
g0001_0100.s0064_minimum_path_sum.readme.md Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
The newest version!
64\. Minimum Path Sum
Medium
Given a `m x n` `grid` filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right, which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
**Note:** You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
**Example 1:**
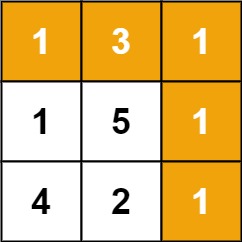
**Input:** grid = [[1,3,1],[1,5,1],[4,2,1]]
**Output:** 7
**Explanation:** Because the path 1 → 3 → 1 → 1 → 1 minimizes the sum.
**Example 2:**
**Input:** grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]
**Output:** 12
**Constraints:**
* `m == grid.length`
* `n == grid[i].length`
* `1 <= m, n <= 200`
* `0 <= grid[i][j] <= 100`
To solve the "Minimum Path Sum" problem in Java with the Solution class, follow these steps:
1. Define a method `minPathSum` in the `Solution` class that takes a 2D grid of non-negative numbers as input and returns the minimum sum of all numbers along the path from the top-left corner to the bottom-right corner of the grid.
2. Initialize a 2D array `dp` of size `m x n`, where `dp[i][j]` represents the minimum sum of the path from the top-left corner to position `(i, j)` in the grid.
3. Initialize `dp[0][0]` to the value of the top-left cell in the grid.
4. Initialize the first row and first column of `dp` based on the grid values and the previous cells in the same row or column.
5. Iterate over each position `(i, j)` in the grid, starting from the second row and second column:
- Update `dp[i][j]` by adding the current grid value at `(i, j)` to the minimum of the values of the previous cells `(i-1, j)` and `(i, j-1)` in `dp`.
6. Return `dp[m-1][n-1]`, which represents the minimum path sum from the top-left corner to the bottom-right corner of the grid.
Here's the implementation of the `minPathSum` method in Java:
```java
class Solution {
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
dp[0][0] = grid[0][0];
// Initialize first row
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j-1] + grid[0][j];
}
// Initialize first column
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0] + grid[i][0];
}
// Fill in the rest of the dp array
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = grid[i][j] + Math.min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
}
```
This implementation efficiently calculates the minimum path sum using dynamic programming, with a time complexity of O(m * n) and a space complexity of O(m * n).© 2015 - 2024 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy