
g1701_1800.s1782_count_pairs_of_nodes.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g1701_1800.s1782_count_pairs_of_nodes;
// #Hard #Binary_Search #Two_Pointers #Graph
// #2022_04_30_Time_128_ms_(86.96%)_Space_175.4_MB_(39.13%)
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 1782 - Count Pairs Of Nodes\.
*
* Hard
*
* You are given an undirected graph defined by an integer `n`, the number of nodes, and a 2D integer array `edges`, the edges in the graph, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an **undirected** edge between ui and vi. You are also given an integer array `queries`.
*
* Let `incident(a, b)` be defined as the **number of edges** that are connected to **either** node `a` or `b`.
*
* The answer to the jth query is the **number of pairs** of nodes `(a, b)` that satisfy **both** of the following conditions:
*
* * `a < b`
* * `incident(a, b) > queries[j]`
*
* Return _an array_ `answers` _such that_ `answers.length == queries.length` _and_ `answers[j]` _is the answer of the_ jth _query_.
*
* Note that there can be **multiple edges** between the same two nodes.
*
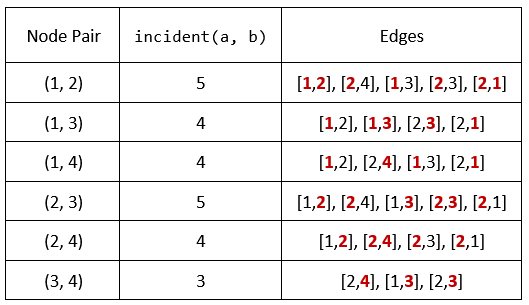
* **Example 1:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** n = 4, edges = \[\[1,2],[2,4],[1,3],[2,3],[2,1]], queries = [2,3]
*
* **Output:** [6,5]
*
* **Explanation:** The calculations for incident(a, b) are shown in the table above. The answers for each of the queries are as follows:
*
* - answers[0] = 6. All the pairs have an incident(a, b) value greater than 2.
*
* - answers[1] = 5. All the pairs except (3, 4) have an incident(a, b) value greater than 3.
*
* **Example 2:**
*
* **Input:** n = 5, edges = \[\[1,5],[1,5],[3,4],[2,5],[1,3],[5,1],[2,3],[2,5]], queries = [1,2,3,4,5]
*
* **Output:** [10,10,9,8,6]
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * 2 <= n <= 2 * 104
* * 1 <= edges.length <= 105
* * 1 <= ui, vi <= n
* * ui != vi
* * `1 <= queries.length <= 20`
* * `0 <= queries[j] < edges.length`
**/
public class Solution {
public int[] countPairs(int n, int[][] edges, int[] queries) {
Map edgeCount = new HashMap<>();
int[] degree = new int[n];
for (int[] e : edges) {
int u = e[0] - 1;
int v = e[1] - 1;
degree[u]++;
degree[v]++;
int eId = Math.min(u, v) * n + Math.max(u, v);
edgeCount.put(eId, edgeCount.getOrDefault(eId, 0) + 1);
}
Map degreeCount = new HashMap<>();
int maxDegree = 0;
for (int d : degree) {
degreeCount.put(d, degreeCount.getOrDefault(d, 0) + 1);
maxDegree = Math.max(maxDegree, d);
}
int[] count = new int[2 * maxDegree + 1];
for (Map.Entry d1 : degreeCount.entrySet()) {
for (Map.Entry d2 : degreeCount.entrySet()) {
count[d1.getKey() + d2.getKey()] +=
(d1 == d2)
? d1.getValue() * (d1.getValue() - 1)
: d1.getValue() * d2.getValue();
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < count.length; i++) {
count[i] /= 2;
}
for (Map.Entry e : edgeCount.entrySet()) {
int u = e.getKey() / n;
int v = e.getKey() % n;
count[degree[u] + degree[v]]--;
count[degree[u] + degree[v] - e.getValue()]++;
}
for (int i = count.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
count[i] += count[i + 1];
}
int[] res = new int[queries.length];
for (int q = 0; q < queries.length; q++) {
res[q] = ((queries[q] + 1) >= count.length) ? 0 : count[queries[q] + 1];
}
return res;
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy