
g1701_1800.s1766_tree_of_coprimes.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g1701_1800.s1766_tree_of_coprimes;
// #Hard #Math #Depth_First_Search #Breadth_First_Search #Tree
// #2022_04_30_Time_111_ms_(94.07%)_Space_155.4_MB_(40.68%)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 1766 - Tree of Coprimes\.
*
* Hard
*
* There is a tree (i.e., a connected, undirected graph that has no cycles) consisting of `n` nodes numbered from `0` to `n - 1` and exactly `n - 1` edges. Each node has a value associated with it, and the **root** of the tree is node `0`.
*
* To represent this tree, you are given an integer array `nums` and a 2D array `edges`. Each `nums[i]` represents the ith node's value, and each edges[j] = [uj, vj] represents an edge between nodes uj and vj in the tree.
*
* Two values `x` and `y` are **coprime** if `gcd(x, y) == 1` where `gcd(x, y)` is the **greatest common divisor** of `x` and `y`.
*
* An ancestor of a node `i` is any other node on the shortest path from node `i` to the **root**. A node is **not** considered an ancestor of itself.
*
* Return _an array_ `ans` _of size_ `n`, _where_ `ans[i]` _is the closest ancestor to node_ `i` _such that_ `nums[i]` _and_ `nums[ans[i]]` are **coprime** , or `-1` _if there is no such ancestor_.
*
* **Example 1:**
*
* **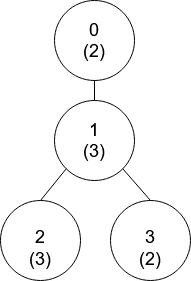**
*
* **Input:** nums = [2,3,3,2], edges = \[\[0,1],[1,2],[1,3]]
*
* **Output:** [-1,0,0,1]
*
* **Explanation:** In the above figure, each node's value is in parentheses.
*
* - Node 0 has no coprime ancestors.
*
* - Node 1 has only one ancestor, node 0. Their values are coprime (gcd(2,3) == 1). - Node 2 has two ancestors, nodes 1 and 0. Node 1's value is not coprime (gcd(3,3) == 3), but node 0's value is (gcd(2,3) == 1), so node 0 is the closest valid ancestor.
*
* - Node 3 has two ancestors, nodes 1 and 0. It is coprime with node 1 (gcd(3,2) == 1), so node 1 is its closest valid ancestor.
*
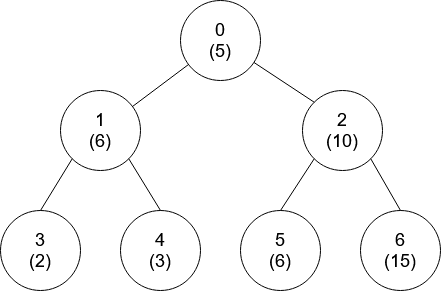
* **Example 2:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** nums = [5,6,10,2,3,6,15], edges = \[\[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]]
*
* **Output:** [-1,0,-1,0,0,0,-1]
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * `nums.length == n`
* * `1 <= nums[i] <= 50`
* * 1 <= n <= 105
* * `edges.length == n - 1`
* * `edges[j].length == 2`
* * 0 <= uj, vj < n
* * uj != vj
**/
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "java:S107"})
public class Solution {
private void dfs(
int[] v2n,
int[] v2d,
int depth,
int parent,
int node,
int[] ans,
int[] nums,
ArrayList[] neighbors) {
int d = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int n = -1;
int v = nums[node];
for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++) {
if (v2n[i] != -1 && v2d[i] > d && gcd(i, v) == 1) {
d = v2d[i];
n = v2n[i];
}
}
ans[node] = n;
int v2NOld = v2n[v];
int v2DOld = v2d[v];
v2n[v] = node;
v2d[v] = depth;
for (int child : neighbors[node]) {
if (child == parent) {
continue;
}
dfs(v2n, v2d, depth + 1, node, child, ans, nums, neighbors);
}
v2n[v] = v2NOld;
v2d[v] = v2DOld;
}
private int gcd(int x, int y) {
return x == 0 ? y : gcd(y % x, x);
}
public int[] getCoprimes(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {
int n = nums.length;
ArrayList[] neighbors = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
neighbors[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
neighbors[edge[0]].add(edge[1]);
neighbors[edge[1]].add(edge[0]);
}
int[] ans = new int[n];
int[] v2n = new int[51];
int[] v2d = new int[51];
Arrays.fill(v2n, -1);
dfs(v2n, v2d, 0, -1, 0, ans, nums, neighbors);
return ans;
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy