
g0801_0900.s0834_sum_of_distances_in_tree.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g0801_0900.s0834_sum_of_distances_in_tree;
// #Hard #Dynamic_Programming #Depth_First_Search #Tree #Graph
// #2022_03_24_Time_52_ms_(91.09%)_Space_96.7_MB_(75.86%)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 834 - Sum of Distances in Tree\.
*
* Hard
*
* There is an undirected connected tree with `n` nodes labeled from `0` to `n - 1` and `n - 1` edges.
*
* You are given the integer `n` and the array `edges` where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
*
* Return an array `answer` of length `n` where `answer[i]` is the sum of the distances between the ith node in the tree and all other nodes.
*
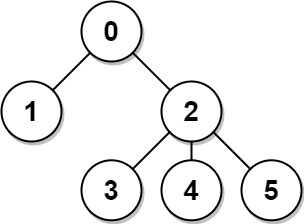
* **Example 1:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** n = 6, edges = \[\[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[2,4],[2,5]]
*
* **Output:** [8,12,6,10,10,10]
*
* **Explanation:** The tree is shown above.
*
* We can see that dist(0,1) + dist(0,2) + dist(0,3) + dist(0,4) + dist(0,5) equals 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8.
*
* Hence, answer[0] = 8, and so on.
*
* **Example 2:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** n = 1, edges = []
*
* **Output:** [0]
*
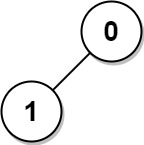
* **Example 3:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** n = 2, edges = \[\[1,0]]
*
* **Output:** [1,1]
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * 1 <= n <= 3 * 104
* * `edges.length == n - 1`
* * `edges[i].length == 2`
* * 0 <= ai, bi < n
* * ai != bi
* * The given input represents a valid tree.
**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public class Solution {
private int n;
private int[] count;
private int[] answer;
private List[] graph;
private void postorder(int node, int parent) {
for (int child : graph[node]) {
if (child != parent) {
postorder(child, node);
count[node] += count[child];
answer[node] += answer[child] + count[child];
}
}
}
private void preorder(int node, int parent) {
for (int child : graph[node]) {
if (child != parent) {
answer[child] = answer[node] - count[child] + n - count[child];
preorder(child, node);
}
}
}
public int[] sumOfDistancesInTree(int n, int[][] edges) {
this.n = n;
count = new int[n];
answer = new int[n];
graph = new List[n];
Arrays.fill(count, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
graph[edge[0]].add(edge[1]);
graph[edge[1]].add(edge[0]);
}
postorder(0, -1);
preorder(0, -1);
return answer;
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy