
g0301_0400.s0391_perfect_rectangle.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g0301_0400.s0391_perfect_rectangle;
// #Hard #Array #Line_Sweep #2022_07_13_Time_67_ms_(54.55%)_Space_65.4_MB_(20.00%)
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 391 - Perfect Rectangle\.
*
* Hard
*
* Given an array `rectangles` where rectangles[i] = [xi, yi, ai, bi] represents an axis-aligned rectangle. The bottom-left point of the rectangle is (xi, yi) and the top-right point of it is (ai, bi).
*
* Return `true` _if all the rectangles together form an exact cover of a rectangular region_.
*
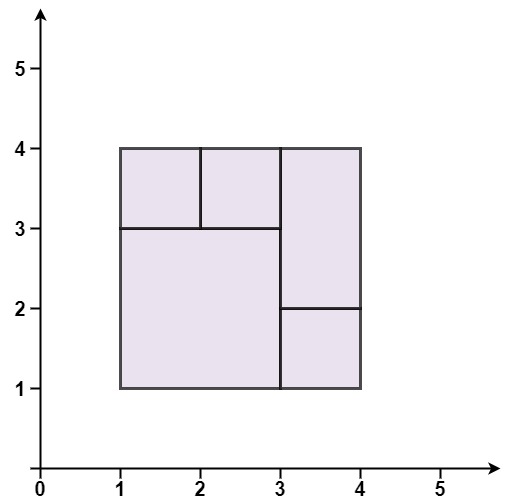
* **Example 1:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** rectangles = \[\[1,1,3,3],[3,1,4,2],[3,2,4,4],[1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,4]]
*
* **Output:** true
*
* **Explanation:** All 5 rectangles together form an exact cover of a rectangular region.
*
* **Example 2:**
*
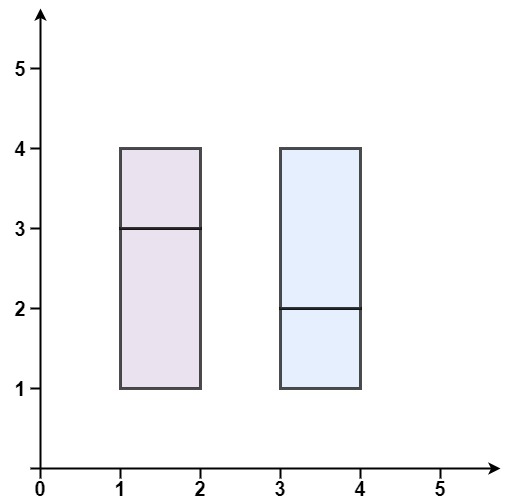
* 
*
* **Input:** rectangles = \[\[1,1,2,3],[1,3,2,4],[3,1,4,2],[3,2,4,4]]
*
* **Output:** false
*
* **Explanation:** Because there is a gap between the two rectangular regions.
*
* **Example 3:**
*
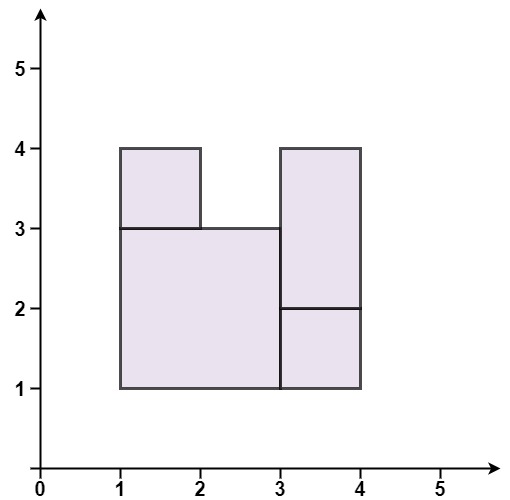
* 
*
* **Input:** rectangles = \[\[1,1,3,3],[3,1,4,2],[1,3,2,4],[3,2,4,4]]
*
* **Output:** false
*
* **Explanation:** Because there is a gap in the top center.
*
* **Example 4:**
*
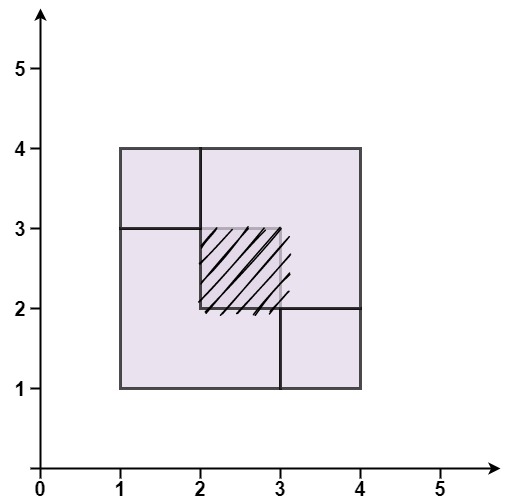
* 
*
* **Input:** rectangles = \[\[1,1,3,3],[3,1,4,2],[1,3,2,4],[2,2,4,4]]
*
* **Output:** false
*
* **Explanation:** Because two of the rectangles overlap with each other.
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * 1 <= rectangles.length <= 2 * 104
* * `rectangles[i].length == 4`
* * -105 <= xi, yi, ai, bi <= 105
**/
public class Solution {
public boolean isRectangleCover(int[][] rectangles) {
Set container = new HashSet<>();
// add each rectangle area to totalArea
int totalArea = 0;
// A rectangle has four points, if a point appears twice, it will be deleted it from the set
for (int[] rectangle : rectangles) {
totalArea += (rectangle[2] - rectangle[0]) * (rectangle[3] - rectangle[1]);
Point p1 = new Point(rectangle[0], rectangle[1]);
Point p2 = new Point(rectangle[2], rectangle[1]);
Point p3 = new Point(rectangle[2], rectangle[3]);
Point p4 = new Point(rectangle[0], rectangle[3]);
if (container.contains(p1)) {
container.remove(p1);
} else {
container.add(p1);
}
if (container.contains(p2)) {
container.remove(p2);
} else {
container.add(p2);
}
if (container.contains(p3)) {
container.remove(p3);
} else {
container.add(p3);
}
if (container.contains(p4)) {
container.remove(p4);
} else {
container.add(p4);
}
}
// A perfect rectangle must has four points
if (container.size() != 4) {
return false;
}
// these four points represent the last perfect rectangle, check this rectangle area to the
// totalArea
int minX = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int maxX = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int minY = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int maxY = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (Point p : container) {
minX = Math.min(minX, p.x);
maxX = Math.max(maxX, p.x);
minY = Math.min(minY, p.y);
maxY = Math.max(maxY, p.y);
}
return totalArea == (maxX - minX) * (maxY - minY);
}
private static class Point {
private final int x;
private final int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Point point = (Point) o;
return x == point.x && y == point.y;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(x, y);
}
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy