g0801_0900.s0883_projection_area_of_3d_shapes.readme.md Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Go to download
Show more of this group Show more artifacts with this name
Show all versions of leetcode-in-kotlin Show documentation
Show all versions of leetcode-in-kotlin Show documentation
Kotlin-based LeetCode algorithm problem solutions, regularly updated
883\. Projection Area of 3D Shapes
Easy
You are given an `n x n` `grid` where we place some `1 x 1 x 1` cubes that are axis-aligned with the `x`, `y`, and `z` axes.
Each value `v = grid[i][j]` represents a tower of `v` cubes placed on top of the cell `(i, j)`.
We view the projection of these cubes onto the `xy`, `yz`, and `zx` planes.
A **projection** is like a shadow, that maps our **3-dimensional** figure to a **2-dimensional** plane. We are viewing the "shadow" when looking at the cubes from the top, the front, and the side.
Return _the total area of all three projections_.
**Example 1:**
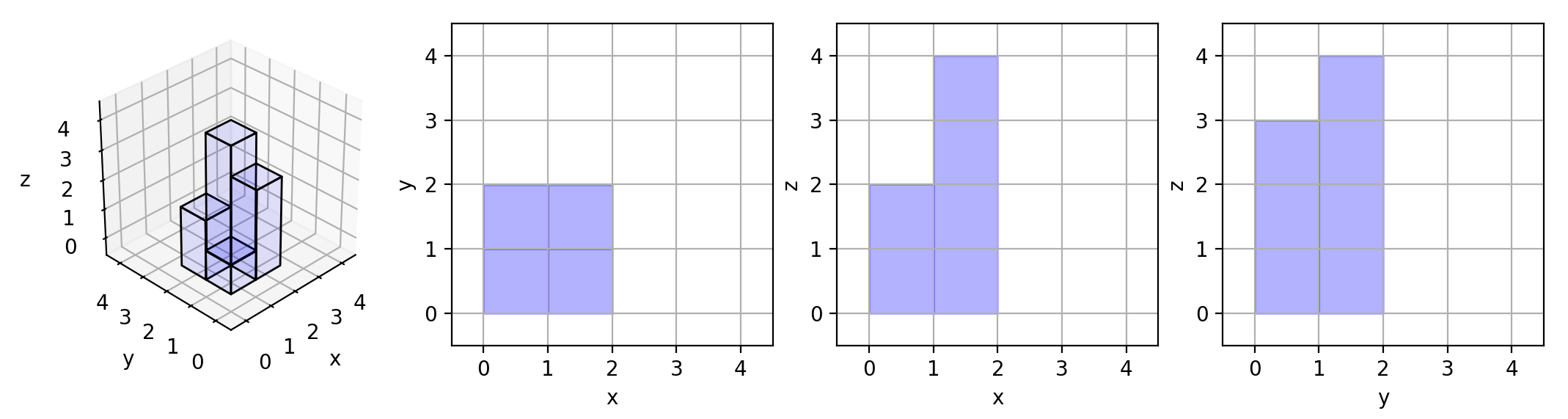
**Input:** grid = [[1,2],[3,4]]
**Output:** 17
**Explanation:** Here are the three projections ("shadows") of the shape made with each axis-aligned plane.
**Example 2:**
**Input:** grid = [[2]]
**Output:** 5
**Example 3:**
**Input:** grid = [[1,0],[0,2]]
**Output:** 8
**Constraints:**
* `n == grid.length == grid[i].length`
* `1 <= n <= 50`
* `0 <= grid[i][j] <= 50`