reactor.core.publisher.FluxProcessor Maven / Gradle / Ivy
Show all versions of neo4j-java-driver Show documentation
/*
* Copyright (c) 2011-2017 Pivotal Software Inc, All Rights Reserved.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package reactor.core.publisher;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.concurrent.CancellationException;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
import org.reactivestreams.Processor;
import org.reactivestreams.Publisher;
import org.reactivestreams.Subscriber;
import reactor.core.CoreSubscriber;
import reactor.core.Disposable;
import reactor.core.Scannable;
import reactor.util.annotation.Nullable;
/**
* A base processor that exposes {@link Flux} API for {@link Processor}.
*
* Implementors include {@link UnicastProcessor}, {@link EmitterProcessor},
* {@link ReplayProcessor}, {@link WorkQueueProcessor} and {@link TopicProcessor}.
*
* @author Stephane Maldini
*
* @param the input value type
* @param the output value type
*/
public abstract class FluxProcessor extends Flux
implements Processor, CoreSubscriber, Scannable, Disposable {
/**
* Build a {@link FluxProcessor} whose data are emitted by the most recent emitted {@link Publisher}.
* The {@link Flux} will complete once both the publishers source and the last switched to {@link Publisher} have
* completed.
*
*
* 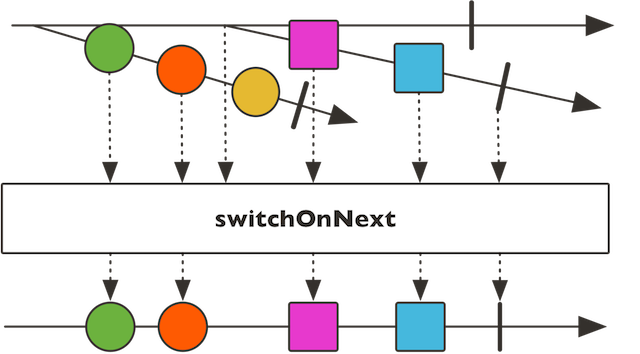 *
* @param
*
* @param the produced type
* @return a {@link FluxProcessor} accepting publishers and producing T
*/
public static FluxProcessor, T> switchOnNext() {
UnicastProcessor> emitter = UnicastProcessor.create();
FluxProcessor, T> p = FluxProcessor.wrap(emitter, switchOnNext(emitter));
return p;
}
/**
* Transform a receiving {@link Subscriber} and a producing {@link Publisher} in a logical {@link FluxProcessor}.
* The link between the passed upstream and returned downstream will not be created automatically, e.g. not
* subscribed together. A {@link Processor} might choose to have orthogonal sequence input and output.
*
* @param the receiving type
* @param the producing type
*
* @param upstream the upstream subscriber
* @param downstream the downstream publisher
* @return a new blackboxed {@link FluxProcessor}
*/
public static FluxProcessor wrap(final Subscriber upstream, final Publisher downstream) {
return new DelegateProcessor<>(downstream, upstream);
}
@Override
public void dispose() {
onError(new CancellationException("Disposed"));
}
/**
* Return the number of active {@link Subscriber} or {@literal -1} if untracked.
*
* @return the number of active {@link Subscriber} or {@literal -1} if untracked
*/
public long downstreamCount(){
return inners().count();
}
/**
* Return the processor buffer capacity if any or {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}
*
* @return processor buffer capacity if any or {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}
*/
public int getBufferSize() {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
/**
* Current error if any, default to null
*
* @return Current error if any, default to null
*/
@Nullable
public Throwable getError() {
return null;
}
/**
* Return true if any {@link Subscriber} is actively subscribed
*
* @return true if any {@link Subscriber} is actively subscribed
*/
public boolean hasDownstreams() {
return downstreamCount() != 0L;
}
/**
* Return true if terminated with onComplete
*
* @return true if terminated with onComplete
*/
public final boolean hasCompleted() {
return isTerminated() && getError() == null;
}
/**
* Return true if terminated with onError
*
* @return true if terminated with onError
*/
public final boolean hasError() {
return isTerminated() && getError() != null;
}
@Override
public Stream inners() {
return Stream.empty();
}
/**
* Has this upstream finished or "completed" / "failed" ?
*
* @return has this upstream finished or "completed" / "failed" ?
*/
public boolean isTerminated() {
return false;
}
/**
* Return true if this {@link FluxProcessor} supports multithread producing
*
* @return true if this {@link FluxProcessor} supports multithread producing
*/
public boolean isSerialized() {
return false;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object scanUnsafe(Attr key) {
if (key == Attr.TERMINATED) return isTerminated();
if (key == Attr.ERROR) return getError();
if (key == Attr.CAPACITY) return getBufferSize();
return null;
}
/**
* Create a {@link FluxProcessor} that safely gates multi-threaded producer
* {@link Subscriber#onNext(Object)}.
*
* @return a serializing {@link FluxProcessor}
*/
public final FluxProcessor serialize() {
return new DelegateProcessor<>(this, Operators.serialize(this));
}
/**
* Create a {@link FluxSink} that safely gates multi-threaded producer
* {@link Subscriber#onNext(Object)}. This processor will be subscribed to
* that {@link FluxSink}, and any previous subscribers will be unsubscribed.
*
* The returned {@link FluxSink} will not apply any
* {@link FluxSink.OverflowStrategy} and overflowing {@link FluxSink#next(Object)}
* will behave in two possible ways depending on the Processor:
*
* - an unbounded processor will handle the overflow itself by dropping or
* buffering
* - a bounded processor will block/spin
*
*
* @return a serializing {@link FluxSink}
*/
public final FluxSink sink() {
return sink(FluxSink.OverflowStrategy.IGNORE);
}
/**
* Create a {@link FluxSink} that safely gates multi-threaded producer
* {@link Subscriber#onNext(Object)}. This processor will be subscribed to
* that {@link FluxSink}, and any previous subscribers will be unsubscribed.
*
* The returned {@link FluxSink} will not apply any
* {@link FluxSink.OverflowStrategy} and overflowing {@link FluxSink#next(Object)}
* will behave in two possible ways depending on the Processor:
*
* - an unbounded processor will handle the overflow itself by dropping or
* buffering
* - a bounded processor will block/spin on IGNORE strategy, or apply the
* strategy behavior
*
*
* @param strategy the overflow strategy, see {@link FluxSink.OverflowStrategy}
* for the
* available strategies
* @return a serializing {@link FluxSink}
*/
public final FluxSink sink(FluxSink.OverflowStrategy strategy) {
Objects.requireNonNull(strategy, "strategy");
if (getBufferSize() == Integer.MAX_VALUE){
strategy = FluxSink.OverflowStrategy.IGNORE;
}
FluxCreate.BaseSink s = FluxCreate.createSink(this, strategy);
onSubscribe(s);
if(s.isCancelled() ||
(isSerialized() && getBufferSize() == Integer.MAX_VALUE)){
return s;
}
if (serializeAlways())
return new FluxCreate.SerializedSink<>(s);
else
return new FluxCreate.SerializeOnRequestSink<>(s);
}
/**
* Returns serialization strategy. If true, {@link FluxProcessor#sink()} will always
* be serialized. Otherwise sink is serialized only if {@link FluxSink#onRequest(java.util.function.LongConsumer)}
* is invoked.
* @return true to serialize any sink, false to delay serialization till onRequest
*/
protected boolean serializeAlways() {
return true;
}
}
