
rx.subjects.ReplaySubject Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Show all versions of rxjava-core Show documentation
/**
* Copyright 2014 Netflix, Inc.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package rx.subjects;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater;
import rx.Observer;
import rx.Scheduler;
import rx.functions.Action1;
import rx.functions.Func1;
import rx.functions.Functions;
import rx.internal.operators.NotificationLite;
import rx.schedulers.Timestamped;
import rx.subjects.ReplaySubject.NodeList.Node;
import rx.subjects.SubjectSubscriptionManager.SubjectObserver;
/**
* Subject that buffers all items it observes and replays them to any {@link Observer} that subscribes.
*
* 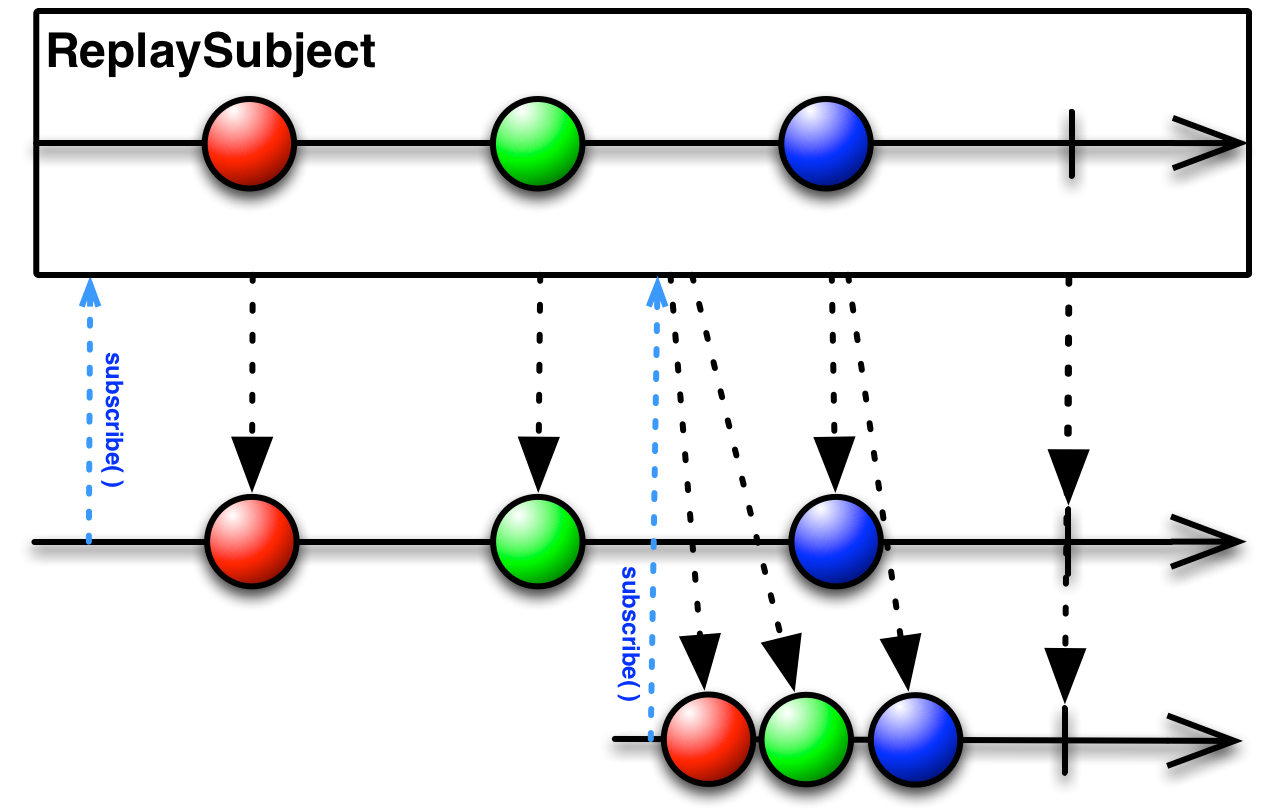 *
*
* Example usage:
*
*
{@code
ReplaySubject
*
* @param
* the type of items observed and emitted by the Subject
*/
public final class ReplaySubject extends Subject {
/**
* Creates an unbounded replay subject.
*
* The internal buffer is backed by an {@link ArrayList} and starts with an initial capacity of 16. Once the
* number of items reaches this capacity, it will grow as necessary (usually by 50%). However, as the
* number of items grows, this causes frequent array reallocation and copying, and may hurt performance
* and latency. This can be avoided with the {@link #create(int)} overload which takes an initial capacity
* parameter and can be tuned to reduce the array reallocation frequency as needed.
*
* @param
* the type of items observed and emitted by the Subject
* @return the created subject
*/
public static ReplaySubject create() {
return create(16);
}
/**
* Creates an unbounded replay subject with the specified initial buffer capacity.
*
* Use this method to avoid excessive array reallocation while the internal buffer grows to accomodate new
* items. For example, if you know that the buffer will hold 32k items, you can ask the
* {@code ReplaySubject} to preallocate its internal array with a capacity to hold that many items. Once
* the items start to arrive, the internal array won't need to grow, creating less garbage and no overhead
* due to frequent array-copying.
*
* @param
* the type of items observed and emitted by the Subject
* @param capacity
* the initial buffer capacity
* @return the created subject
*/
public static ReplaySubject create(int capacity) {
final UnboundedReplayState state = new UnboundedReplayState(capacity);
SubjectSubscriptionManager ssm = new SubjectSubscriptionManager();
ssm.onStart = new Action1>() {
@Override
public void call(SubjectObserver o) {
// replay history for this observer using the subscribing thread
int lastIndex = state.replayObserverFromIndex(0, o);
// now that it is caught up add to observers
o.index(lastIndex);
}
};
ssm.onTerminated = new Action1>() {
@Override
public void call(SubjectObserver o) {
Integer idx = o.index();
if (idx == null) {
idx = 0;
}
// we will finish replaying if there is anything left
state.replayObserverFromIndex(idx, o);
}
};
return new ReplaySubject(ssm, ssm, state);
}
/**
* Creates an unbounded replay subject with the bounded-implementation for testing purposes.
*
* This variant behaves like the regular unbounded {@code ReplaySubject} created via {@link #create()} but
* uses the structures of the bounded-implementation. This is by no means intended for the replacement of
* the original, array-backed and unbounded {@code ReplaySubject} due to the additional overhead of the
* linked-list based internal buffer. The sole purpose is to allow testing and reasoning about the behavior
* of the bounded implementations without the interference of the eviction policies.
*
* @param
* the type of items observed and emitted by the Subject
* @return the created subject
*/
/* public */ static ReplaySubject createUnbounded() {
final BoundedState state = new BoundedState(
new EmptyEvictionPolicy(),
Functions.identity(),
Functions.identity()
);
return createWithState(state, new DefaultOnAdd(state));
}
/**
* Creates a size-bounded replay subject.
*
* In this setting, the {@code ReplaySubject} holds at most {@code size} items in its internal buffer and
* discards the oldest item.
*
* When observers subscribe to a terminated {@code ReplaySubject}, they are guaranteed to see at most
* {@code size} {@code onNext} events followed by a termination event.
*
* If an observer subscribes while the {@code ReplaySubject} is active, it will observe all items in the
* buffer at that point in time and each item observed afterwards, even if the buffer evicts items due to
* the size constraint in the mean time. In other words, once an Observer subscribes, it will receive items
* without gaps in the sequence.
*
* @param
* the type of items observed and emitted by the Subject
* @param size
* the maximum number of buffered items
* @return the created subject
*/
public static ReplaySubject createWithSize(int size) {
final BoundedState state = new BoundedState(
new SizeEvictionPolicy(size),
Functions.identity(),
Functions.identity()
);
return createWithState(state, new DefaultOnAdd(state));
}
/**
* Creates a time-bounded replay subject.
*
* In this setting, the {@code ReplaySubject} internally tags each observed item with a timestamp value
* supplied by the {@link Scheduler} and keeps only those whose age is less than the supplied time value
* converted to milliseconds. For example, an item arrives at T=0 and the max age is set to 5; at T>=5
* this first item is then evicted by any subsequent item or termination event, leaving the buffer empty.
*
* Once the subject is terminated, observers subscribing to it will receive items that remained in the
* buffer after the terminal event, regardless of their age.
*
* If an observer subscribes while the {@code ReplaySubject} is active, it will observe only those items
* from within the buffer that have an age less than the specified time, and each item observed thereafter,
* even if the buffer evicts items due to the time constraint in the mean time. In other words, once an
* observer subscribes, it observes items without gaps in the sequence except for any outdated items at the
* beginning of the sequence.
*
* Note that terminal notifications ({@code onError} and {@code onCompleted}) trigger eviction as well. For
* example, with a max age of 5, the first item is observed at T=0, then an {@code onCompleted} notification
* arrives at T=10. If an observer subscribes at T=11, it will find an empty {@code ReplaySubject} with just
* an {@code onCompleted} notification.
*
* @param
* the type of items observed and emitted by the Subject
* @param time
* the maximum age of the contained items
* @param unit
* the time unit of {@code time}
* @param scheduler
* the {@link Scheduler} that provides the current time
* @return the created subject
*/
public static ReplaySubject createWithTime(long time, TimeUnit unit, final Scheduler scheduler) {
final BoundedState state = new BoundedState(
new TimeEvictionPolicy(unit.toMillis(time), scheduler),
new AddTimestamped(scheduler),
new RemoveTimestamped()
);
return createWithState(state, new TimedOnAdd(state, scheduler));
}
/**
* Creates a time- and size-bounded replay subject.
*
* In this setting, the {@code ReplaySubject} internally tags each received item with a timestamp value
* supplied by the {@link Scheduler} and holds at most {@code size} items in its internal buffer. It evicts
* items from the start of the buffer if their age becomes less-than or equal to the supplied age in
* milliseconds or the buffer reaches its {@code size} limit.
*
* When observers subscribe to a terminated {@code ReplaySubject}, they observe the items that remained in
* the buffer after the terminal notification, regardless of their age, but at most {@code size} items.
*
* If an observer subscribes while the {@code ReplaySubject} is active, it will observe only those items
* from within the buffer that have age less than the specified time and each subsequent item, even if the
* buffer evicts items due to the time constraint in the mean time. In other words, once an observer
* subscribes, it observes items without gaps in the sequence except for the outdated items at the beginning
* of the sequence.
*
* Note that terminal notifications ({@code onError} and {@code onCompleted}) trigger eviction as well. For
* example, with a max age of 5, the first item is observed at T=0, then an {@code onCompleted} notification
* arrives at T=10. If an observer subscribes at T=11, it will find an empty {@code ReplaySubject} with just
* an {@code onCompleted} notification.
*
* @param
* the type of items observed and emitted by the Subject
* @param time
* the maximum age of the contained items
* @param unit
* the time unit of {@code time}
* @param size
* the maximum number of buffered items
* @param scheduler
* the {@link Scheduler} that provides the current time
* @return the created subject
*/
public static ReplaySubject createWithTimeAndSize(long time, TimeUnit unit, int size, final Scheduler scheduler) {
final BoundedState state = new BoundedState(
new PairEvictionPolicy(
new SizeEvictionPolicy(size),
new TimeEvictionPolicy(unit.toMillis(time), scheduler)
),
new AddTimestamped(scheduler),
new RemoveTimestamped()
);
return createWithState(state, new TimedOnAdd(state, scheduler));
}
/**
* Creates a bounded replay subject with the given state shared between the subject and the
* {@link OnSubscribe} functions.
*
* @param
* the type of items observed and emitted by the Subject
* @param state
* the shared state
* @return the created subject
*/
static final ReplaySubject createWithState(final BoundedState state,
Action1> onStart) {
SubjectSubscriptionManager ssm = new SubjectSubscriptionManager();
ssm.onStart = onStart;
ssm.onTerminated = new Action1>() {
@Override
public void call(SubjectObserver t1) {
NodeList.Node