
g1201_1300.s1206_design_skiplist.Skiplist Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g1201_1300.s1206_design_skiplist;
// #Hard #Design #Linked_List #2022_03_08_Time_14_ms_(96.71%)_Space_48_MB_(85.19%)
/**
* 1206 - Design Skiplist\.
*
* Hard
*
* Design a **Skiplist** without using any built-in libraries.
*
* A **skiplist** is a data structure that takes `O(log(n))` time to add, erase and search. Comparing with treap and red-black tree which has the same function and performance, the code length of Skiplist can be comparatively short and the idea behind Skiplists is just simple linked lists.
*
* For example, we have a Skiplist containing `[30,40,50,60,70,90]` and we want to add `80` and `45` into it. The Skiplist works this way:
*
* 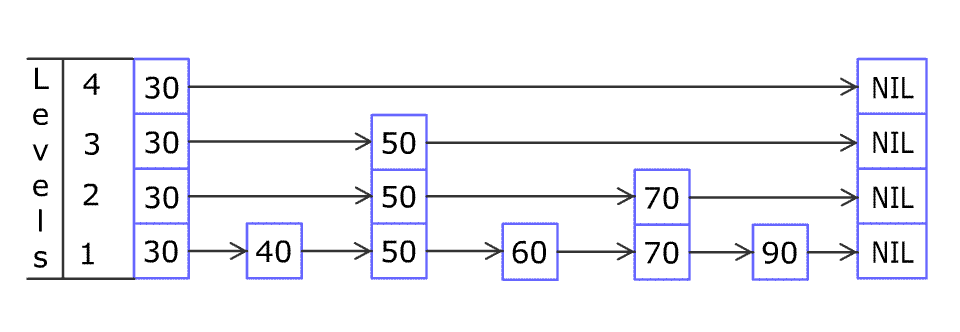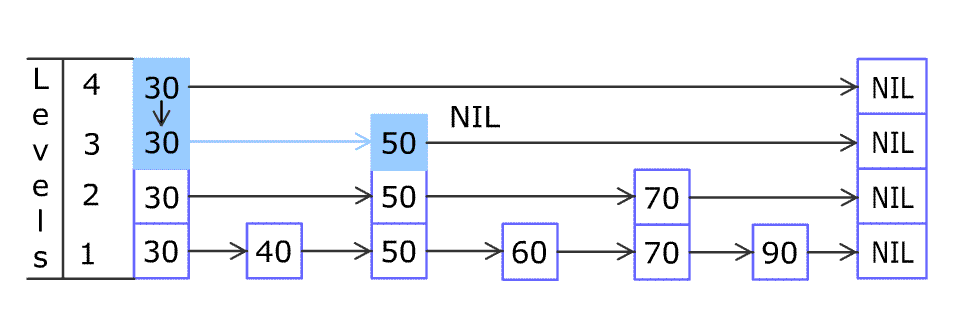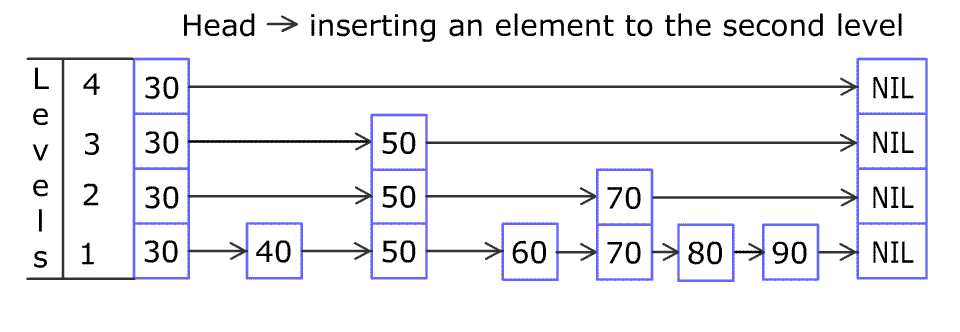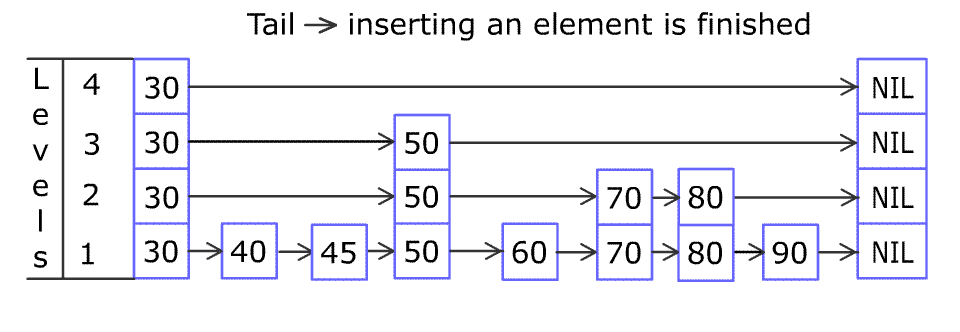
* Artyom Kalinin [CC BY-SA 3.0], via [Wikimedia Commons](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Skip_list_add_element-en.gif "Artyom Kalinin [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons")
*
* You can see there are many layers in the Skiplist. Each layer is a sorted linked list. With the help of the top layers, add, erase and search can be faster than `O(n)`. It can be proven that the average time complexity for each operation is `O(log(n))` and space complexity is `O(n)`.
*
* See more about Skiplist: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip\_list](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list)
*
* Implement the `Skiplist` class:
*
* * `Skiplist()` Initializes the object of the skiplist.
* * `bool search(int target)` Returns `true` if the integer `target` exists in the Skiplist or `false` otherwise.
* * `void add(int num)` Inserts the value `num` into the SkipList.
* * `bool erase(int num)` Removes the value `num` from the Skiplist and returns `true`. If `num` does not exist in the Skiplist, do nothing and return `false`. If there exist multiple `num` values, removing any one of them is fine.
*
* Note that duplicates may exist in the Skiplist, your code needs to handle this situation.
*
* **Example 1:**
*
* **Input**
*
* ["Skiplist", "add", "add", "add", "search", "add", "search", "erase", "erase", "search"]
*
* [ [], [1], [2], [3], [0], [4], [1], [0], [1], [1]]
*
* **Output:** [null, null, null, null, false, null, true, false, true, false]
*
* **Explanation:**
*
* Skiplist skiplist = new Skiplist();
* skiplist.add(1);
* skiplist.add(2);
* skiplist.add(3);
* skiplist.search(0); // return False
* skiplist.add(4);
* skiplist.search(1); // return True
* skiplist.erase(0); // return False, 0 is not in skiplist.
* skiplist.erase(1); // return True
* skiplist.search(1); // return False, 1 has already been erased.
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * 0 <= num, target <= 2 * 104
* * At most 5 * 104 calls will be made to `search`, `add`, and `erase`.
**/
@SuppressWarnings("java:S2245")
public class Skiplist {
private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 8;
private final int minBoundary;
private final Node head;
private int headCapacity;
private int headLevel = 0;
private static class Node {
private final int val;
private Node[] next;
private Node(int val, int level) {
this.val = val;
next = new Node[level];
}
}
public Skiplist() {
this(INIT_CAPACITY);
}
public Skiplist(int size) {
if (size == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("size should be greater than 0");
}
if (size < INIT_CAPACITY) {
size = INIT_CAPACITY;
}
minBoundary = size / 2;
headCapacity = size;
head = new Node(0, size);
}
public boolean search(int target) {
Node curr = head;
for (int i = headLevel - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (curr.next[i] != null) {
int cmp = target - curr.next[i].val;
if (cmp < 0) {
break;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
curr = curr.next[i];
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public void add(int num) {
Node[] update = new Node[headLevel + 1];
update[headLevel] = head;
buildUpdate(num, update);
int level = getRandomLevel();
if (level > headLevel) {
if (headLevel == headCapacity) {
resizeHead(2 * headCapacity);
}
headLevel++;
}
Node x = new Node(num, level);
for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
Node n = update[i].next[i];
update[i].next[i] = x;
x.next[i] = n;
}
}
public boolean erase(int num) {
if (headLevel == 0) {
return false;
}
Node[] update = new Node[headLevel];
buildUpdate(num, update);
if (update[0].next[0] == null || update[0].next[0].val != num) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < headLevel; i++) {
if (update[i].next[i] == null || update[i].next[i].val != num) {
break;
}
update[i].next[i] = update[i].next[i].next[i];
}
if (head.next[headLevel - 1] == null
&& --headLevel >= minBoundary
&& headLevel == headCapacity / 4) {
resizeHead(headCapacity / 2);
}
return true;
}
private void buildUpdate(int x, Node[] update) {
Node curr = head;
for (int i = headLevel - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (curr.next[i] != null && curr.next[i].val < x) {
curr = curr.next[i];
}
update[i] = curr;
}
}
private int getRandomLevel() {
int maxLevel = 14;
int level = 1;
int limit = Math.min(maxLevel, headLevel + 1);
double p = 0.5;
while (Math.random() < p && level < limit) {
level++;
}
return level;
}
private void resizeHead(int size) {
Node[] copy = new Node[size];
System.arraycopy(head.next, 0, copy, 0, headLevel);
head.next = copy;
headCapacity = size;
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy