
com.codename1.io.Storage Maven / Gradle / Ivy
/*
* Copyright (c) 2008, 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS FILE HEADER.
* This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 only, as
* published by the Free Software Foundation. Oracle designates this
* particular file as subject to the "Classpath" exception as provided
* by Oracle in the LICENSE file that accompanied this code.
*
* This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
* version 2 for more details (a copy is included in the LICENSE file that
* accompanied this code).
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License version
* 2 along with this work; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,
* Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*
* Please contact Oracle, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores
* CA 94065 USA or visit www.oracle.com if you need additional information or
* have any questions.
*/
package com.codename1.io;
import com.codename1.util.StringUtil;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* Abstracts the underlying application specific storage system, unlike the {@link com.codename1.io.FileSystemStorage}
* this class is a higher level abstraction. The {@code Storage} class is designed to be very portable and as
* such it has no support for staple file system capabilities such as hierarchies.
* Check out a more thorough discussion of this API {@link com.codename1.io here}.
*
*
* The sample code below shows a simple storage browser tool in action:
*
*
*
* 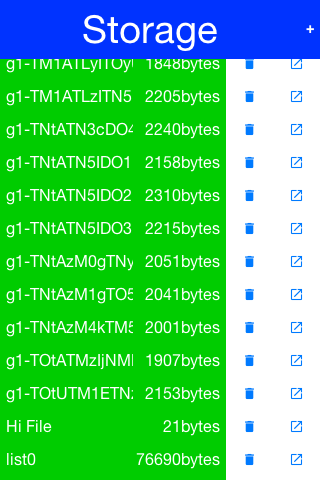 *
* @author Shai Almog
*/
public class Storage {
private final CacheMap cache = new CacheMap();
private static Storage INSTANCE;
private boolean normalizeNames = true;
/**
* Indicates the caching size, storage can be pretty slow
*
* @param size size in elements (not kb!)
*/
public void setHardCacheSize(int size) {
cache.setCacheSize(size);
}
/**
* If a file name contains slashes replace them with underscores, same goes for *, %, ? etc.
* @param name the file name
* @return the fixed filename
*/
private String fixFileName(String name) {
if(normalizeNames) {
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, "/", "_");
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, "\\", "_");
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, "%", "_");
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, "?", "_");
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, "*", "_");
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, ":", "_");
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, "=", "_");
}
return name;
}
/**
* This method must be invoked before using the storage otherwise some platforms
* might fail without the application data.
*
* @param data either the name of the application e.g. on CDC platforms or
* a context object on other platforms
*/
private static void init(Object data) {
Util.getImplementation().setStorageData(data);
if(INSTANCE == null) {
INSTANCE = new Storage();
}
}
/**
* Returns true if the storage is initialized
*
* @return true if the storage is initialized
*/
public static boolean isInitialized(){
return INSTANCE != null;
}
/**
* Returns the storage instance or null if the storage wasn't initialized using
* a call to init(String) first.
*
* @return storage instance
*/
public static Storage getInstance() {
if(INSTANCE == null) {
init("cn1");
}
return INSTANCE;
}
/**
* Storage is cached for faster access, however this might cause a problem with refreshing
* objects since they are not cloned. Clearing the cache allows to actually reload from the
* storage file.
*/
public void clearCache() {
cache.clearAllCache();
}
/**
* Flush the storage cache allowing implementations that cache storage objects
* to store
*/
public void flushStorageCache() {
Util.getImplementation().flushStorageCache();
}
/**
* Deletes the given file name from the storage
*
* @param name the name of the storage file
*/
public void deleteStorageFile(String name) {
name = fixFileName(name);
Util.getImplementation().deleteStorageFile(name);
cache.delete(name);
}
/**
* Deletes all the files in the application storage
*/
public void clearStorage() {
Util.getImplementation().clearStorage();
cache.clearAllCache();
}
/**
* Creates an output stream to the storage with the given name
*
* @param name the storage file name
* @return an output stream of limited capacity
*/
public OutputStream createOutputStream(String name) throws IOException {
name = fixFileName(name);
return Util.getImplementation().createStorageOutputStream(name);
}
/**
* Creates an input stream to the given storage source file
*
* @param name the name of the source file
* @return the input stream
*/
public InputStream createInputStream(String name) throws IOException {
if (!exists(name)) {
throw new IOException("Storage key "+name+" does not exist");
}
name = fixFileName(name);
return Util.getImplementation().createStorageInputStream(name);
}
/**
* Returns true if the given storage file exists
*
* @param name the storage file name
* @return true if it exists
*/
public boolean exists(String name) {
name = fixFileName(name);
return Util.getImplementation().storageFileExists(name);
}
/**
* Lists the names of the storage files
*
* @return the names of all the storage files
*/
public String[] listEntries() {
return Util.getImplementation().listStorageEntries();
}
/**
* Returns the size in bytes of the given entry
* @param name the name of the entry
* @return the size in bytes
*/
public int entrySize(String name) {
name = fixFileName(name);
return Util.getImplementation().getStorageEntrySize(name);
}
/**
*
*
* @author Shai Almog
*/
public class Storage {
private final CacheMap cache = new CacheMap();
private static Storage INSTANCE;
private boolean normalizeNames = true;
/**
* Indicates the caching size, storage can be pretty slow
*
* @param size size in elements (not kb!)
*/
public void setHardCacheSize(int size) {
cache.setCacheSize(size);
}
/**
* If a file name contains slashes replace them with underscores, same goes for *, %, ? etc.
* @param name the file name
* @return the fixed filename
*/
private String fixFileName(String name) {
if(normalizeNames) {
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, "/", "_");
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, "\\", "_");
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, "%", "_");
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, "?", "_");
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, "*", "_");
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, ":", "_");
name = StringUtil.replaceAll(name, "=", "_");
}
return name;
}
/**
* This method must be invoked before using the storage otherwise some platforms
* might fail without the application data.
*
* @param data either the name of the application e.g. on CDC platforms or
* a context object on other platforms
*/
private static void init(Object data) {
Util.getImplementation().setStorageData(data);
if(INSTANCE == null) {
INSTANCE = new Storage();
}
}
/**
* Returns true if the storage is initialized
*
* @return true if the storage is initialized
*/
public static boolean isInitialized(){
return INSTANCE != null;
}
/**
* Returns the storage instance or null if the storage wasn't initialized using
* a call to init(String) first.
*
* @return storage instance
*/
public static Storage getInstance() {
if(INSTANCE == null) {
init("cn1");
}
return INSTANCE;
}
/**
* Storage is cached for faster access, however this might cause a problem with refreshing
* objects since they are not cloned. Clearing the cache allows to actually reload from the
* storage file.
*/
public void clearCache() {
cache.clearAllCache();
}
/**
* Flush the storage cache allowing implementations that cache storage objects
* to store
*/
public void flushStorageCache() {
Util.getImplementation().flushStorageCache();
}
/**
* Deletes the given file name from the storage
*
* @param name the name of the storage file
*/
public void deleteStorageFile(String name) {
name = fixFileName(name);
Util.getImplementation().deleteStorageFile(name);
cache.delete(name);
}
/**
* Deletes all the files in the application storage
*/
public void clearStorage() {
Util.getImplementation().clearStorage();
cache.clearAllCache();
}
/**
* Creates an output stream to the storage with the given name
*
* @param name the storage file name
* @return an output stream of limited capacity
*/
public OutputStream createOutputStream(String name) throws IOException {
name = fixFileName(name);
return Util.getImplementation().createStorageOutputStream(name);
}
/**
* Creates an input stream to the given storage source file
*
* @param name the name of the source file
* @return the input stream
*/
public InputStream createInputStream(String name) throws IOException {
if (!exists(name)) {
throw new IOException("Storage key "+name+" does not exist");
}
name = fixFileName(name);
return Util.getImplementation().createStorageInputStream(name);
}
/**
* Returns true if the given storage file exists
*
* @param name the storage file name
* @return true if it exists
*/
public boolean exists(String name) {
name = fixFileName(name);
return Util.getImplementation().storageFileExists(name);
}
/**
* Lists the names of the storage files
*
* @return the names of all the storage files
*/
public String[] listEntries() {
return Util.getImplementation().listStorageEntries();
}
/**
* Returns the size in bytes of the given entry
* @param name the name of the entry
* @return the size in bytes
*/
public int entrySize(String name) {
name = fixFileName(name);
return Util.getImplementation().getStorageEntrySize(name);
}
/**
* Writes the given object to storage assuming it is an externalizable type
* or one of the supported types.
*
*
* The sample below demonstrates the usage and registration of the {@link com.codename1.io.Externalizable} interface:
*
*
*
* @param name store name
* @param o object to store
* @return true for success, false for failure
*/
public boolean writeObject(String name, Object o) {
name = fixFileName(name);
cache.put(name, o);
DataOutputStream d = null;
try {
d = new DataOutputStream(createOutputStream(name));
Util.writeObject(o, d);
d.close();
return true;
} catch(Exception err) {
Log.e(err);
if(Log.isCrashBound()) {
Log.sendLog();
}
Util.getImplementation().deleteStorageFile(name);
Util.getImplementation().cleanup(d);
return false;
}
}
/**
* Reads the object from the storage, returns null if the object isn't there
*
* The sample below demonstrates the usage and registration of the {@link com.codename1.io.Externalizable} interface:
*
*
*
*
* @param name name of the store
* @return object stored under that name
*/
public Object readObject(String name) {
name = fixFileName(name);
Object o = cache.get(name);
if(o != null) {
return o;
}
DataInputStream d = null;
try {
if(!exists(name)) {
return null;
}
d = new DataInputStream(createInputStream(name));
o = Util.readObject(d);
d.close();
cache.put(name, o);
return o;
} catch(Throwable err) {
Log.e(err);
if(Log.isCrashBound()) {
Log.sendLog();
}
Util.getImplementation().cleanup(d);
return null;
}
}
/**
* Indicates whether characters that are typically illegal in filesystems should
* be sanitized and replaced with underscore
* @return the normalizeNames
*/
public boolean isNormalizeNames() {
return normalizeNames;
}
/**
* Indicates whether characters that are typically illegal in filesystems should
* be sanitized and replaced with underscore
* @param normalizeNames the normalizeNames to set
*/
public void setNormalizeNames(boolean normalizeNames) {
this.normalizeNames = normalizeNames;
}
/**
* Allows installing a custom storage instance to provide functionality such as seamless encryption
* @param s the storage instance
*/
public static void setStorageInstance(Storage s) {
INSTANCE = s;
}
}