g0001_0100.s0084_largest_rectangle_in_histogram.readme.md Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-java21 Show documentation
Java-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
84\. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Hard
Given an array of integers `heights` representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is `1`, return _the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram_.
**Example 1:**
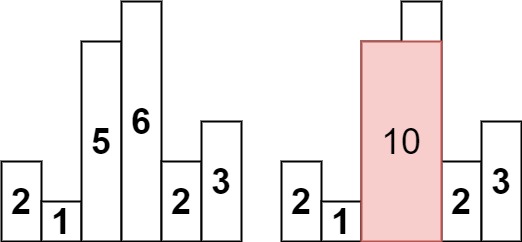
**Input:** heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3]
**Output:** 10
**Explanation:** The above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1. The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area = 10 units.
**Example 2:**
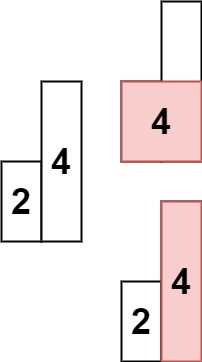
**Input:** heights = [2,4]
**Output:** 4
**Constraints:**
* 1 <= heights.length <= 105
* 0 <= heights[i] <= 104
To solve the "Largest Rectangle in Histogram" problem in Java with the Solution class, follow these steps:
1. Define a method `largestRectangleArea` in the `Solution` class that takes an array of integers `heights` as input and returns the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram.
2. Implement a stack-based algorithm to find the largest rectangle:
- Initialize a stack to store indices of bars in the histogram.
- Iterate through each bar in the histogram:
- If the stack is empty or the current bar's height is greater than or equal to the height of the bar at the top of the stack, push the current bar's index onto the stack.
- If the current bar's height is less than the height of the bar at the top of the stack, keep popping bars from the stack until either the stack is empty or the height of the bar at the top of the stack is less than the height of the current bar.
- Calculate the area of the rectangle formed by the popped bar using its height and width (the difference between the current index and the index of the previous bar in the stack or -1 if the stack is empty).
- Update the maximum area if the calculated area is greater.
- After iterating through all bars, pop the remaining bars from the stack and calculate the area of rectangles formed by them using the same method as above.
3. Return the maximum area calculated.
Here's the implementation of the `largestRectangleArea` method in Java:
```java
import java.util.Stack;
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
int maxArea = 0;
int i = 0;
while (i < heights.length) {
if (stack.isEmpty() || heights[i] >= heights[stack.peek()]) {
stack.push(i++);
} else {
int top = stack.pop();
int width = stack.isEmpty() ? i : i - stack.peek() - 1;
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, heights[top] * width);
}
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int top = stack.pop();
int width = stack.isEmpty() ? i : i - stack.peek() - 1;
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, heights[top] * width);
}
return maxArea;
}
}
```
This implementation uses a stack-based approach to find the largest rectangle in the histogram, with a time complexity of O(N), where N is the number of bars in the histogram. 