``
* * If the `OperationLocks` parameter in the response contains `"LockReason" : "security"` when you query the instance information, the instance is locked for security reasons and all operations are prohibited on the instance.
* * DetachDisk is an asynchronous operation. After you call the operation to detach a disk from an ECS instance, the disk is detached in approximately 1 minute.
* * If you want to attach an elastic ephemeral disk that you detached from an instance, you can attach the disk only to the instance.
*
*/
CompletableFuture detachDisk(DetachDiskRequest request);
CompletableFuture detachInstanceRamRole(DetachInstanceRamRoleRequest request);
/**
* When you call this operation, take note of the following items:
* * After you unbind an SSH key pair from an instance, you must call the [RebootInstance](~~25502~~) operation to restart the instance to allow the unbind operation to take effect.
* * After you unbind an SSH key pair from an instance, the username and password authentication method is selected for the instance.
*
*/
CompletableFuture detachKeyPair(DetachKeyPairRequest request);
/**
* Take note of the following items:
* * You cannot detach the primary ENI of an instance.
* * Make sure that the ENI to be detached is in the Detaching (Unbinding) or InUse (Bound) state.
* * Make sure that the instance from which you want to detach an ENI is in the Running (Running) or Stopped (Stopped) state.
* * The DetachNetworkInterface operation is an asynchronous operation. After this operation is called to detach an ENI, you can check the status or events of the ENI to determine whether the ENI is detached. The following figure shows the transitions between the states of the ENI.
* * If the ENI is in the Detaching state, the ENI detachment request is sent and the ENI is being detached from the associated instance.
* * If the ENI is in the Available state, the ENI is detached from the associated instance.
* * If the ENI is stuck in the Detaching state, the ENI may fail to be detached from the associated instance due to specific reasons. For example, the ENI may fail to be detached because the operating system of the instance did not respond to the ENI detachment request. If this issue occurs, you can re-initiate the request to detach the ENI. If the issue persists, restart the instance.
* For information about examples on how to call the DetachNetworkInterface operation, see [Detach an ENI from an ECS instance](~~471551~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture detachNetworkInterface(DetachNetworkInterfaceRequest request);
/**
* The region ID. The following regions are supported: China (Qingdao), China (Beijing), China (Zhangjiakou), China (Hohhot), China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Shenzhen), China (Heyuan), and China (Hong Kong).
* You can call the [DescribeRegions](~~25609~~) operation to query the most recent region list.
*
*/
CompletableFuture disableActivation(DisableActivationRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture eipFillParams(EipFillParamsRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture eipFillProduct(EipFillProductRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture eipNotifyPaid(EipNotifyPaidRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture enablePhysicalConnection(EnablePhysicalConnectionRequest request);
/**
* ## [](#)Usage notes
* Before you export images, take note of the following items:
* * Make sure that you are familiar with the prerequisites and considerations. For more information, see [Export a custom image](~~58181~~).
* * The `ImageFormat` parameter is available only for the following regions: India (Mumbai) Closing Down, Japan (Tokyo), Australia (Sydney), Indonesia (Jakarta), Germany (Frankfurt), UAE (Dubai), US (Virginia), UK (London), Singapore, Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), and US (Silicon Valley). Alibaba Cloud services will be discontinued in the India (Mumbai) region. By default, custom images are exported in the RAW format in regions where the ImageFormat parameter is unsupported.
* * Use Resource Access Management (RAM) to authorize Elastic Compute Service (ECS) to write data to OSS. To complete the authorization, perform the following operations:
* * Create a role named `AliyunECSImageExportDefaultRole` and attach the following policy to the role:
* {
* "Statement": [
* {
* "Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
* "Effect": "Allow",
* "Principal": {
* "Service": [
* "ecs.aliyuncs.com"
* ]
* }
* }
* ],
* "Version": "1"
* }
* * Attach the `AliyunECSImageExportRolePolicy` system policy, which is the default policy that grants ECS the permissions to export images, to the `AliyunECSImageExportDefaultRole` role. For more information, go to the [Cloud Resource Access Authorization](https://ram.console.aliyun.com/?spm=5176.2020520101.0.0.64c64df5dfpmdY#/role/authorize?request=%7B%22Requests%22:%20%7B%22request1%22:%20%7B%22RoleName%22:%20%22AliyunECSImageImportDefaultRole%22,%20%22TemplateId%22:%20%22ECSImportRole%22%7D,%20%22request2%22:%20%7B%22RoleName%22:%20%22AliyunECSImageExportDefaultRole%22,%20%22TemplateId%22:%20%22ECSExportRole%22%7D%7D,%20%22ReturnUrl%22:%20%22https:%2F%2Fecs.console.aliyun.com%2F%22,%20%22Service%22:%20%22ECS%22%7D) page. You can also create a custom policy that contains the following content and attach the policy to the role:
* {
* "Version": "1",
* "Statement": [
* {
* "Action": [
* "oss:GetObject",
* "oss:PutObject",
* "oss:DeleteObject",
* "oss:GetBucketLocation",
* "oss:GetBucketInfo",
* "oss:AbortMultipartUpload",
* "oss:ListMultipartUploads",
* "oss:ListParts"
* ],
* "Resource": "*",
* "Effect": "Allow"
* }
* ]
* }
* After you export the images, take note of the following items:
* Each exported custom image is stored in the specified OSS bucket. You can download the custom image. For more information, see [Download objects](~~31912~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture exportImage(ExportImageRequest request);
/**
* @deprecated
*
*/
CompletableFuture exportSnapshot(ExportSnapshotRequest request);
/**
* * ECS is a virtualized cloud-based service and cannot be connected to display devices. Alibaba Cloud caches system command outputs for the last start, restart, or shutdown of ECS instances. You can call the GetInstanceConsoleOutput operation to query the command outputs.
* * For instances of the retired instance types, you cannot obtain command outputs. For more information, see [Retired instance types](~~55263~~).
* * You cannot obtain the command outputs of Windows instances.
*
*/
CompletableFuture getInstanceConsoleOutput(GetInstanceConsoleOutputRequest request);
/**
* After ECS returns a Base64-encoded instance screenshot in the JPG format, you must decode the screenshot. We recommend that you call this operation for troubleshooting and diagnosis. When you call this operation, take note of the following items:
* * The instance must be in the Running state.
* * For instances of the retired instance types, you cannot obtain screenshots. For more information, see [Retired instance types](~~55263~~).
* * If you call this operation on an instance for multiple times, the call interval must be at least 10 seconds. Otherwise, the `Throttling` error is returned.
*
*/
CompletableFuture getInstanceScreenshot(GetInstanceScreenshotRequest request);
/**
* ### [](#)Usage notes
* Take note of the following items:
* * Before you import an image, you must upload the image to an Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket. For more information, see [Upload objects](~~31886~~).
* * In specific scenarios, you may want to create a custom image based on the operating system data of a source server, import the image to Alibaba Cloud, and then create an ECS instance from the image. The source server can be a physical server, a virtual machine, or a cloud host. If the virtio driver is not installed on the source server, the created ECS instance may be unable to start. To prevent this issue, verify that the virtio driver is installed on the source server before you import the image to Alibaba Cloud. For more information, see [Install the virtio driver](~~62423~~).
* * Before you import images for the first time, you must use Resource Access Management (RAM) to authorize ECS to access your OSS buckets. If ECS is not authorized to access your OSS buckets, the `NoSetRoletoECSServiceAccount` or `InvalidOperation.CloudBoxImageImportRoleRequired` error code is returned when you call the ImportImage operation. The authorization configuration varies based on whether the image files are imported from a cloud box.
* * **If the image files are not imported from a cloud box**, you can complete the authorization on the [Cloud Resource Access Authorization](https://ram.console.aliyun.com/?spm=5176.2020520101image.0.0.2ffa4df57kSoHX#/role/authorize?request=%7B%22Requests%22%3A%20%7B%22request1%22%3A%20%7B%22RoleName%22%3A%20%22AliyunECSImageImportDefaultRole%22%2C%20%22TemplateId%22%3A%20%22ECSImportRole%22%7D%2C%20%22request2%22%3A%20%7B%22RoleName%22%3A%20%22AliyunECSImageExportDefaultRole%22%2C%20%22TemplateId%22%3A%20%22ECSExportRole%22%7D%7D%2C%20%22ReturnUrl%22%3A%20%22https%3A//ecs.console.aliyun.com/%22%2C%20%22Service%22%3A%20%22ECS%22%7D) page of the RAM console. You can also complete the authorization by using a RAM role and RAM policies. The following example shows the policies and permissions required for specific steps in the authorization procedure. For more information, see [Control access to ECS resources by using RAM users](~~25481~~).
* 1. Create a RAM role named `AliyunECSImageImportDefaultRole`. You must use this exact role name. Otherwise, the image cannot be imported. Configure the following trust policy for the role:
* {
* "Statement": [
* {
* "Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
* "Effect": "Allow",
* "Principal": {
* "Service": [
* "ecs.aliyuncs.com"
* ]
* }
* }
* ],
* "Version": "1"
* }
* 2. Attach the `AliyunECSImageImportRolePolicy` system policy to the RAM role. You can also create a custom policy that contains the following content and attach the policy to the role:
* ```
* {
* "Version": "1",
* "Statement": [
* {
* "Action": [
* "oss:GetObject",
* "oss:GetBucketLocation",
* "oss:GetBucketInfo"
* ],
* "Resource": "*",
* "Effect": "Allow"
* }
* ]
* }
* ```
* * **If the image files are imported from a cloud box**, you can complete the authorization on the [Cloud Resource Access Authorization](https://ram.console.aliyun.com/role/authorize?request=%7B%22ReturnUrl%22%3A%22https%3A%2F%2Fecs.console.aliyun.com%2F%22%2C%22Services%22%3A%5B%7B%22Roles%22%3A%5B%7B%22RoleName%22%3A%22AliyunECSCloudBoxImageImportDefaultRole%22%2C%22TemplateId%22%3A%22AliyunECSCloudBoxImageImportDefaultRole%22%7D%5D%2C%22Service%22%3A%22ECS%22%7D%5D%7D) page of the RAM console. You can also complete the authorization by using a RAM role and RAM policies. The following example shows the policies and permissions required for specific steps in the authorization procedure. For more information, see [Control access to ECS resources by using RAM users](~~25481~~).
* 1. Create a RAM role named `AliyunECSCloudBoxImageImportDefaultRole`. You must use this exact role name. Otherwise, the image cannot be imported. Configure the following trust policy for the role:
* {
* "Statement": [
* {
* "Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
* "Effect": "Allow",
* "Principal": {
* "Service": [
* "ecs.aliyuncs.com"
* ]
* }
* }
* ],
* "Version": "1"
* }
* 2. Attach the `AliyunECSCloudBoxImageImportRolePolicy` system policy to the RAM role. You can also create a custom policy that contains the following content and attach the policy to the role:
* ```
* {
* "Version": "1",
* "Statement": [
* {
* "Action": [
* "oss-cloudbox:GetObject",
* "oss-cloudbox:GetBucketLocation",
* "oss-cloudbox:GetBucketInfo"
* ],
* "Resource": "*",
* "Effect": "Allow"
* }
* ]
* }
* ```
* * You cannot delete an image that is being imported. However, you can call the [CancelTask](~~25624~~) operation to cancel the image import task.
* * You can import an image only to the same region as the OSS bucket to which the image file is uploaded.
* * The valid values of N in `DiskDeviceMapping.N` range from 1 to 17. When N is set to 1, the disk is a system disk. When N is set to a value from 2 to 17, the disk is a data disk. When N is set to a value greater than 17, parameters prefixed with DiskDeviceMapping.N are ignored.
* * When you set `Architecture` to `arm64` or when you set `Platform` to `CentOS Stream`, `Anolis`, `AlmaLinux`, `UOS`, `Kylin`, or `Rocky Linux`, take note of the following items:
* * To ensure that the password can be set or the key pair can be modified for an imported image, make sure that the image meets the following requirements before you import it:
* * The kernel of the operating system supports the `CONFIG_FW_CFG_SYSFS` feature. By default, Linux community kernel 4.6 and later and CentOS kernel 3.10.0-826.el7 and later support the CONFIG_FW_CFG_SYSFS feature. You can run the `grep -nr CONFIG_FW_CFG_SYSFS /boot/config-$(uname -r)` command on the source server of the image. If the command output contains `CONFIG_FW_CFG_SYSFS=y`, the kernel of the image supports the `CONFIG_FW_CFG_SYSFS` feature.
* * Alibaba Cloud cloud-init of the latest version is installed on the operating system. If the version of cloud-init is 19.1, the minor version must be 19.1.3 or later. If the version of cloud-init is 0.7.6a in some early versions of operating systems, the minor version must be 0.7.6a15 or later. For more information, see [Install cloud-init](~~57803~~).
* * The operating system supports the SHA-512 encryption algorithm.
* * If you want an imported image to support the resizing of disks and file systems, make sure that the image meets the following requirements before you import it:
* * The kernel version of the operating system is later than 3.6.
* * The image supports the growpart command. To support this command, you must install the `cloud-utils-growpart` package. The methods of installing the package vary based on operating systems. For more information, see [Extend the partitions and file systems of disks on a Linux instance](~~25451~~).
* * The image supports the resize2fs command. To support this command, you must install the `e2fsprogs` package. By default, the package is installed on the operating system. If the package is not installed, install it.
* * Alibaba Cloud cloud-init of the latest version is installed on the operating system. If the version of cloud-init is 19.1, the minor version must be 19.1.3 or later. If the version of cloud-init is 0.7.6a in some early versions of operating systems, the minor version must be 0.7.6a15 or later. For more information, see [Install cloud-init](~~57803~~).
* * If the image that you want to import uses the Arm64 architecture, configure the real-time clock (RTC) to use the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) time standard. For more information, see [Linux time and time zones](~~405080~~).
* * When you import images, we recommend that you specify DetectionStrategy. This way, you can optimize the images based on the image check results. For more information, see [Overview of image check](~~439819~~).
*
*/
CompletableFuture importImage(ImportImageRequest request);
/**
* Take note of the following items:
* * A maximum of 500 key pairs can be created in each region.
* * The key pair to be imported must support one of the following encryption methods:
* * rsa
* * dsa
* * ssh-rsa
* * ssh-dss
* * ecdsa
* *
* *
* *
* *
* *