
g2401_2500.s2440_create_components_with_same_value.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g2401_2500.s2440_create_components_with_same_value;
// #Hard #Array #Math #Depth_First_Search #Tree #Enumeration
// #2022_12_13_Time_114_ms_(73.23%)_Space_115.7_MB_(68.01%)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 2440 - Create Components With Same Value\.
*
* Hard
*
* There is an undirected tree with `n` nodes labeled from `0` to `n - 1`.
*
* You are given a **0-indexed** integer array `nums` of length `n` where `nums[i]` represents the value of the ith node. You are also given a 2D integer array `edges` of length `n - 1` where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
*
* You are allowed to **delete** some edges, splitting the tree into multiple connected components. Let the **value** of a component be the sum of **all** `nums[i]` for which node `i` is in the component.
*
* Return _the **maximum** number of edges you can delete, such that every connected component in the tree has the same value._
*
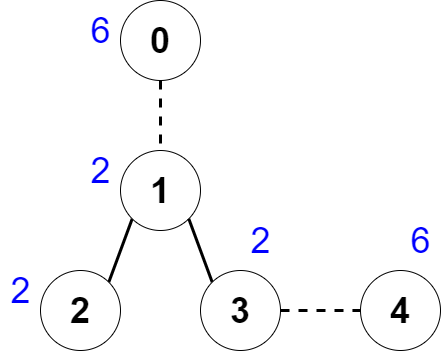
* **Example 1:**
*
* 
*
* **Input:** nums = [6,2,2,2,6], edges = \[\[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[3,4]]
*
* **Output:** 2
*
* **Explanation:** The above figure shows how we can delete the edges [0,1] and [3,4]. The created components are nodes [0], [1,2,3] and [4]. The sum of the values in each component equals 6. It can be proven that no better deletion exists, so the answer is 2.
*
* **Example 2:**
*
* **Input:** nums = [2], edges = []
*
* **Output:** 0
*
* **Explanation:** There are no edges to be deleted.
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * 1 <= n <= 2 * 104
* * `nums.length == n`
* * `1 <= nums[i] <= 50`
* * `edges.length == n - 1`
* * `edges[i].length == 2`
* * `0 <= edges[i][0], edges[i][1] <= n - 1`
* * `edges` represents a valid tree.
**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public class Solution {
private int[] nums;
public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {
int n = nums.length;
this.nums = nums;
List[] graph = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] e : edges) {
graph[e[0]].add(e[1]);
graph[e[1]].add(e[0]);
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i : nums) {
sum += i;
}
for (int k = n; k > 0; k--) {
if (sum % k != 0) {
continue;
}
int ans = helper(graph, 0, -1, sum / k);
if (ans == 0) {
return k - 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
private int helper(List[] graph, int i, int prev, int target) {
if (graph[i].size() == 1 && graph[i].get(0) == prev) {
if (nums[i] > target) {
return -1;
}
if (nums[i] == target) {
return 0;
}
return nums[i];
}
int sum = nums[i];
for (int k : graph[i]) {
if (k == prev) {
continue;
}
int ans = helper(graph, k, i, target);
if (ans == -1) {
return -1;
}
sum += ans;
}
if (sum > target) {
return -1;
}
if (sum == target) {
return 0;
}
return sum;
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy