
g1501_1600.s1514_path_with_maximum_probability.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g1501_1600.s1514_path_with_maximum_probability;
// #Medium #Heap_Priority_Queue #Graph #Shortest_Path
// #2022_04_09_Time_31_ms_(93.10%)_Space_51.7_MB_(98.80%)
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* 1514 - Path with Maximum Probability\.
*
* Medium
*
* You are given an undirected weighted graph of `n` nodes (0-indexed), represented by an edge list where `edges[i] = [a, b]` is an undirected edge connecting the nodes `a` and `b` with a probability of success of traversing that edge `succProb[i]`.
*
* Given two nodes `start` and `end`, find the path with the maximum probability of success to go from `start` to `end` and return its success probability.
*
* If there is no path from `start` to `end`, **return 0**. Your answer will be accepted if it differs from the correct answer by at most **1e-5**.
*
* **Example 1:**
*
* **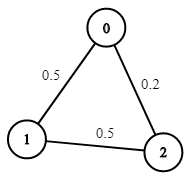**
*
* **Input:** n = 3, edges = \[\[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.2], start = 0, end = 2
*
* **Output:** 0.25000
*
* **Explanation:** There are two paths from start to end, one having a probability of success = 0.2 and the other has 0.5 \* 0.5 = 0.25.
*
* **Example 2:**
*
* **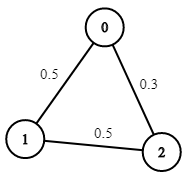**
*
* **Input:** n = 3, edges = \[\[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.3], start = 0, end = 2
*
* **Output:** 0.30000
*
* **Example 3:**
*
* **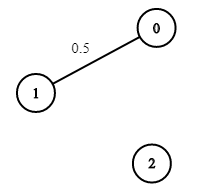**
*
* **Input:** n = 3, edges = \[\[0,1]], succProb = [0.5], start = 0, end = 2
*
* **Output:** 0.00000
*
* **Explanation:** There is no path between 0 and 2.
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * `2 <= n <= 10^4`
* * `0 <= start, end < n`
* * `start != end`
* * `0 <= a, b < n`
* * `a != b`
* * `0 <= succProb.length == edges.length <= 2*10^4`
* * `0 <= succProb[i] <= 1`
* * There is at most one edge between every two nodes.
**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public class Solution {
public double maxProbability(int n, int[][] edges, double[] succProb, int start, int end) {
List[] nodeToNodesList = new List[n];
List[] nodeToProbabilitiesList = new List[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nodeToNodesList[i] = new ArrayList<>();
nodeToProbabilitiesList[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
int u = edges[i][0];
int v = edges[i][1];
double w = succProb[i];
nodeToNodesList[u].add(v);
nodeToProbabilitiesList[u].add(w);
nodeToNodesList[v].add(u);
nodeToProbabilitiesList[v].add(w);
}
double[] probabilities = new double[n];
probabilities[start] = 1.0;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
Queue queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(start);
visited[start] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int u = queue.poll();
visited[u] = false;
for (int i = 0; i < nodeToNodesList[u].size(); i++) {
int v = nodeToNodesList[u].get(i);
double w = nodeToProbabilitiesList[u].get(i);
if (probabilities[u] * w > probabilities[v]) {
probabilities[v] = probabilities[u] * w;
if (!visited[v]) {
visited[v] = true;
queue.add(v);
}
}
}
}
return probabilities[end];
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy