
g0401_0500.s0417_pacific_atlantic_water_flow.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g0401_0500.s0417_pacific_atlantic_water_flow;
// #Medium #Array #Depth_First_Search #Breadth_First_Search #Matrix
// #Graph_Theory_I_Day_4_Matrix_Related_Problems #Level_2_Day_10_Graph/BFS/DFS #Udemy_Graph
// #2022_07_16_Time_5_ms_(92.62%)_Space_54.8_MB_(59.96%)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 417 - Pacific Atlantic Water Flow\.
*
* Medium
*
* There is an `m x n` rectangular island that borders both the **Pacific Ocean** and **Atlantic Ocean**. The **Pacific Ocean** touches the island's left and top edges, and the **Atlantic Ocean** touches the island's right and bottom edges.
*
* The island is partitioned into a grid of square cells. You are given an `m x n` integer matrix `heights` where `heights[r][c]` represents the **height above sea level** of the cell at coordinate `(r, c)`.
*
* The island receives a lot of rain, and the rain water can flow to neighboring cells directly north, south, east, and west if the neighboring cell's height is **less than or equal to** the current cell's height. Water can flow from any cell adjacent to an ocean into the ocean.
*
* Return _a **2D list** of grid coordinates_ `result` _where_ result[i] = [ri, ci] _denotes that rain water can flow from cell_ (ri, ci) _to **both** the Pacific and Atlantic oceans_.
*
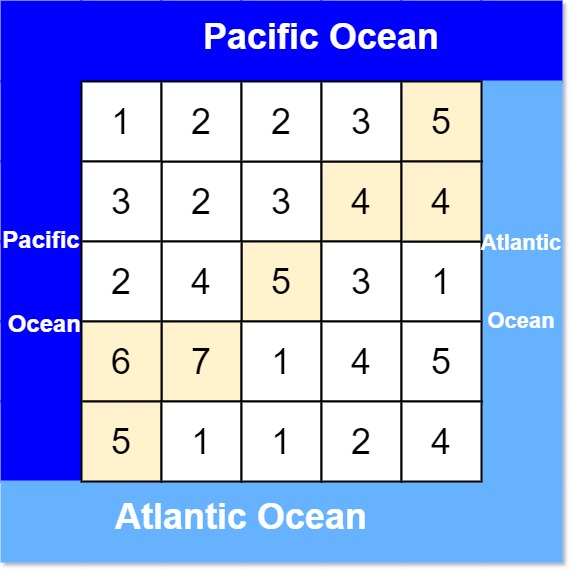
* **Example 1:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** heights = \[\[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]]
*
* **Output:** [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]
*
* **Example 2:**
*
* **Input:** heights = \[\[2,1],[1,2]]
*
* **Output:** [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * `m == heights.length`
* * `n == heights[r].length`
* * `1 <= m, n <= 200`
* * 0 <= heights[r][c] <= 105
**/
public class Solution {
private int col = 0;
private int row = 0;
public List> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix.length == 0) {
return res;
}
col = matrix.length;
row = matrix[0].length;
boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[col][row];
boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[col][row];
for (int i = 0; i < col; i++) {
dfs(i, 0, matrix, pacific);
dfs(i, row - 1, matrix, atlantic);
}
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
dfs(0, i, matrix, pacific);
dfs(col - 1, i, matrix, atlantic);
}
for (int i = 0; i < col; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < row; j++) {
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {
List temp = new ArrayList<>();
temp.add(i);
temp.add(j);
res.add(temp);
}
}
}
return res;
}
private void dfs(int i, int j, int[][] matrix, boolean[][] visited) {
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= matrix.length || j >= matrix[0].length || visited[i][j]) {
return;
}
visited[i][j] = true;
if (i < col - 1 && matrix[i][j] <= matrix[i + 1][j]) {
dfs(i + 1, j, matrix, visited);
}
if (i > 0 && matrix[i][j] <= matrix[i - 1][j]) {
dfs(i - 1, j, matrix, visited);
}
if (j < row - 1 && matrix[i][j] <= matrix[i][j + 1]) {
dfs(i, j + 1, matrix, visited);
}
if (j > 0 && matrix[i][j] <= matrix[i][j - 1]) {
dfs(i, j - 1, matrix, visited);
}
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy