g1901_2000.s1948_delete_duplicate_folders_in_system.readme.md Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
1948\. Delete Duplicate Folders in System
Hard
Due to a bug, there are many duplicate folders in a file system. You are given a 2D array `paths`, where `paths[i]` is an array representing an absolute path to the ith folder in the file system.
* For example, `["one", "two", "three"]` represents the path `"/one/two/three"`.
Two folders (not necessarily on the same level) are **identical** if they contain the **same non-empty** set of identical subfolders and underlying subfolder structure. The folders **do not** need to be at the root level to be identical. If two or more folders are **identical**, then **mark** the folders as well as all their subfolders.
* For example, folders `"/a"` and `"/b"` in the file structure below are identical. They (as well as their subfolders) should **all** be marked:
* `/a`
* `/a/x`
* `/a/x/y`
* `/a/z`
* `/b`
* `/b/x`
* `/b/x/y`
* `/b/z`
* However, if the file structure also included the path `"/b/w"`, then the folders `"/a"` and `"/b"` would not be identical. Note that `"/a/x"` and `"/b/x"` would still be considered identical even with the added folder.
Once all the identical folders and their subfolders have been marked, the file system will **delete** all of them. The file system only runs the deletion once, so any folders that become identical after the initial deletion are not deleted.
Return _the 2D array_ `ans` _containing the paths of the **remaining** folders after deleting all the marked folders. The paths may be returned in **any** order_.
**Example 1:**
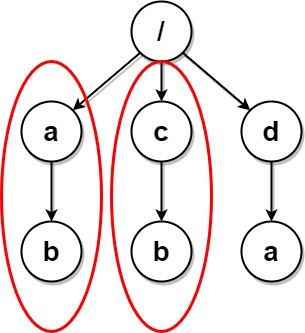
**Input:** paths = [["a"],["c"],["d"],["a","b"],["c","b"],["d","a"]]
**Output:** [["d"],["d","a"]]
**Explanation:** The file structure is as shown. Folders "/a" and "/c" (and their subfolders) are marked for deletion because they both contain an empty folder named "b".
**Example 2:**
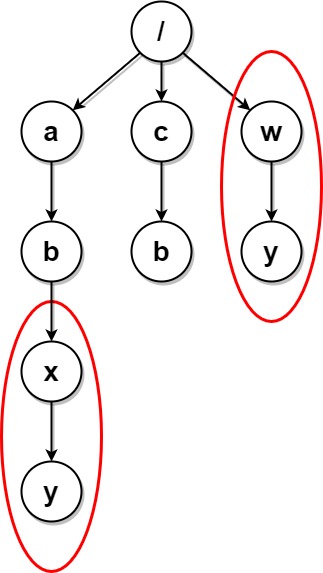
**Input:** paths = [["a"],["c"],["a","b"],["c","b"],["a","b","x"],["a","b","x","y"],["w"],["w","y"]]
**Output:** [["c"],["c","b"],["a"],["a","b"]]
**Explanation:** The file structure is as shown. Folders "/a/b/x" and "/w" (and their subfolders) are marked for deletion because they both contain an empty folder named "y". Note that folders "/a" and "/c" are identical after the deletion, but they are not deleted because they were not marked beforehand.
**Example 3:**
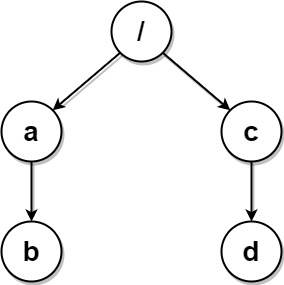
**Input:** paths = [["a","b"],["c","d"],["c"],["a"]]
**Output:** [["c"],["c","d"],["a"],["a","b"]]
**Explanation:** All folders are unique in the file system. Note that the returned array can be in a different order as the order does not matter.
**Constraints:**
* 1 <= paths.length <= 2 * 104
* `1 <= paths[i].length <= 500`
* `1 <= paths[i][j].length <= 10`
* 1 <= sum(paths[i][j].length) <= 2 * 105
* `path[i][j]` consists of lowercase English letters.
* No two paths lead to the same folder.
* For any folder not at the root level, its parent folder will also be in the input.