
g0101_0200.s0124_binary_tree_maximum_path_sum.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
package g0101_0200.s0124_binary_tree_maximum_path_sum;
// #Hard #Top_100_Liked_Questions #Top_Interview_Questions #Dynamic_Programming #Depth_First_Search
// #Tree #Binary_Tree #Udemy_Tree_Stack_Queue #Big_O_Time_O(N)_Space_O(N)
// #2022_06_23_Time_1_ms_(99.46%)_Space_47.2_MB_(77.68%)
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
/*
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
/**
* 124 - Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum\.
*
* Hard
*
* A **path** in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence **at most once**. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
*
* The **path sum** of a path is the sum of the node's values in the path.
*
* Given the `root` of a binary tree, return _the maximum **path sum** of any **non-empty** path_.
*
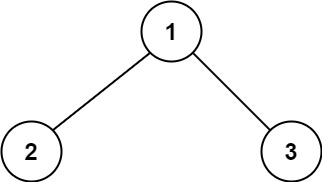
* **Example 1:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** root = [1,2,3]
*
* **Output:** 6
*
* **Explanation:** The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
*
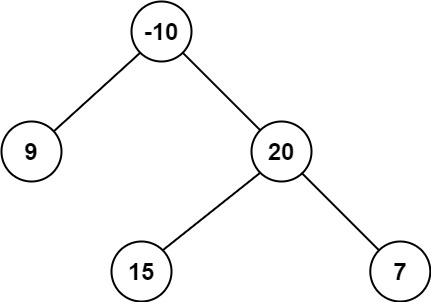
* **Example 2:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
*
* **Output:** 42
*
* **Explanation:** The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 3 * 104].
* * `-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000`
**/
public class Solution {
private int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
private int helper(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
// to avoid the -ve values in left side we will compare them with 0
int left = Math.max(0, helper(root.left));
int right = Math.max(0, helper(root.right));
int current = root.val + left + right;
if (current > max) {
max = current;
}
return root.val + Math.max(left, right);
}
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
helper(root);
return max;
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy