
g0101_0200.s0124_binary_tree_maximum_path_sum.readme.md Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
The newest version!
124\. Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
Hard
A **path** in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence **at most once**. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The **path sum** of a path is the sum of the node's values in the path.
Given the `root` of a binary tree, return _the maximum **path sum** of any **non-empty** path_.
**Example 1:**
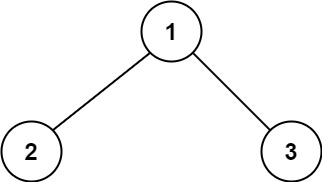
**Input:** root = [1,2,3]
**Output:** 6
**Explanation:** The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
**Example 2:**
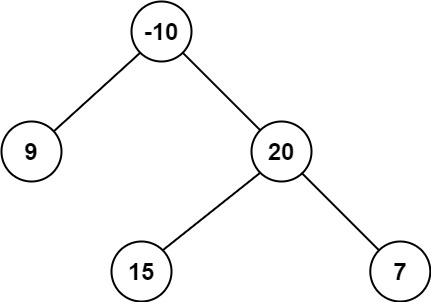
**Input:** root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
**Output:** 42
**Explanation:** The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
**Constraints:**
* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 3 * 104].
* `-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000`
To solve the "Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum" problem in Java with a `Solution` class, we'll use a recursive approach. Below are the steps:
1. **Create a `Solution` class**: Define a class named `Solution` to encapsulate our solution methods.
2. **Create a `maxPathSum` method**: This method takes the root node of the binary tree as input and returns the maximum path sum.
3. **Define a recursive helper method**: Define a recursive helper method `maxSumPath` to compute the maximum path sum rooted at the current node.
- The method should return the maximum path sum that can be obtained from the current node to any of its descendants.
- We'll use a post-order traversal to traverse the tree.
- For each node:
- Compute the maximum path sum for the left and right subtrees recursively.
- Update the maximum path sum by considering three cases:
1. The current node itself.
2. The current node plus the maximum path sum of the left subtree.
3. The current node plus the maximum path sum of the right subtree.
- Update the global maximum path sum if necessary by considering the sum of the current node, left subtree, and right subtree.
4. **Initialize a variable to store the maximum path sum**: Initialize a global variable `maxSum` to store the maximum path sum.
5. **Call the helper method**: Call the `maxSumPath` method with the root node.
6. **Return the maximum path sum**: After traversing the entire tree, return the `maxSum`.
Here's the Java implementation:
```java
class Solution {
int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // Initialize global variable to store maximum path sum
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
maxSumPath(root);
return maxSum; // Return maximum path sum
}
// Recursive helper method to compute maximum path sum rooted at current node
private int maxSumPath(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return 0; // Base case
// Compute maximum path sum for left and right subtrees recursively
int leftSum = Math.max(maxSumPath(node.left), 0); // Ignore negative sums
int rightSum = Math.max(maxSumPath(node.right), 0); // Ignore negative sums
// Update maximum path sum by considering three cases:
// 1. Current node itself
// 2. Current node + maximum path sum of left subtree
// 3. Current node + maximum path sum of right subtree
int currentSum = node.val + leftSum + rightSum;
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, currentSum); // Update global maximum path sum
// Return the maximum path sum that can be obtained from the current node to any of its descendants
return node.val + Math.max(leftSum, rightSum);
}
// Definition for a binary tree node
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
```
This implementation follows the steps outlined above and efficiently computes the maximum path sum in a binary tree in Java.© 2015 - 2024 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy