
com.dp4j.Singleton Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Show all versions of dp4j Show documentation
package com.dp4j;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
Intent:
- Ensure that only one instance of a class is created.
- Provide a global point of access to the object.
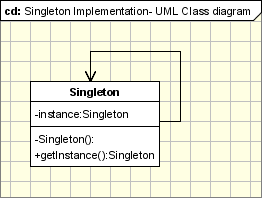
Motivation
Sometimes it's important to have only one instance for a class. For example, in a system there should be only one window manager (or only a file system or only a print spooler). Usually singletons are used for centralized management of internal or external resources and they provide a global point of access to themselves.
The singleton pattern is one of the simplest design patterns and involves only one class which is responsible to instantiate itself, ti make sure it creates only one instance and in the same time to provide a global point of access to that instance. In that case the instance can be used from everywhere without calling the directly the constructor each time.
Applicability & Examples
According to the definition the singleton pattern should be used when there must be exactly one instance of a class, and when it must be accessible to clients from a global access point. Here are some real situations where the singleton is used:
Example 1 - Logger Classes
The Singleton pattern is used in the design of logger classes. This classes are ussualy implemented as a singletons, and provides a global logging access point in all the application components without being necessary to create an object each time a logging operations is performed.
Example 2 - Configuration Classes
The Singleton pattern is used to design the classes that provide the configuration settings for an application. By implementing configuration classes as Singleton not only that we provide a global access point, but we also keep the instance we use as a cache object. When the class is instantiated( or when a value is read ) the singleton will keep the values in its internal structure. If the values are read from the database or from files this avoid reloading the values each time the configuration parameters are used.
Example 3 - Accesing resources in shared mode
It can be used in the design of an application that needs to work with the serial port. Let's say that there are many classs in the application, working in an multithreading environment, that needs to operate actions on the serial port. In this case a singleton with synchronized methods has to be used to manage all the operations on the serial port.
Example 4 - Factories implemented as Singletons
Let's assume that we design an application with a factory to generate new objects(Acount, Customer, Site, Address objects) with their ids, in an multithreading environment. If the factory is instantiated twice in 2 different threads then is possible to have 2 overlapping ids for 2 different objects. If we implement the Factory as a singleton we avoid this problem. Combining Abstarct Factory or Factory Method and Singleton design patterns is a common practice.
@see http://www.oodesign.com/singleton-pattern.html
*/
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface Singleton {
}