
g2601_2700.s2699_modify_graph_edge_weights.Solution Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
package g2601_2700.s2699_modify_graph_edge_weights;
// #Hard #Heap_Priority_Queue #Graph #Shortest_Path
// #2023_09_14_Time_88_ms_(85.25%)_Space_49.9_MB_(85.25%)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
/**
* 2699 - Modify Graph Edge Weights\.
*
* Hard
*
* You are given an **undirected weighted** **connected** graph containing `n` nodes labeled from `0` to `n - 1`, and an integer array `edges` where edges[i] = [ai, bi, wi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi with weight wi.
*
* Some edges have a weight of `-1` (wi = -1), while others have a **positive** weight (wi > 0).
*
* Your task is to modify **all edges** with a weight of `-1` by assigning them **positive integer values** in the range [1, 2 * 109] so that the **shortest distance** between the nodes `source` and `destination` becomes equal to an integer `target`. If there are **multiple** **modifications** that make the shortest distance between `source` and `destination` equal to `target`, any of them will be considered correct.
*
* Return _an array containing all edges (even unmodified ones) in any order if it is possible to make the shortest distance from_ `source` _to_ `destination` _equal to_ `target`_, or an **empty array** if it's impossible._
*
* **Note:** You are not allowed to modify the weights of edges with initial positive weights.
*
* **Example 1:**
*
* **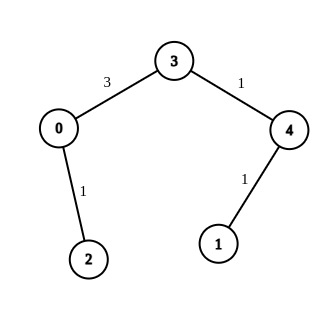**
*
* **Input:** n = 5, edges = \[\[4,1,-1],[2,0,-1],[0,3,-1],[4,3,-1]], source = 0, destination = 1, target = 5
*
* **Output:** [[4,1,1],[2,0,1],[0,3,3],[4,3,1]]
*
* **Explanation:** The graph above shows a possible modification to the edges, making the distance from 0 to 1 equal to 5.
*
* **Example 2:**
*
* **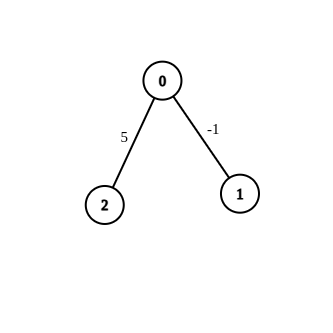**
*
* **Input:** n = 3, edges = \[\[0,1,-1],[0,2,5]], source = 0, destination = 2, target = 6
*
* **Output:** []
*
* **Explanation:** The graph above contains the initial edges. It is not possible to make the distance from 0 to 2 equal to 6 by modifying the edge with weight -1. So, an empty array is returned.
*
* **Example 3:**
*
* **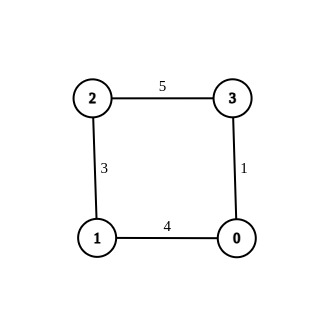**
*
* **Input:** n = 4, edges = \[\[1,0,4],[1,2,3],[2,3,5],[0,3,-1]], source = 0, destination = 2, target = 6
*
* **Output:** [[1,0,4],[1,2,3],[2,3,5],[0,3,1]]
*
* **Explanation:** The graph above shows a modified graph having the shortest distance from 0 to 2 as 6.
*
* **Constraints:**
*
* * `1 <= n <= 100`
* * `1 <= edges.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2`
* * `edges[i].length == 3`
* * 0 <= ai, bi < n
* * wi = -1 or 1 <= wi <= 107
* * ai != bi
* * `0 <= source, destination < n`
* * `source != destination`
* * 1 <= target <= 109
* * The graph is connected, and there are no self-loops or repeated edges
**/
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "java:S135"})
public class Solution {
public int[][] modifiedGraphEdges(
int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination, int target) {
List[] graph = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
int[] e = edges[i];
graph[e[0]].add(new int[] {e[1], i});
graph[e[1]].add(new int[] {e[0], i});
}
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(v -> v[1]));
pq.add(new int[] {destination, 0});
Integer[] distances = new Integer[n];
processQueue(edges, source, pq, distances, graph);
if (distances[source] > target) {
return new int[][] {};
}
pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(v -> v[1]));
if (distances[source] != target) {
pq.add(new int[] {source, 0});
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int[] c = pq.poll();
if (visited[c[0]]) {
continue;
}
visited[c[0]] = true;
if (c[0] == destination) {
return new int[][] {};
}
for (int[] e : graph[c[0]]) {
if (visited[e[0]] || distances[e[0]] == null) {
continue;
}
int dif = target - c[1] - distances[e[0]];
if (Math.abs(edges[e[1]][2]) >= dif) {
continue;
}
if (edges[e[1]][2] == -1) {
edges[e[1]][2] = dif;
continue;
}
pq.add(new int[] {e[0], c[1] + edges[e[1]][2]});
}
}
for (int[] e : edges) {
if (e[2] == -1) {
e[2] = 1;
}
}
return edges;
}
private void processQueue(
int[][] edges,
int source,
PriorityQueue pq,
Integer[] distances,
List[] graph) {
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int[] c = pq.poll();
if (distances[c[0]] != null) {
continue;
}
distances[c[0]] = c[1];
if (c[0] == source) {
continue;
}
for (int[] e : graph[c[0]]) {
if (distances[e[0]] != null) {
continue;
}
pq.add(new int[] {e[0], c[1] + Math.abs(edges[e[1]][2])});
}
}
}
}
© 2015 - 2025 Weber Informatics LLC | Privacy Policy