
g0701_0800.s0778_swim_in_rising_water.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g0701_0800.s0778_swim_in_rising_water;
// #Hard #Array #Depth_First_Search #Breadth_First_Search #Binary_Search #Matrix
// #Heap_Priority_Queue #Union_Find #2022_03_26_Time_13_ms_(69.75%)_Space_51.8_MB_(12.57%)
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* 778 - Swim in Rising Water\.
*
* Hard
*
* You are given an `n x n` integer matrix `grid` where each value `grid[i][j]` represents the elevation at that point `(i, j)`.
*
* The rain starts to fall. At time `t`, the depth of the water everywhere is `t`. You can swim from a square to another 4-directionally adjacent square if and only if the elevation of both squares individually are at most `t`. You can swim infinite distances in zero time. Of course, you must stay within the boundaries of the grid during your swim.
*
* Return _the least time until you can reach the bottom right square_ `(n - 1, n - 1)` _if you start at the top left square_ `(0, 0)`.
*
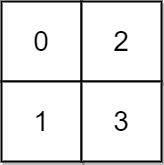
* **Example 1:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** grid = \[\[0,2],[1,3]]
*
* **Output:** 3
*
* **Explanation:**
*
* At time 0, you are in grid location (0, 0).
* You cannot go anywhere else because 4-directionally adjacent neighbors have a higher elevation than t = 0.
* You cannot reach point (1, 1) until time 3.
* When the depth of water is 3, we can swim anywhere inside the grid.
*
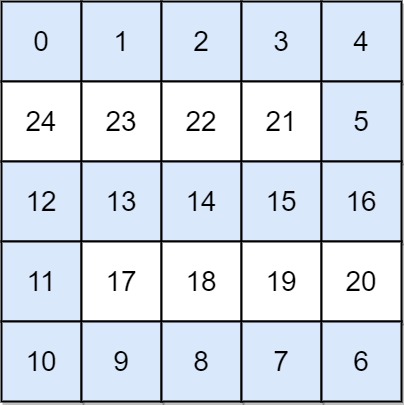
* **Example 2:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** grid = \[\[0,1,2,3,4],[24,23,22,21,5],[12,13,14,15,16],[11,17,18,19,20],[10,9,8,7,6]]
*
* **Output:** 16
*
* **Explanation:**
*
* The final route is shown.
* We need to wait until time 16 so that (0, 0) and (4, 4) are connected.
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * `n == grid.length`
* * `n == grid[i].length`
* * `1 <= n <= 50`
* * 0 <= grid[i][j] < n2
* * Each value `grid[i][j]` is **unique**.
**/
public class Solution {
private int[] dir = new int[] {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
public int swimInWater(int[][] grid) {
int max = 0;
// find the maximum value in the matrix
for (int[] ints : grid) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
max = Math.max(max, ints[j]);
}
}
int l = 0;
int r = max;
int res = 0;
// perform binary search
while (l <= r) {
// find test water level
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
// if you can reach destination with current water level, store it as an answer and try
// lowering water level
if (bfs(grid, mid)) {
res = mid;
r = mid - 1;
} else {
// otherwise increase water level and try again
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return res;
}
public boolean bfs(int[][] grid, int limit) {
// use queue to process cells starting from top left corner
Queue que = new LinkedList<>();
// boolean array to keep track of visited cells
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[grid.length][grid[0].length];
// we start from top left corner
que.add(new int[] {0, 0});
visited[0][0] = true;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
// get current cell
int[] cur = que.poll();
int x = cur[0];
int y = cur[1];
// if value of current cell is greater than limit return false
if (grid[x][y] > limit) {
return false;
}
// if we reached the destination return true
if (x == grid.length - 1 && y == grid[0].length - 1) {
return true;
}
// check cells in all 4 directions
for (int i = 0; i < dir.length - 1; i++) {
int dx = x + dir[i];
int dy = y + dir[i + 1];
// if neighboring cell is in bounds, and hasn't been visited yet,
// and its value is less than current water level, add it to visited array and to
// the queue
if (dx >= 0
&& dy >= 0
&& dx < grid.length
&& dy < grid[0].length
&& !visited[dx][dy]
&& grid[dx][dy] <= limit) {
visited[dx][dy] = true;
que.add(new int[] {dx, dy});
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy