
g2001_2100.s2090_k_radius_subarray_averages.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g2001_2100.s2090_k_radius_subarray_averages;
// #Medium #Array #Sliding_Window #2022_05_23_Time_12_ms_(83.19%)_Space_166.5_MB_(16.59%)
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 2090 - K Radius Subarray Averages\.
*
* Medium
*
* You are given a **0-indexed** array `nums` of `n` integers, and an integer `k`.
*
* The **k-radius average** for a subarray of `nums` **centered** at some index `i` with the **radius** `k` is the average of **all** elements in `nums` between the indices `i - k` and `i + k` ( **inclusive** ). If there are less than `k` elements before **or** after the index `i`, then the **k-radius average** is `-1`.
*
* Build and return _an array_ `avgs` _of length_ `n` _where_ `avgs[i]` _is the **k-radius average** for the subarray centered at index_ `i`.
*
* The **average** of `x` elements is the sum of the `x` elements divided by `x`, using **integer division**. The integer division truncates toward zero, which means losing its fractional part.
*
* * For example, the average of four elements `2`, `3`, `1`, and `5` is `(2 + 3 + 1 + 5) / 4 = 11 / 4 = 2.75`, which truncates to `2`.
*
* **Example 1:**
*
* 
*
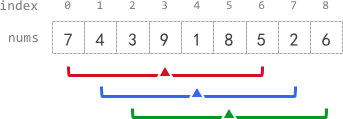
* **Input:** nums = [7,4,3,9,1,8,5,2,6], k = 3
*
* **Output:** [-1,-1,-1,5,4,4,-1,-1,-1]
*
* **Explanation:**
*
* - avg[0], avg[1], and avg[2] are -1 because there are less than k elements **before** each index.
*
* - The sum of the subarray centered at index 3 with radius 3 is: 7 + 4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 = 37.
*
* Using **integer division** , avg[3] = 37 / 7 = 5.
*
* - For the subarray centered at index 4, avg[4] = (4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2) / 7 = 4.
*
* - For the subarray centered at index 5, avg[5] = (3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2 + 6) / 7 = 4.
*
* - avg[6], avg[7], and avg[8] are -1 because there are less than k elements **after** each index.
*
* **Example 2:**
*
* **Input:** nums = [100000], k = 0
*
* **Output:** [100000]
*
* **Explanation:**
*
* - The sum of the subarray centered at index 0 with radius 0 is: 100000.
*
* avg[0] = 100000 / 1 = 100000.
*
* **Example 3:**
*
* **Input:** nums = [8], k = 100000
*
* **Output:** [-1]
*
* **Explanation:**
*
* - avg[0] is -1 because there are less than k elements before and after index 0.
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * `n == nums.length`
* * 1 <= n <= 105
* * 0 <= nums[i], k <= 105
**/
public class Solution {
public int[] getAverages(int[] nums, int k) {
// initialize result array with -1
int[] res = new int[nums.length];
Arrays.fill(res, -1);
if (nums.length <= (k * 2)) {
// return if not enough elements
return res;
}
long sum = 0;
long range = 2 * k + 1L;
// take sum of all elements from 0 to k*2 index
for (int i = 0; i <= 2 * k; ++i) {
sum += nums[i];
}
// update first valid avg
res[k] = (int) (sum / range);
// update other valid averages using sliding window
for (int i = k + 1; i < nums.length - k; ++i) {
sum = sum - nums[i - k - 1] + nums[i + k];
res[i] = (int) (sum / range);
}
return res;
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy