
g0901_1000.s0935_knight_dialer.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g0901_1000.s0935_knight_dialer;
// #Medium #Dynamic_Programming #2022_03_30_Time_4_ms_(99.08%)_Space_42.2_MB_(81.87%)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 935 - Knight Dialer\.
*
* Medium
*
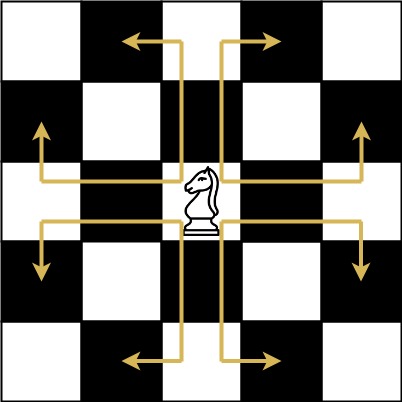
* The chess knight has a **unique movement** , it may move two squares vertically and one square horizontally, or two squares horizontally and one square vertically (with both forming the shape of an **L** ). The possible movements of chess knight are shown in this diagaram:
*
* A chess knight can move as indicated in the chess diagram below:
*
* 
*
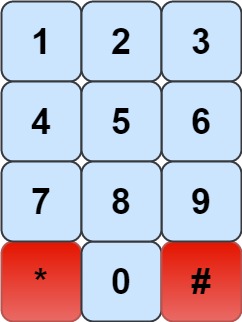
* We have a chess knight and a phone pad as shown below, the knight **can only stand on a numeric cell** (i.e. blue cell).
*
* 
*
* Given an integer `n`, return how many distinct phone numbers of length `n` we can dial.
*
* You are allowed to place the knight **on any numeric cell** initially and then you should perform `n - 1` jumps to dial a number of length `n`. All jumps should be **valid** knight jumps.
*
* As the answer may be very large, **return the answer modulo** 109 + 7.
*
* **Example 1:**
*
* **Input:** n = 1
*
* **Output:** 10
*
* **Explanation:** We need to dial a number of length 1, so placing the knight over any numeric cell of the 10 cells is sufficient.
*
* **Example 2:**
*
* **Input:** n = 2
*
* **Output:** 20
*
* **Explanation:** All the valid number we can dial are [04, 06, 16, 18, 27, 29, 34, 38, 40, 43, 49, 60, 61, 67, 72, 76, 81, 83, 92, 94]
*
* **Example 3:**
*
* **Input:** n = 3131
*
* **Output:** 136006598
*
* **Explanation:** Please take care of the mod.
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * `1 <= n <= 5000`
**/
public class Solution {
private static final int[][] MAP = new int[10][];
private static final List MEMO = new ArrayList<>();
static {
MAP[0] = new int[] {4, 6};
MAP[1] = new int[] {6, 8};
MAP[2] = new int[] {7, 9};
MAP[3] = new int[] {4, 8};
MAP[4] = new int[] {3, 9, 0};
MAP[5] = new int[0];
MAP[6] = new int[] {1, 7, 0};
MAP[7] = new int[] {2, 6};
MAP[8] = new int[] {1, 3};
MAP[9] = new int[] {2, 4};
MEMO.add(new int[] {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1});
}
public int knightDialer(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 10;
}
int mod = 1000_000_007;
while (MEMO.size() < n) {
int[] cur = MEMO.get(MEMO.size() - 1);
int[] next = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int d : MAP[i]) {
next[d] = (next[d] + cur[i]) % mod;
}
}
MEMO.add(next);
}
int sum = 0;
for (int x : MEMO.get(n - 1)) {
sum = (sum + x) % mod;
}
return sum;
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy