com.feilong.core.util.MapUtil Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Show all versions of feilong Show documentation
/*
* Copyright (C) 2008 feilong
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.feilong.core.util;
import static com.feilong.core.Validator.isNotNullOrEmpty;
import static com.feilong.core.Validator.isNullOrEmpty;
import static com.feilong.core.bean.ConvertUtil.toArray;
import static com.feilong.core.bean.ConvertUtil.toBigDecimal;
import static com.feilong.core.bean.ConvertUtil.toSet;
import static com.feilong.core.lang.ObjectUtil.defaultIfNull;
import static java.util.Collections.emptyMap;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.EnumMap;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.feilong.core.Validate;
import com.feilong.core.bean.PropertyUtil;
import com.feilong.core.lang.NumberUtil;
import com.feilong.lib.collection4.MapUtils;
/**
* {@link Map}工具类.
*
* hashCode与equals:
*
*
*
* hashCode重要么?
* 对于{@link java.util.List List}集合、数组而言,不重要,他就是一个累赘;
* 但是对于{@link java.util.HashMap HashMap}、{@link java.util.HashSet HashSet}、 {@link java.util.Hashtable Hashtable} 而言,它变得异常重要.
*
*
*
* 在Java中hashCode的实现总是伴随着equals,他们是紧密配合的,你要是自己设计了其中一个,就要设计另外一个。
*
*
*  *
*
*
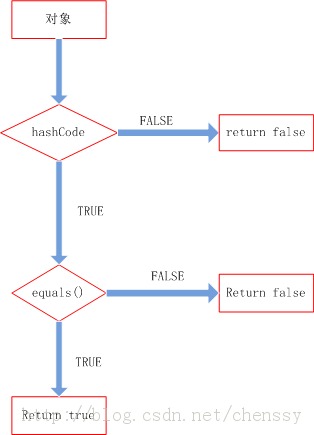
* 整个处理流程是:
*
* - 判断两个对象的hashcode是否相等,若不等,则认为两个对象不等,完毕,若相等,则比较equals。
* - 若两个对象的equals不等,则可以认为两个对象不等,否则认为他们相等。
*
*
*
* 关于 {@link java.util.Map }:
*
*
*
*
* interface/class
* 说明
*
*
*
* {@link java.util.Map Map}
*
*
* - An object that maps keys to values.
* - A map cannot contain duplicate keys
* - Takes the place of the Dictionary class
*
*
*
*
*
* {@link java.util.HashMap HashMap}
*
*
* - Hash table based implementation of the Map interface.
* - permits null values and the null key.
* - makes no guarantees as to the order of the map
*
*
* 扩容:
*
*
*
* - {@link java.util.HashMap HashMap} 初始容量 {@link java.util.HashMap#DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY }是16,DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR 是0.75
*
java.util.HashMap#addEntry 是 2 * table.length 2倍
*
*
*
*
*
*
* {@link java.util.LinkedHashMap LinkedHashMap}
*
*
* - Hash table and linked list implementation of the Map interface,
* - with predictable iteration order.
*
* Note that: insertion order is not affected if a key is re-inserted into the map.
*
*
*
*
* {@link java.util.TreeMap TreeMap}
*
*
* - A Red-Black tree based NavigableMap implementation
* - sorted according to the natural ordering of its keys, or by a Comparator.
* - 默认情况 key不能为null,如果传入了
NullComparator那么key 可以为null.
*
*
*
*
*
* {@link java.util.Hashtable Hashtable}
*
*
* - This class implements a hashtable, which maps keys to values.
* - synchronized.
* - Any non-null object can be used as a key or as a value.
*
*
*
*
*
* {@link java.util.Properties Properties}
*
*
* - The Properties class represents a persistent set of properties.
* - can be saved to a stream or loaded from a stream.
* - Each key and its corresponding value in the property list is a string.
*
*
*
*
*
* {@link java.util.IdentityHashMap IdentityHashMap}
*
*
* - using reference-equality in place of object-equality when comparing keys (and values).
* - 使用==代替equals()对key进行比较的散列表.专为特殊问题而设计的
*
*
* 注意:此类不是 通用 Map 实现!它有意违反 Map 的常规协定,此类设计仅用于其中需要引用相等性语义的罕见情况
*
*
*
*
*
* {@link java.util.WeakHashMap WeakHashMap}
*
*
* - A hashtable-based Map implementation with weak keys.
* - 它对key实行"弱引用",如果一个key不再被外部所引用,那么该key可以被GC回收
*
*
*
*
*
* {@link java.util.EnumMap EnumMap}
*
*
* - A specialized Map implementation for use with enum type keys.
* - Enum maps are maintained in the natural order of their keys
* - 不允许空的key
*
*
*
*
*
*
* @author feilong
* @see java.util.AbstractMap.SimpleEntry
* @see "com.google.common.collect.Maps"
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@SuppressWarnings("squid:S1192") //String literals should not be duplicated
public final class MapUtil{
/** The Constant LOGGER. */
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MapUtil.class);
/** Don't let anyone instantiate this class. */
private MapUtil(){
//AssertionError不是必须的. 但它可以避免不小心在类的内部调用构造器. 保证该类在任何情况下都不会被实例化.
//see 《Effective Java》 2nd
throw new AssertionError("No " + getClass().getName() + " instances for you!");
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 根据索引来获得map 的entry.
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - 传入的map 最好是 {@link LinkedHashMap},{@link EnumMap}等自身有顺序的map,否则如 {@link HashMap}每次结果都不一样
*
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
*
* 场景: 获得下面bookSectionUrlMap 第一个entry value值
*
*
*
*
* public void createFile(Novel novel){
* Map{@code } bookSectionUrlMap = parseBookSectionUrlMap(novel);
*
* if (isNullOrEmpty(bookSectionUrlMap)){
* LOGGER.warn("bookSectionUrlMap is null/empty,Perhaps you read the latest chapter");
* return;
* }
*
* //---------------------------------------------------------------
* String beginName = null; // 开始章节名称
*
* for (Map.Entry{@code } entry : bookSectionUrlMap.entrySet()){
* String sectionName = entry.getValue();
* if (isNullOrEmpty(beginName)){
* beginName = sectionName;//①这里纯粹只是为了获得 map 第一个 entry value 值
* }
* try{
*
* //do some big logic
*
* }catch (ChapterParseException e){
* break; //如果出现了异常 就跳出
* }
* }
*
* //---------------------------------------------------------------
* write(novel, beginName);
*
* // do something logic
* }
*
*
*
*
* 对于上述代码 ①处的代码,虽然只是寥寥几行,但是会减低代码的可读性,也不利于循环体代码抽取,通过sonar 扫描的时候,明显方法的复杂度很高
*
*
* 此时,你可以优化成:
*
*
*
* public void createFile(Novel novel){
* Map{@code } bookSectionUrlMap = parseBookSectionUrlMap(novel);
*
* if (isNullOrEmpty(bookSectionUrlMap)){
* LOGGER.warn("bookSectionUrlMap is null/empty,Perhaps you read the latest chapter");
* return;
* }
*
* //---------------------------------------------------------------
*
* for (Map.Entry{@code } entry : bookSectionUrlMap.entrySet()){
* try{
*
* //do some big logic
*
* }catch (ChapterParseException e){
* break; //如果出现了异常 就跳出
* }
* }
*
* //---------------------------------------------------------------
* write(novel, MapUtil.get(bookSectionUrlMap, 0).getValue());
*
* // do something logic
* }
*
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param map
* 最好是 {@link LinkedHashMap},{@link EnumMap}等自身有顺序的map,否则每次出来的结果都不一样
* @param index
* the index
* @return 如果 map 是null,抛出 {@link NullPointerException}
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
* if the index is invalid
* @see "org.apache.commons.collections4.CollectionUtils#get(Iterable, int)"
* @see "org.apache.commons.collections4.CollectionUtils#get(Map, int)"
* @since 1.10.1
*/
public static Map.Entry get(Map map,int index){
Validate.notNull(map, "map can't be null!");
return com.feilong.lib.collection4.CollectionUtils.get(map, index);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 将多值的arrayValueMap 转成单值的map.
*
* 示例1:
*
*
*
* Map{@code } arrayValueMap = new LinkedHashMap{@code <>}();
*
* arrayValueMap.put("province", new String[] { "江苏省" });
* arrayValueMap.put("city", new String[] { "南通市" });
* LOGGER.info(JsonUtil.format(ParamUtil.toSingleValueMap(arrayValueMap)));
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
* {
* "province": "江苏省",
* "city": "南通市"
* }
*
*
*
*
*
* 如果arrayValueMap其中有key的值是多值的数组,那么转换到新的map中的时候,value取第一个值,
*
*
* 示例2:
*
*
*
* Map{@code } arrayValueMap = new LinkedHashMap{@code <>}();
*
* arrayValueMap.put("province", new String[] { "浙江省", "江苏省" });
* arrayValueMap.put("city", new String[] { "南通市" });
* LOGGER.info(JsonUtil.format(ParamUtil.toSingleValueMap(arrayValueMap)));
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
* {
* "province": "浙江省",
* "city": "南通市"
* }
*
*
*
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - 返回的map是 提取参数
arrayValueMap的key做为key,value数组的第一个元素做value
* - 返回的是 {@link LinkedHashMap},保证顺序和参数
arrayValueMap顺序相同
* - 和该方法正好相反的是 {@link #toArrayValueMap(Map)}
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param arrayValueMap
* the array value map
* @return 如果arrayValueMap是null或者empty,那么返回 {@link Collections#emptyMap()},
* 如果arrayValueMap其中有key的值是多值的数组,那么转换到新的map中的时候,value取第一个值,
* 如果arrayValueMap其中有key的value是null,那么转换到新的map中的时候,value以 null替代
* @since 1.8.0 change type to generics
*/
public static Map toSingleValueMap(Map arrayValueMap){
if (isNullOrEmpty(arrayValueMap)){
return emptyMap();
}
Map singleValueMap = newLinkedHashMap(arrayValueMap.size());//保证顺序和参数 arrayValueMap 顺序相同
for (Map.Entry entry : arrayValueMap.entrySet()){
singleValueMap.put(entry.getKey(), null == entry.getValue() ? null : entry.getValue()[0]);
}
return singleValueMap;
}
/**
* 将单值的singleValueMap 转成多值的map.
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
* Map{@code } singleValueMap = new LinkedHashMap{@code <>}();
*
* singleValueMap.put("province", "江苏省");
* singleValueMap.put("city", "南通市");
*
* LOGGER.info(JsonUtil.format(ParamUtil.toArrayValueMap(singleValueMap)));
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
* {
* "province": ["江苏省"],
* "city": ["南通市"]
* }
*
*
*
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - 返回的是 {@link LinkedHashMap},保证顺序和参数
singleValueMap顺序相同
* - 和该方法正好相反的是 {@link #toSingleValueMap(Map)}
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param singleValueMap
* the name and value map
* @return 如果参数 singleValueMap 是null或者empty,那么返回 {@link Collections#emptyMap()}
* 否则迭代 singleValueMap 将value转成数组,返回新的 arrayValueMap
* @since 1.6.2
*/
public static Map toArrayValueMap(Map singleValueMap){
if (isNullOrEmpty(singleValueMap)){
return emptyMap();
}
Map arrayValueMap = newLinkedHashMap(singleValueMap.size());//保证顺序和参数singleValueMap顺序相同
for (Map.Entry entry : singleValueMap.entrySet()){
arrayValueMap.put(entry.getKey(), toArray(entry.getValue()));//注意此处的Value不要声明成V,否则会变成Object数组
}
return arrayValueMap;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 仅当 null != map 并且 null != value才将key/value put到map中.
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - 如果
map 是null,什么都不做
* - 如果
value 是null,也什么都不做
* - 如果
key 是null,依照map的key是否允许是null的 规则
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param map
* the map to add to
* @param key
* the key
* @param value
* the value
* @see "org.apache.commons.collections4.MapUtils#safeAddToMap(Map, Object, Object)"
* @since 1.4.0
*/
public static void putIfValueNotNull(final Map map,final K key,final V value){
if (null != map && null != value){
map.put(key, value);
}
}
/**
* 仅当 {@code null != map && null != m},才会进行 {@code map.putAll(m)} 操作
*
* 重构:
*
*
*
* 对于以下代码:
*
*
*
* if (isNotNullOrEmpty(specialSignMap)){
* map.putAll(specialSignMap);
* }
*
*
* 可以重构成:
*
*
* MapUtil.putAllIfNotNull(map, specialSignMap)
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param map
* the map
* @param m
* mappings to be stored in this map
* @see java.util.Map#putAll(Map)
* @since 1.6.3
*/
public static void putAllIfNotNull(final Map map,Map m){
if (null != map && null != m){
map.putAll(m);// m 如果是null 会报错
}
}
/**
* 仅当 null != map 并且 isNotNullOrEmpty(value)才将key/value put到map中.
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - 如果
map 是null,什么都不做
* - 如果
value 是null或者empty,也什么都不做
* - 如果
key 是null,依照map的key是否允许是null的规则
*
*
*
* 重构:
*
*
*
* 对于以下代码:
*
*
*
*
* if (isNotNullOrEmpty(taoBaoOAuthLoginForCodeEntity.getState())){
* nameAndValueMap.put("state", taoBaoOAuthLoginForCodeEntity.getState());
* }
*
*
*
* 可以重构成:
*
*
* MapUtil.putIfValueNotNullOrEmpty(nameAndValueMap, "state", taoBaoOAuthLoginForCodeEntity.getState());
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param map
* the map
* @param key
* the key
* @param value
* the value
* @since 1.6.3
*/
public static void putIfValueNotNullOrEmpty(final Map map,final K key,final V value){
if (null != map && isNotNullOrEmpty(value)){
map.put(key, value);
}
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 将key和value 累加的形式put到 map中,如果map中存在key,那么累加value值;如果不存在那么直接put.
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = new HashMap{@code <>}();
* MapUtil.putSumValue(map, "1000001", 5);
* MapUtil.putSumValue(map, "1000002", 5);
* MapUtil.putSumValue(map, "1000002", 5);
* LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(map));
*
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
* {
* "1000001": 5,
* "1000002": 10
* }
*
*
*
*
* 重构:
*
*
*
* 对于以下代码:
*
*
*
*
* if (disadvantageMap.containsKey(disadvantageToken)){
* disadvantageMap.put(disadvantageToken, disadvantageMap.get(disadvantageToken) + 1);
* }else{
* disadvantageMap.put(disadvantageToken, 1);
* }
*
*
*
* 可以重构成:
*
*
* MapUtil.putSumValue(disadvantageMap, disadvantageToken, 1);
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param map
* the map
* @param key
* the key
* @param value
* 数值,不能为null,可以是负数
* @return 如果 map 是null,抛出 {@link NullPointerException}
* 如果 value 是null,抛出 {@link NullPointerException}
* @see "org.apache.commons.collections4.bag.HashBag"
* @see "org.apache.commons.lang3.mutable.MutableInt"
* @see "java.util.Map#getOrDefault(Object, Object)"
* @see most-efficient-way-to-
* increment-a-map-value-in-java
* @since 1.5.5
*/
public static Map putSumValue(Map map,K key,Integer value){
Validate.notNull(map, "map can't be null!");
Validate.notNull(value, "value can't be null!");
Integer v = map.get(key);//这里不要使用 map.containsKey(key),否则会有2次 two potentially expensive operations
map.put(key, null == v ? value : value + v);//Suggestion: you should care about code readability more than little performance gain in most of the time.
return map;
}
/**
* 将key和value 累加的形式put到 map中,如果map中存在key,那么累加value值;如果不存在那么直接put.
*
*
* 常用于数据统计, 比如 {@link com.feilong.core.util.AggregateUtil#groupSum(Iterable, String, String)}
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = new HashMap{@code <>}();
* MapUtil.putSumValue(map, "1000001", 5);
* MapUtil.putSumValue(map, "1000002", 5);
* MapUtil.putSumValue(map, "1000002", 5);
* LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(map));
*
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
* {
* "1000001": 5,
* "1000002": 10
* }
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param map
* the map
* @param key
* the key
* @param value
* 数值,不能为null,可以是负数
* @return 如果 map 是null,抛出 {@link NullPointerException}
* 如果 value 是null,抛出 {@link NullPointerException}
* @see "org.apache.commons.collections4.bag.HashBag"
* @see "java.util.Map#getOrDefault(Object, Object)"
* @see most-efficient-way-to-
* increment-a-map-value-in-java
* @since 1.13.2
*/
public static Map putSumValue(Map map,K key,Number value){
Validate.notNull(map, "map can't be null!");
Validate.notNull(value, "value can't be null!");
BigDecimal v = map.get(key);//这里不要使用 map.containsKey(key),否则会有2次 two potentially expensive operations
map.put(key, null == v ? toBigDecimal(value) : NumberUtil.getAddValue(value, v));//Suggestion: you should care about code readability more than little performance gain in most of the time.
return map;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 往 map 中put 指定 key value(多值形式).
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - map已经存在相同名称的key,那么value以list的形式累加.
* - 如果map中不存在指定名称的key,那么会构建一个ArrayList
*
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
*
*
* Map{@code >} mutiMap = newLinkedHashMap(2);
* MapUtil.putMultiValue(mutiMap, "name", "张飞");
* MapUtil.putMultiValue(mutiMap, "name", "关羽");
* MapUtil.putMultiValue(mutiMap, "age", "30");
*
* LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(mutiMap));
*
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
{
"name": [
"张飞",
"关羽"
],
"age": ["30"]
}
*
*
*
*
*
* 对于下面的代码:
*
*
*
*
*
* private void putItemToMap(Map{@code >} map,String tagName,Item item){
* List{@code - } itemList = map.get(tagName);
*
* if (isNullOrEmpty(itemList)){
* itemList = new ArrayList{@code
- }();
* }
* itemList.add(item);
* map.put(tagName, itemList);
* }
*
*
*
* 可以重构成:
*
*
*
* private void putItemToMap(Map{@code >} map,String tagName,Item item){
* com.feilong.core.util.MapUtil.putMultiValue(map, tagName, item);
* }
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param map
* the map
* @param key
* the key
* @param value
* the value
* @return 如果 map 是null,抛出 {@link NullPointerException}
* @see "com.google.common.collect.ArrayListMultimap"
* @see "org.apache.commons.collections4.MultiValuedMap"
* @see "org.apache.commons.collections4.IterableMap"
* @see "org.apache.commons.collections4.MultiMapUtils"
* @see "org.apache.commons.collections4.multimap.AbstractMultiValuedMap#put(Object, Object)"
* @since 1.6.2
*/
public static Map> putMultiValue(Map> map,K key,V value){
Validate.notNull(map, "map can't be null!");
List list = defaultIfNull(map.get(key), new ArrayList());
list.add(value);
map.put(key, list);
return map;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 获得一个map 中,按照指定的keys 整理成新的map.
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - 原
map 不变
* - 返回的map为 {@link LinkedHashMap},key的顺序 按照参数
keys的顺序
* - 如果循环的 key不在map key里面,则忽略该key,并输出debug level log
*
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = new HashMap{@code <>}();
* map.put("a", 3007);
* map.put("b", 3001);
* map.put("c", 3001);
* map.put("d", 3003);
* LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(MapUtil.getSubMap(map, "a", "c")));
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
* {
* "a": 3007,
* "c": 3001
* }
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the generic type
* @param map
* the map
* @param keys
* 如果循环的 key不在map key里面,则忽略该key,并输出debug level log
* @return 如果 map 是null或者empty,返回 {@link Collections#emptyMap()};
* 如果 keys 是null或者empty,直接返回 map
* 如果循环的 key不在map key里面,则忽略该key,并输出debug level log
*/
@SafeVarargs
public static Map getSubMap(Map map,K...keys){
if (isNullOrEmpty(keys)){
return map;
}
return getSubMap(map, toSet(keys));
}
/**
* 获得一个map 中,按照指定的keys 整理成新的map.
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - 原
map 不变
* - 返回的map为 {@link LinkedHashMap},key的顺序 按照参数
keys的顺序
* - 如果循环的 key不在map key里面,则忽略该key,并输出debug level log
*
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = new HashMap{@code <>}();
* map.put("a", 3007);
* map.put("b", 3001);
* map.put("c", 3001);
* map.put("d", 3003);
* LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(MapUtil.getSubMap(map,toList("a", "c"))));
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
* {
* "a": 3007,
* "c": 3001
* }
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the generic type
* @param map
* the map
* @param keys
* 如果循环的 key不在map key里面,则忽略该key,并输出debug level log
* @return 如果 map 是null或者empty,返回 {@link Collections#emptyMap()};
* 如果 keys 是null或者empty,直接返回 map
* 如果循环的 key不在map key里面,则忽略该key,并输出debug level log
* @since 1.10.4
*/
public static Map getSubMap(Map map,Iterable keys){
if (isNullOrEmpty(map)){
return emptyMap();
}
if (isNullOrEmpty(keys)){
return map;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
//保证元素的顺序,key的顺序 按照参数 keys的顺序
Map returnMap = newLinkedHashMap(10);
for (K key : keys){
if (map.containsKey(key)){
returnMap.put(key, map.get(key));
}else{
LOGGER.debug("map don't contains key:[{}],but has keys:[{}]", key, map.keySet());
}
}
return returnMap;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 获得 sub map(排除指定的 excludeKeys).
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - 原
map 不变
* - 此方法可以提取{@link Collections#unmodifiableMap(Map)}
* - 返回值为 {@link LinkedHashMap},key的顺序按照参数
map的顺序
*
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = new LinkedHashMap{@code <>}();
*
* map.put("a", 3007);
* map.put("b", 3001);
* map.put("c", 3002);
* map.put("g", -1005);
*
* LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(MapUtil.getSubMapExcludeKeys(map, "a", "g", "m")));
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
* {
* "b": 3001,
* "c": 3002
* }
*
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the generic type
* @param map
* the map
* @param excludeKeys
* the keys
* @return 如果 map 是null或者empty,返回 {@link Collections#emptyMap()};
* 如果 excludeKeys 是null或者empty,直接返回 map
* @since 1.0.9
*/
@SafeVarargs
public static Map getSubMapExcludeKeys(Map map,K...excludeKeys){
if (isNullOrEmpty(excludeKeys)){
return map;
}
return getSubMapExcludeKeys(map, toSet(excludeKeys));
}
/**
* 获得 sub map(排除指定的 excludeKeys).
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - 原
map 不变
* - 此方法可以提取{@link Collections#unmodifiableMap(Map)}
* - 返回值为 {@link LinkedHashMap},key的顺序按照参数
map的顺序
*
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = new LinkedHashMap{@code <>}();
*
* map.put("a", 3007);
* map.put("b", 3001);
* map.put("c", 3002);
* map.put("g", -1005);
*
* LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(MapUtil.getSubMapExcludeKeys(map, toList("a", "g", "m"))));
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
* {
* "b": 3001,
* "c": 3002
* }
*
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the generic type
* @param map
* the map
* @param excludeKeys
* the exclude keys
* @return 如果 map 是null或者empty,返回 {@link Collections#emptyMap()};
* 如果 excludeKeys 是null或者empty,直接返回 map
* @since 1.10.4
*/
public static Map getSubMapExcludeKeys(Map map,Iterable excludeKeys){
if (isNullOrEmpty(map)){
return emptyMap();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
if (isNullOrEmpty(excludeKeys)){
return map;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
Map returnMap = newLinkedHashMap(map.size());//保证元素的顺序
for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()){
K key = entry.getKey();
if (!com.feilong.lib.collection4.IterableUtils.contains(excludeKeys, key)){
returnMap.put(key, entry.getValue());
}
}
return returnMap;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 删除 map 的指定的 keys.
*
* 注意:
*
*
*
* -
*
*
* 原 map会改变,
*
*
* 如果你只是需要从原map中获取非指定的keys,你可以调用
* {@link #getSubMapExcludeKeys(Map, Object...)} 或者{@link #getSubMapExcludeKeys(Map, Iterable)} 方法
*
*
*
* - 此方法删除不了 {@link Collections#unmodifiableMap(Map)}
* - 如果
map包含key,那么直接调用 {@link Map#remove(Object)}
* - 如果不包含,那么输出debug级别日志
*
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = newLinkedHashMap(3);
*
* map.put("name", "feilong");
* map.put("age", "18");
* map.put("country", "china");
*
* LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(MapUtil.removeKeys(map, "country")));
*
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
* {
* "name": "feilong",
* "age": "18"
* }
*
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param map
* the map
* @param keys
* the keys
* @return 如果 map 是null,返回null
* 如果 keys 是null或者empty,直接返回 map
* @since 1.6.3
*/
@SafeVarargs
public static Map removeKeys(Map map,K...keys){
if (null == map){// since 1.8.6
return null;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
if (isNullOrEmpty(keys)){
return map;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
for (K key : keys){
if (map.containsKey(key)){
map.remove(key);
}else{
LOGGER.debug("map has keys:[{}],but don't contains key:[{}]", map.keySet(), key);
}
}
return map;
}
/**
* 将 map 的key和value互转.
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - 这个操作map预先良好的定义.
* - 如果传过来的map,不同的key有相同的value,那么返回的map(key)只会有一个(value),其他重复的key被丢掉了
*
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = new HashMap{@code <>}();
* map.put("a", 3007);
* map.put("b", 3001);
* map.put("c", 3001);
* map.put("d", 3003);
* LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(MapUtil.invertMap(map)));
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
* {
* "3001": "c",
* "3007": "a",
* "3003": "d"
* }
*
*
* 可以看出 b元素被覆盖了
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param map
* the map
* @return 如果map 是null,返回 null
* 如果map 是empty,返回 一个 new HashMap
* @see com.feilong.lib.collection4.MapUtils#invertMap(Map)
* @since 1.2.2
*/
public static Map invertMap(Map map){
return null == map ? null : MapUtils.invertMap(map);//返回的是 HashMap
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 以参数 map的key为key,以参数 map value的指定extractPropertyName属性值为值,拼装成新的map返回.
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - 返回map的顺序,按照参数 map key的顺序
*
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = new LinkedHashMap{@code <>}();
* map.put(1L, new User(100L));
* map.put(2L, new User(200L));
* map.put(5L, new User(500L));
* map.put(4L, new User(400L));
*
* LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(MapUtil.extractSubMap(map, "id")));
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
{
"1": 100,
"2": 200,
"5": 500,
"4": 400
}
*
*
*
*
* @param
* key的类型
* @param
* map value bean类型
* @param
* map value bean相关 属性名称 extractPropertyName 的值类型
* @param map
* the map
* @param extractPropertyName
* 泛型O对象指定的属性名称,Possibly indexed and/or nested name of the property to be modified,参见
* propertyName
* @return 如果 map 是null或者empty,返回 {@link Collections#emptyMap()}
* 如果 extractPropertyName 是null,抛出 {@link NullPointerException}
* 如果 extractPropertyName 是blank,抛出 {@link IllegalArgumentException}
* @since 1.8.0 remove class param
*/
public static Map extractSubMap(Map map,String extractPropertyName){
return extractSubMap(map, null, extractPropertyName);
}
/**
* 以参数 map的key为key,以参数 mapvalue的指定extractPropertyName
* 属性值为值,拼装成新的map返回.
*
* 说明:
*
*
* - 如果在抽取的过程中,
map没有某个 includeKeys,将会忽略该key的抽取,并输出 warn log
* - 如果参数
includeKeys是null或者 empty,那么会抽取map所有的key
* - 返回map的顺序,按照参数includeKeys的顺序(如果includeKeys是null,那么按照map key的顺序)
*
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = new LinkedHashMap{@code <>}();
* map.put(1L, new User(100L));
* map.put(2L, new User(200L));
* map.put(53L, new User(300L));
* map.put(5L, new User(500L));
* map.put(6L, new User(600L));
* map.put(4L, new User(400L));
*
* Long[] includeKeys = { 5L, 4L };
* LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(MapUtil.extractSubMap(map, includeKeys, "id")));
*
*
* 返回:
*
*
* {
* "5": 500,
* "4": 400
* }
*
*
*
*
* 典型示例:
*
*
*
*
*
* private Map{@code } constructPropertyIdAndItemPropertiesIdMap(
* String properties,
* Map{@code } itemPropertiesIdAndPropertyValueSubViewCommandMap){
* Long[] itemPropertiesIds = StoCommonUtil.toItemPropertiesIdLongs(properties);
*
* Map{@code } itemPropertiesIdAndPropertyIdMap = MapUtil
* .extractSubMap(itemPropertiesIdAndPropertyValueSubViewCommandMap, itemPropertiesIds, "propertyId");
*
* return MapUtil.invertMap(itemPropertiesIdAndPropertyIdMap);
* }
*
*
*
*
*
* @param
* key的类型
* @param
* map value bean类型
* @param
* map value bean相关 属性名称 extractPropertyName 的值类型
* @param map
* the map
* @param includeKeys
* the include keys
* @param extractPropertyName
* 泛型O对象指定的属性名称,Possibly indexed and/or nested name of the property to be modified,参见
* propertyName
* @return 如果 map 是null或者empty,返回 {@link Collections#emptyMap()}
* 如果 extractPropertyName 是null,抛出 {@link NullPointerException}
* 如果 extractPropertyName 是blank,抛出 {@link IllegalArgumentException}
* 如果 includeKeys 是null或者empty, then will extract map total keys
* @since 1.8.0 remove class param
*/
public static Map extractSubMap(Map map,K[] includeKeys,String extractPropertyName){
if (isNullOrEmpty(map)){
return emptyMap();
}
Validate.notBlank(extractPropertyName, "extractPropertyName can't be null/empty!");
//---------------------------------------------------------------
//如果excludeKeys是null,那么抽取所有的key
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // NOPMD - false positive for generics
K[] useIncludeKeys = isNullOrEmpty(includeKeys) ? (K[]) map.keySet().toArray() : includeKeys;
Validate.notEmpty(useIncludeKeys, "useIncludeKeys can't be null/empty!");
//---------------------------------------------------------------
//保证元素的顺序,顺序是参数 includeKeys的顺序
Map returnMap = newLinkedHashMap(useIncludeKeys.length);
for (K key : useIncludeKeys){
if (map.containsKey(key)){
returnMap.put(key, PropertyUtil. getProperty(map.get(key), extractPropertyName));
}else{
LOGGER.warn("map:[{}] don't contains key:[{}]", map.keySet(), key);
}
}
return returnMap;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* New concurrent hash map.
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @return a new, empty {@code ConcurrentHashMap}
* @since 1.10.7
*/
public static Map newConcurrentHashMap(){
return new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
}
/**
* New concurrent hash map.
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param map
* the map
* @return 如果 map 是null,抛出 {@link NullPointerException}
* @since 1.14.0
*/
public static Map newConcurrentHashMap(Map map){
Validate.notNull(map, "map can't be null!");
return new ConcurrentHashMap<>(map);
}
/**
* 创建 {@code ConcurrentHashMap}实例,拥有足够的 "initial capacity" 应该控制{@code expectedSize} elements without growth.
*
*
* This behavior cannot be broadly guaranteed, but it is observed to be true for OpenJDK 1.7.
* It also can't be guaranteed that the method isn't inadvertently oversizing the returned map.
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = MapUtil.newConcurrentHashMap(3);
* map.put("name", "feilong");
* map.put("age", "18");
* map.put("address", "shanghai");
*
*
*
*
* 使用该方法的好处:
*
*
*
* - 简化代码书写方式
*
*
*
*
* 以前你可能需要这么写代码:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new ConcurrentHashMap{@code >>}(16);
*
*
*
* 如果你是使用JDK1.7或者以上,你可以使用钻石符:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new ConcurrentHashMap{@code <>}(16);
*
*
*
* 不过只要你是使用1.5+,你都可以写成:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = MapUtil.newConcurrentHashMap(16);// 如果搭配static import 使用会更加简洁
*
*
*
*
*
* - 减少扩容次数
*
*
*
*
* 如果你要一次性初始一个能存放100个元素的map,并且不需要扩容,提高性能的话,你需要
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new ConcurrentHashMap{@code >>}(100/0.75+1);
*
*
*
* 使用这个方法,你可以直接写成:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = MapUtil.newConcurrentHashMap(100);// 如果搭配static import 使用会更加简洁
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param expectedSize
* the number of entries you expect to add to the returned map
* @return a new, empty {@code ConcurrentHashMap} with enough capacity to hold {@code expectedSize} entries without resizing
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* 如果 expectedSize{@code < }0
* @since 1.11.1
*/
public static Map newConcurrentHashMap(int expectedSize){
return new ConcurrentHashMap<>(toInitialCapacity(expectedSize));
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* New tree map.
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @return a new, empty {@code ConcurrentHashMap}
* @since 1.10.7
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public static Map newTreeMap(){
return new TreeMap<>();
}
/**
* New tree map.
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param map
* the map
* @return 如果 map 是null,抛出 {@link NullPointerException}
* @since 1.14.0
*/
public static Map newTreeMap(Map map){
Validate.notNull(map, "map can't be null!");
return new TreeMap<>(map);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 创建 {@code HashMap}实例.
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
*
* Map{@code } newHashMap = MapUtil.newHashMap();
* newHashMap.put("name", "feilong");
* newHashMap.put("age", "18");
* newHashMap.put("address", "shanghai");
*
*
*
*
* 使用该方法的好处:
*
*
*
* - 简化代码书写方式
*
*
*
*
* 以前你可能需要这么写代码:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new HashMap{@code >>}();
*
*
*
* 如果你是使用JDK1.7或者以上,你可以使用钻石符:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new HashMap{@code <>}();
*
*
*
* 不过只要你是使用1.5+,你都可以写成:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = MapUtil.newHashMap(); // 如果搭配static import 使用会更加简洁
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @return the hash map
* @see "com.google.common.collect.Maps#newHashMap()"
* @see java.util.HashMap#HashMap()
* @since 1.10.7
*/
public static Map newHashMap(){
return new HashMap<>();
}
/**
* New hash map.
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param map
* the map
* @return 如果 map 是null,抛出 {@link NullPointerException}
* @since 1.14.0
*/
public static Map newHashMap(Map map){
Validate.notNull(map, "map can't be null!");
return new HashMap<>(map);
}
/**
* 创建 {@code HashMap}实例,拥有足够的 "initial capacity" 应该控制{@code expectedSize} elements without growth.
*
*
* This behavior cannot be broadly guaranteed, but it is observed to be true for OpenJDK 1.7.
* It also can't be guaranteed that the method isn't inadvertently oversizing the returned map.
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
*
* Map{@code } newHashMap = MapUtil.newHashMap(3);
* newHashMap.put("name", "feilong");
* newHashMap.put("age", "18");
* newHashMap.put("address", "shanghai");
*
*
*
*
* 使用该方法的好处:
*
*
*
* - 简化代码书写方式
*
*
*
*
* 以前你可能需要这么写代码:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new HashMap{@code >>}(16);
*
*
*
* 如果你是使用JDK1.7或者以上,你可以使用钻石符:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new HashMap{@code <>}(16);
*
*
*
* 不过只要你是使用1.5+,你都可以写成:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = MapUtil.newHashMap(16);// 如果搭配static import 使用会更加简洁
*
*
*
*
*
* - 减少扩容次数
*
*
*
*
* 如果你要一次性初始一个能存放100个元素的map,并且不需要扩容,提高性能的话,你需要
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new HashMap{@code >>}(100/0.75+1);
*
*
*
* 使用这个方法,你可以直接写成:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = MapUtil.newHashMap(100);// 如果搭配static import 使用会更加简洁
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param expectedSize
* the number of entries you expect to add to the returned map
* @return a new, empty {@code HashMap} with enough capacity to hold {@code expectedSize} entries without resizing
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* 如果 expectedSize{@code < }0
* @see "com.google.common.collect.Maps#newHashMapWithExpectedSize(int)"
* @see java.util.HashMap#HashMap(int)
* @since 1.7.1
*/
public static Map newHashMap(int expectedSize){
return new HashMap<>(toInitialCapacity(expectedSize));
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 创建 {@code LinkedHashMap}实例.
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = MapUtil.newLinkedHashMap();
* map.put("name", "feilong");
* map.put("age", "18");
* map.put("address", "shanghai");
*
*
*
*
* 使用该方法的好处:
*
*
*
* - 简化代码书写方式
*
*
*
*
* 以前你可能需要这么写代码:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new LinkedHashMap{@code >>}();
*
*
*
* 如果你是使用JDK1.7或者以上,你可以使用钻石符:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new LinkedHashMap{@code <>}();
*
*
*
* 不过只要你是使用1.5+,你都可以写成:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = MapUtil.newLinkedHashMap();// 如果搭配static import 使用会更加简洁
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @return the linked hash map
* @see "com.google.common.collect.Maps#newLinkedHashMapWithExpectedSize(int)"
* @see java.util.LinkedHashMap#LinkedHashMap()
* @since 1.10.7
*/
public static Map newLinkedHashMap(){
return new LinkedHashMap<>();
}
/**
* New linked hash map.
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param map
* the map
* @return 如果 map 是null,抛出 {@link NullPointerException}
* @since 1.14.0
*/
public static Map newLinkedHashMap(Map map){
Validate.notNull(map, "map can't be null!");
return new LinkedHashMap<>(map);
}
/**
* 创建 {@code LinkedHashMap}实例,拥有足够的 "initial capacity" 应该控制{@code expectedSize} elements without growth.
*
*
* This behavior cannot be broadly guaranteed, but it is observed to be true for OpenJDK 1.7.
* It also can't be guaranteed that the method isn't inadvertently oversizing the returned map.
*
*
* 示例:
*
*
*
*
* Map{@code } map = MapUtil.newLinkedHashMap(3);
* map.put("name", "feilong");
* map.put("age", "18");
* map.put("address", "shanghai");
*
*
*
*
* 使用该方法的好处:
*
*
*
* - 简化代码书写方式
*
*
*
*
* 以前你可能需要这么写代码:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new LinkedHashMap{@code >>}(16);
*
*
*
* 如果你是使用JDK1.7或者以上,你可以使用钻石符:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new LinkedHashMap{@code <>}(16);
*
*
*
* 不过只要你是使用1.5+,你都可以写成:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = MapUtil.newLinkedHashMap(16);// 如果搭配static import 使用会更加简洁
*
*
*
*
*
*
* - 减少扩容次数
*
*
*
*
* 如果你要一次性初始一个能存放100个元素的map,并且不需要扩容,提高性能的话,你需要
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = new LinkedHashMap{@code >>}(100/0.75+1);
*
*
*
* 使用这个方法,你可以直接写成:
*
*
*
* Map{@code >>} map = MapUtil.newLinkedHashMap(100);// 如果搭配static import 使用会更加简洁
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* @param
* the key type
* @param
* the value type
* @param expectedSize
* the number of entries you expect to add to the returned map
* @return a new, empty {@code LinkedHashMap} with enough capacity to hold {@code expectedSize} entries without resizing
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* 如果 size{@code < }0
* @see "com.google.common.collect.Maps#newLinkedHashMapWithExpectedSize(int)"
* @see java.util.LinkedHashMap#LinkedHashMap(int)
* @since 1.7.1
*/
public static Map newLinkedHashMap(int expectedSize){
return new LinkedHashMap<>(toInitialCapacity(expectedSize));
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 将size转成 initialCapacity (for {@link java.util.HashMap}).
*
*
* 适合于明确知道 hashmap size,现在需要初始化的情况
*
*
* @param size
* map的 size
* @return the int
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* 如果 size{@code < }0
* @see java hashmap,如果确定只装载100个元素,new HashMap(?)多少是最佳的,why?
* @see
* Difference between new HashMap(int) and guava Maps.newHashMapWithExpectedSize(int)
* @see Best HashMap initial
* capacity while indexing a List
* @see java.util.HashMap#HashMap(Map)
* @see "com.google.common.collect.Maps#capacity(int)"
* @see java.util.HashMap#inflateTable(int)
* @see org.apache.commons.collections4.map.AbstractHashedMap#calculateNewCapacity(int)
* @since 1.7.1
*/
private static int toInitialCapacity(int size){
Validate.isTrue(size >= 0, "size :[%s] must >=0", size);
//借鉴了 google guava 的实现,不过 guava 不同版本实现不同
//guava 19 (int) (expectedSize / 0.75F + 1.0F)
//guava 18 expectedSize + expectedSize / 3
//google-collections 1.0 Math.max(expectedSize * 2, 16)
//This is the calculation used in JDK8 to resize when a putAll happens it seems to be the most conservative calculation we can make.
return (int) (size / 0.75f) + 1;//0.75 is the default load factor
}
}
