
g0801_0900.s0894_all_possible_full_binary_trees.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g0801_0900.s0894_all_possible_full_binary_trees;
// #Medium #Dynamic_Programming #Tree #Binary_Tree #Recursion #Memoization
// #2022_03_28_Time_3_ms_(68.56%)_Space_55.3_MB_(75.50%)
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/*
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
/**
* 894 - All Possible Full Binary Trees\.
*
* Medium
*
* Given an integer `n`, return _a list of all possible **full binary trees** with_ `n` _nodes_. Each node of each tree in the answer must have `Node.val == 0`.
*
* Each element of the answer is the root node of one possible tree. You may return the final list of trees in **any order**.
*
* A **full binary tree** is a binary tree where each node has exactly `0` or `2` children.
*
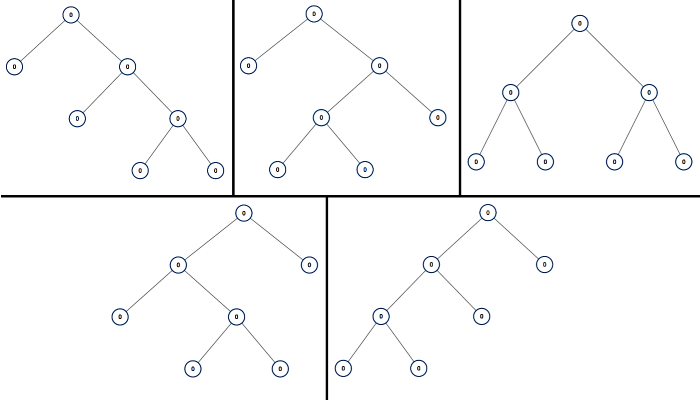
* **Example 1:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** n = 7
*
* **Output:** [[0,0,0,null,null,0,0,null,null,0,0],[0,0,0,null,null,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,null,null,null,null,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,null,null,0,0]]
*
* **Example 2:**
*
* **Input:** n = 3
*
* **Output:** [[0,0,0]]
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * `1 <= n <= 20`
**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
class Solution {
public List allPossibleFBT(int n) {
if (n % 2 == 0) {
// no complete binary tree possible
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List[] dp = new ArrayList[n + 1];
// form left to right
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i += 2) {
helper(i, dp);
}
return dp[n];
}
// Using tabulation
public void helper(int n, List[] dp) {
if (n <= 0) {
return;
}
if (n == 1) {
dp[1] = new ArrayList<>();
dp[1].add(new TreeNode(0));
return;
}
dp[n] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i += 2) {
// left
for (TreeNode nodeL : dp[i]) {
// right
for (TreeNode nodeR : dp[n - i - 1]) {
// 1 node used here
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(0);
root.left = nodeL;
root.right = nodeR;
dp[n].add(root);
}
}
}
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy